SQL入门(4): 嵌入式SQL语言
本节讲述内容:
1.嵌入式SQL 语言概述
2.变量声明与数据库连接
3.数据集与游标
4.可滚动游标与数据库的增删改
5.状态捕捉以及错误处理机制
(一)嵌入式SQL语言
之前我们所学的都是交互式SQL 语言: select .. from .. where..
嵌入式SQL语言 表示 将SQL语言嵌入到 某一种高级语言中使用, 比如C++ ,Java, powerbuilder等
它们也称为宿主语言(host language).
复杂的检索不能用一条SQL语句完成, 需要结合高级语言中的顺序\分支\循环结构帮助处理.
if [conditon] then SQL_query else SQL_query end if
do while [condition] SQL_query end do
还有在SQL语句的检索结果基础上,再进行处理的
SQL_query1 for ... do process the record next SQL_query 2 if .. then else end if
交互式SQL: select sname, sage from student where sname='xy';
嵌入式SQL: 以宿主语言C语言为例,
exec sql select sname, sage into :vsname, :vsage from student where sname='xy';
主要区别:
(1) exex sql 是一个引导词, 它引导sql 语句, 将SQL语句预编译成C编译器可识别的语句.
(2) 增加 into 子句, 用于把SQL 语句的检索结果赋给高级语言的程序变量
(3) 用冒号开头 表示高级语言的程序变量 :vsname , :vsage
冒号很重要, 用于区分是程序变量 还是 表的字段!! .... 还有很多特点之后在详细介绍
为啥要学嵌入式SQL , 用来解决啥问题?
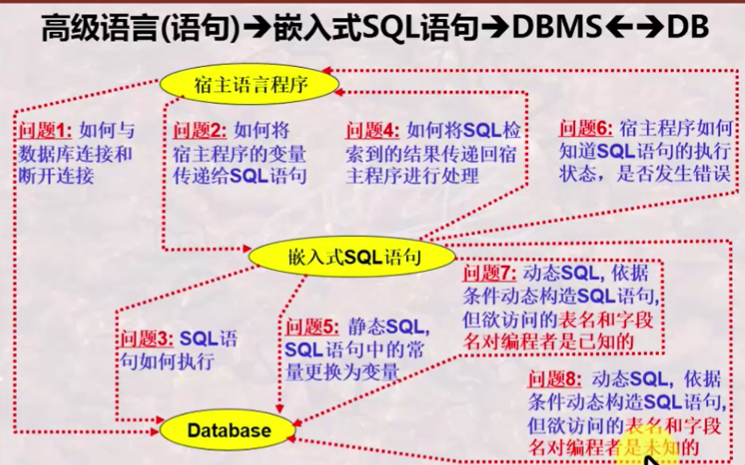
下面逐个解决上述8个问题
(一) 数据库的连接(问题1)
在嵌入式SQL 操作之前, 首先需要与数据库进行连接
不同的DMBS 的语句是有差别的,

在嵌入式SQL程序执行之后, 需要断开数据库

SQL 执行的提交与撤销
SQL语句在执行过程中, 必须要有提交, 撤销语句
提交: exec sql commit work;
撤销: exec sql rollback work;
很多DBMS 都设计了捆绑 提交\撤销 与断开连接在一起的语句, 以保证在断开连接之前
使用户确认提交或 撤销先前的工作, Oracle 中就是这样:
exec sql commit release;
exec sql rollback release;
为什么需要提交和撤销呢? 这个设计到数据库中的'' 事务 ''处理
什么是事务? 从应用程序员角度来看, 事物是一个存取或者改变数据库内容的程序的一次执行,
或者说是一条或者多条SQL 语句的一次执行被看做是一个事务
事务 一般由应用程序员提出, 因此有开始和结束, 结束前需要提交或者撤销
begin transaction exec sql... exec sql... exec sql commit work | exec sql rollback work --提交或者撤销 end transaction
注意: 提交表示这一系列操作对数据库的更新是有效的, 撤销则表示无效
其实从 任何一个SQL语句执行 就表示了一个事务的开始, 到了 commit 或 rollback 则结束一个事务,
因此上述的 begin end 可以省略.
事务的ACID 特性
A : atomicity 原子性, DBMS保证表示事务中的一组操作是不可分的,要么全做,要么一条也不做
C : consistency 一致性,例如两个人同时在买车票,会不会买到同一张车票
I: isolation 隔离性 两个事务操作互不干扰
D: durability 已提交事务的影响是持久的, 被撤销的事务影响可以恢复
事务处理技术是DBMS的核心处理技术!!
(二) 变量声明(问题2)
exec sql select sname, sage into :vsname, :vsage from student where sname=:specname;
加了冒号表示高级语言的程序变量, 这些变量需要声明
exec sql begin declare section; --开始声明 char vsname[10], specname[10] ='xy' ; int vsage; exec sql end declare section; -- 结束声明
注: 宿主程序的字符串变量长度要比字符型字段多1, 因为宿主程序的字符串尾部多一个终止符'\0' .
-- 变量的声明与使用
exec sql begin declare section; char vsname[10], specname[10] ='xy' ; int vsage; exec sql end declare section; -- 用户在此处 可以基于键盘输入给specname 赋值 exec sql select sname, sage into :vsname, :vsage from student where sname=:specname;
实例: 数据库连接+变量定义
#include<stdio.h> #include"prompt.h" exec sql include sqlca; --sqlca 表示SQL的通信区, communication area char cid_prompt[]="please enter customer id:"; int main() { exec sql begin declare section; --下面声明变量 char cust_id[5], cust_name[14]; float cust_discnt; exec sql end declare section; exec sql whenever sqlerror goto report_error;-- 错误捕获 exec sql whenever not found goto notfound; -- 记录没有找到 strcpy(user_name,"poneilsql");-- 字符串赋值 strcpy(user_pwd,"123456"); exec sql connect :user_name identified by :user_pwd; -- 连接数据库 while((prompt(cid_prompt,1,cust_id,4))>=0){ exec sql select cname,discnt into :cust_name,:cust_discnt from customers where cid=:cust_id; -- 根据输入的客户id 找到名字和折扣 exec sql commit work;-- 提交 printf("customer's name is %s and discount is %.1f\n",cust_name, cust_discnt); continue; -- 接着循环,再输入客户id notfound:printf("can't find customer %s, continuing\n", cust_id);} exec sql commit release; -- 断开数据库的连接 return 0; report_error: -- 前面报错的执行 print_dberror(); exec sql rollback release; -- 断开连接 return 1; }
(三) 数据集与游标(问题3 4 5)
问题3: SQL 语句如何执行?
问题4: 如何将SQL 检索到的结果传递回宿主程序进行处理?
问题5: 如何将静态SQL , SQL语句中的常量更换为变量?
如何读取单行数据和多行数据, 单行结果处理与多行结果处理的差异: into 子句 和 游标 cursor
1. 检索单行结果, 可以将结果直接传送到宿主主程序的变量中, select ... into ...
exec sql select sname, sage into :vsname, :vsage from student where sname=:specname;
2. 如果是多行结果, 则需要使用游标cursor
游标是指向某个检索记录的指针, 通过这个指针, 每次读一行, 处理一行,
接着再读一行...,直到全部处理完毕 fetch..into... (一次一行)
需要先定义一个cursor-->再打开-->接着一条一条处理-->最后关闭
exec sql delcare cur_student cursor for --游标名 select sno, sname, sclass from student where sclass='0315'; -- 定义游标 exec sql open cur_student; --打开游标 exec sql fetch cur_student into :vsno, :vsname, :vsclass; --取数据
... exec sql close cur_student; --关闭游标
具体实例:
已知表orders(cid, aid, product, dollars) 客户id, 代理人id, 产品, 金额
游标: 给定一个客户id, 选出该客户下的所有代理商 和 金额(多行数据)
#define True 1 #include<stdio.h> #include"prompt.h" exec sql include sqlca; --sqlca 表示SQL的通信区, communication area exec sql begin declare section; --声明变量 char cust_id[5], agent_id[14]; double dollar_sum; exec sql end declare section; int main() { char cid_prompt[]="please enter customer id:"; -- 定义提示字符串 exec sql declare agent_dollars cursor for -- 定义游标 select aid,sum(dollars) from orders where cid=:cust_id group by aid; exec sql whenever sqlerror goto report_error;-- 错误捕获 exec sql connect to testdbl; --连接数据库 exec sql whenever not found goto finish; -- 记录没有找到 while((prompt(cid_prompt,1,cust_id,4))>=0){ exec sql open agent_dollars; -- 打开游标 while(True){ -- 打印每一条记录 exec sql fetch agent_dollars into :agent_id,:dollar_sum; printf("%s %11.2f\n",agent_id, dollar_sum) }; finish: exec sql close agent_dollars; -- 关闭游标 exec sql commit work; -- 提交 exec sql disconnect current;--断开连接 return 0; report_error: -- 前面报错的执行 print_dberror(); exec sql rollback;-- 撤销 exec sql disconnect current; --断开连接 return 1; }
总结游标:
exec sql delcare cur_student cursor for --游标名 select sno, sname, sclass from student where sclass=:vclass; -- 定义游标 order by sno for read only; --只读, 不可更新
cursor 数据读取 fetch : exec sql fetch cursor_name into host_variable
exec sql delcare cur_student cursor for --游标名 select sno, sname, sclass from student where sclass=:vclass; -- 定义游标 order by sno for read only; --只读, 不可更新 exec sql open cur_student; -- 打开 exec sql fetch cur_student into :vsno, :vsname, :vsage; -- 使用 exec sql close cur_student; -- 关闭
可滚动游标与数据库的增删改
标注的游标 始终是自开始到结束方向移动的, 每fetch 一次,向结束方向移动一次,
每一条记录只能被访问一次, 再次访问该记录只能关闭游标后重新打开
可不可以实现游标的向上移动呢? ODBC (open database connectivity) 是一种跨DBMS
的DB 操作平台, 它在应用程序与实际的DBMS之间提供了一种通用的接口,
很多DBMS不支持可滚动游标, 但是通过ODBC 可实现该功能
定义中增加了 scroll
使用如下:

可滚动游标移动时需要判断 是否到了结束位置, 或者到了起始位置,
EOF表示最后一条记录的后面位置
BOF表示起始位置的前面
如果不需要区分最上 最下, 则可以用whenever not found 进行检测
用游标进行数据库的增删改
1. 查找删除(与交互式delete 语句相同)
exec sql delete from customers c where c.city='harbin' and not exists (select * from orders o where o.cid=c.cid) -- 删除 城市是哈尔滨 且在订单 orders表里面没有记录的.
2. 定位删除
exec sql declare delcust cursor for select cid from customers c where c.city='harbin' and not exists (select * from orders o where o.cid=c.cid) for update of cid; exec sql open delcust while(True){ exec sql fetch delcust into :cust_id; exec sql delete from customers where current of delcust;}
1. 查找更新
exec sql update student s set scalss='0315' where s.sclass='0314';
2.定位更新
exec sql declare stud cursor for select * from student s where s.sclass='0314' and for update of sclass; exec sql open stud while(True){ exec sql fetch stud into :vsno, :vsname,:vsclass; exec sql update student set sclass='0315' where current of stud;}
插入语句
exec sql insert into student(sno,sname,sclass) values ('031501','xy','0315'); exec sql insert into master_stud(sno,sname,sclass) select sno,sname,sclass from student;
综合实例: 求数据库中某一列位于中值的那一行
--已知表 orders(cid,aid,product,dollars) -- 寻找数据库中某一列位于中值的那一行 #include<stdio.h> #include"prompt.h" exec sql include sqlca; --sqlca 表示SQL的通信区, communication area char cid_prompt[]="please enter customer id:"; -- 定义提示字符串 int main() { exec sql begin declare section; --声明变量 char cid[5], user_name[20], user_pwd[10]; double dollars; int ocount; exec sql end declare section; exec sql declare dollars_cursor cursor for -- 定义游标 select dollars from orders where cid=:cid and dollars is not null order by dollars; exec sql whenever sqlerror goto report_error;-- 错误捕获 strcpy(user_name,"poneilsql");-- 字符串赋值 strcpy(user_pwd,"123456"); exec sql connect :user_name identified by :user_pwd; -- 连接数据库 --exec sql whenever not found goto finish; -- 记录没有找到 while((prompt(cid_prompt,1,cust_id,4))>=0){ exec sql select count(dollars) into :ocount from orders where cid=:cid; if(ocount==0) {printf("no record reviewed for cid value %s\n",cid); continue;} exec sql open dollars_cursor; for (i=0;i<(ocount+1)/2;i++) exec sql fetch dollars_cursor into :dollars ; exec sql close dollars_cursor; exec sql commit work; -- 提交 printf("median dollar amount=%f\n",dollars); }


