MongoTemplate字段别名源码分析
背景
在使用 MongoTemplate 进行 upsert 操作时,发现mongodb表中,同一个字段出现了两种命名,如下:
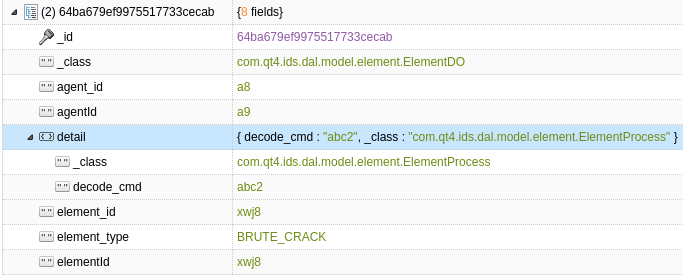
说明:upsert方法中的参数,为 mongodb 中自带Update对象,且该对象的字段使用的是实体类的字段名,实体类如下:
@Document(collection = ElementDO.COLLECTION_NAME) public class ElementDO { public static final String COLLECTION_NAME = "app_ids_element"; @Id private String id; /** * 元素ID */ @Field("element_id") @Indexed(unique = true, background = true) private String elementId; /** * 平台类型 */ @Field("platform_type") private PlatformTypeEnum platformType; /** * 探针ID */ @Field("agent_id") private String agentId; /** * 元素详情 */ private ElementBase detail; }
问题分析
出现如上问题,第一反应就是实体类字段的@Field注解中别名未生效,那为啥没有生效呢?带着这个疑问,又衍生了几个问题:
- 之前使用 save(ElementDO element)时,别名是怎么生效的?
- upsert 在什么情况下,别名才会生效?
源码分析
save方法
1、save方法入口:
protected <T> T doSave(String collectionName, T objectToSave, MongoWriter<T> writer) { objectToSave = maybeEmitEvent(new BeforeConvertEvent<>(objectToSave, collectionName)).getSource(); objectToSave = maybeCallBeforeConvert(objectToSave, collectionName); // 通过objectToSave对象类型,得到对应的AdaptibleEntity子类 AdaptibleEntity<T> entity = operations.forEntity(objectToSave, mongoConverter.getConversionService()); entity.assertUpdateableIdIfNotSet(); // objectToSave对象转Document对象 MappedDocument mapped = entity.toMappedDocument(writer); Document dbDoc = mapped.getDocument(); maybeEmitEvent(new BeforeSaveEvent<>(objectToSave, dbDoc, collectionName)); objectToSave = maybeCallBeforeSave(objectToSave, dbDoc, collectionName); // 保存,返回主键ID Object id = saveDocument(collectionName, dbDoc, objectToSave.getClass()); // 向入参对象中回写主键ID T saved = populateIdIfNecessary(objectToSave, id); maybeEmitEvent(new AfterSaveEvent<>(saved, dbDoc, collectionName)); return maybeCallAfterSave(saved, dbDoc, collectionName); }
2、继续深入:
@Override public MappedDocument toMappedDocument(MongoWriter<? super T> writer) { T bean = propertyAccessor.getBean(); Document document = new Document(); // 通过MappingMongoConverter将javabean转为Document writer.write(bean, document); if (document.containsKey(ID_FIELD) && document.get(ID_FIELD) == null) { document.remove(ID_FIELD); } return MappedDocument.of(document); }
说明:Document为 Map 和 Bson 的子类,也是由一个个的 key: value 组成
3、继续深入:
protected void writeInternal(@Nullable Object obj, Bson bson, @Nullable TypeInformation<?> typeHint) { if (null == obj) { return; } Class<?> entityType = obj.getClass(); Optional<Class<?>> customTarget = conversions.getCustomWriteTarget(entityType, Document.class); if (customTarget.isPresent()) { Document result = doConvert(obj, Document.class); BsonUtils.addAllToMap(bson, result); return; } // 如果为Map对象:遍历map中的每个key,如果有value为javabean,递归走到该方法 if (Map.class.isAssignableFrom(entityType)) { writeMapInternal((Map<Object, Object>) obj, bson, ClassTypeInformation.MAP); return; } // 如果为Collection对象:遍历集合中的每个元素,如果有元素为javabean,递归走到本方法 if (Collection.class.isAssignableFrom(entityType)) { writeCollectionInternal((Collection<?>) obj, ClassTypeInformation.LIST, (Collection<?>) bson); return; } // javabean转为可持久化的entity对象 MongoPersistentEntity<?> entity = mappingContext.getRequiredPersistentEntity(entityType); // 将entity转为bson对象:如果对象中有嵌套对象,也会递归下面的writeInternal方法 writeInternal(obj, bson, entity); addCustomTypeKeyIfNecessary(typeHint, obj, bson); }
说明:writeInternal方法:当_id的值为空时,会从bson中删除该key
4、继续深入上一步的转化,最终会走到:
public void doWithProperties(PropertyHandler<P> handler) { Assert.notNull(handler, "PropertyHandler must not be null!"); // 循环对实体类中的所有字段进行处理 for (P property : persistentPropertiesCache) { handler.doWithPersistentProperty(property); } }
说明:persistentPropertiesCache 中的原始数据,是通过 BeanUtils.getPropertyDescriptors(classType) 得到的
5、继续深入:
private void assertUniqueness(MongoPersistentProperty property) { // 获取保存到mongodb中的字段名 String fieldName = property.getFieldName(); MongoPersistentProperty existingProperty = properties.get(fieldName); if (existingProperty != null) { throw new MappingException( String.format(AMBIGUOUS_FIELD_MAPPING, property.toString(), existingProperty.toString(), fieldName)); } properties.put(fieldName, property); }
6、继续深入,看到获取字段名的方法:
public String getFieldName() { // 主键ID if (isIdProperty()) { if (getOwner().getIdProperty() == null) { return ID_FIELD_NAME; } if (getOwner().isIdProperty(this)) { return ID_FIELD_NAME; } } // 有@Field注解的字段:取注解中的别名 if (hasExplicitFieldName()) { return getAnnotatedFieldName(); } String fieldName = fieldNamingStrategy.getFieldName(this); if (!StringUtils.hasText(fieldName)) { throw new MappingException(String.format("Invalid (null or empty) field name returned for property %s by %s!", this, fieldNamingStrategy.getClass())); } return fieldName; }
update方法
update方法的入参,一般都是Update对象,该对象内部有一个Map对象,所以数据结构类似于Map。
1、更新入口:
protected UpdateResult doUpdate(String collectionName, Query query, UpdateDefinition update, @Nullable Class<?> entityClass, boolean upsert, boolean multi) { MongoPersistentEntity<?> entity = entityClass == null ? null : getPersistentEntity(entityClass); UpdateContext updateContext = multi ? queryOperations.updateContext(update, query, upsert) : queryOperations.updateSingleContext(update, query, upsert); updateContext.increaseVersionForUpdateIfNecessary(entity); // 获取查询条件的Document对象 Document queryObj = updateContext.getMappedQuery(entity); UpdateOptions opts = updateContext.getUpdateOptions(entityClass); // 获取更新对象的Document对象 Document updateObj = updateContext.getMappedUpdate(entity); MongoAction mongoAction = new MongoAction(writeConcern, MongoActionOperation.UPDATE, collectionName, entityClass, updateObj, queryObj); // ... }
2、循环Update对象中的每个key,然后再计算对应的持久化字段名
public Document getMappedObject(Bson query, @Nullable MongoPersistentEntity<?> entity) { Document result = new Document(); for (String key : BsonUtils.asMap(query).keySet()) { Field field = createPropertyField(entity, key, mappingContext); if (field.getProperty() != null && field.getProperty().isUnwrapped()) { Object theNestedObject = BsonUtils.get(query, key); Document mappedValue = (Document) getMappedValue(field, theNestedObject); if (!StringUtils.hasText(field.getMappedKey())) { result.putAll(mappedValue); } else { result.put(field.getMappedKey(), mappedValue); } } else { // 循环每个key,计算可持久化的key Entry<String, Object> entry = getMappedObjectForField(field, BsonUtils.get(query, key)); result.put(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()); } } return result; }
3、继续深入:
protected Object delegateConvertToMongoType(Object source, @Nullable MongoPersistentEntity<?> entity) { if(entity != null && entity.isUnwrapped()) { return converter.convertToMongoType(source, entity); } return converter.convertToMongoType(source, entity == null ? ClassTypeInformation.OBJECT : getTypeHintForEntity(source, entity)); }
4、继续深入:
public Object convertToMongoType(@Nullable Object obj, @Nullable TypeInformation<?> typeInformation) { // 如果是基础类型,直接使用key作为可持久化字段名 if (conversions.isSimpleType(obj.getClass())) { Class<?> conversionTargetType; if (typeInformation != null && conversions.isSimpleType(typeInformation.getType())) { conversionTargetType = typeInformation.getType(); } else { conversionTargetType = Object.class; } return getPotentiallyConvertedSimpleWrite(obj, conversionTargetType); } if (obj instanceof Document) { Document newValueDocument = new Document(); for (String vk : ((Document) obj).keySet()) { Object o = ((Document) obj).get(vk); newValueDocument.put(vk, convertToMongoType(o, typeInformation)); } return newValueDocument; } if (obj instanceof Map) { Document result = new Document(); for (Map.Entry<Object, Object> entry : ((Map<Object, Object>) obj).entrySet()) { result.put(entry.getKey().toString(), convertToMongoType(entry.getValue(), typeInformation)); } return result; } // 如果是javabean Document newDocument = new Document(); this.write(obj, newDocument); return !obj.getClass().equals(typeInformation.getType()) ? newDocument : removeTypeInfo(newDocument, true); }
说明:如果key的类型为 javabean,则和上面 save 方法第3步之后的流程一样了
upsert方法
upsert方法和update方法的入口是同一个,之后的流程也是差不多的,这里就不再重复分析~
结论
save方法:
- 入参为一个javabean时:
- 如果字段上有@Field注解,则使用注解中的别名作为mongo表字段名
- 如果字段上没有@Field注解,则直接使用属性名
- 入参为一个Map对象时:
- 如果key的类型为基础类型,则直接使用key作为作为mongo表字段名,
- 如果key为为嵌套对象,那做法跟javabean是一样的
update/upsert方法:
- Update对象类似于Map结构,所以做法跟上面的save(Map)类似
其他知识点
save和insert区别
save和insert方法的区别就是:
- save 方法:先判断文档是否存在(根据文档的_id字段进行匹配),存在则执行更新操作,否则执行插入操作。
- insert 方法:只执行插入操作,如果文档已经存在(根据文档的_id字段进行匹配),会抛出 DuplicateKeyException 异常。
两个方法的源码分析:
1、save 方法:
protected Object saveDocument(String collectionName, Document dbDoc, Class<?> entityClass) { return execute(collectionName, collection -> { MongoAction mongoAction = new MongoAction(writeConcern, MongoActionOperation.SAVE, collectionName, entityClass, dbDoc, null); WriteConcern writeConcernToUse = prepareWriteConcern(mongoAction); MappedDocument mapped = MappedDocument.of(dbDoc); MongoCollection<Document> collectionToUse = writeConcernToUse == null // ? collection // : collection.withWriteConcern(writeConcernToUse); if (!mapped.hasId()) { // _id不存在则会执行新增操作 collectionToUse.insertOne(dbDoc); } else { MongoPersistentEntity<?> entity = mappingContext.getPersistentEntity(entityClass); UpdateContext updateContext = queryOperations.replaceSingleContext(mapped, true); Document replacement = updateContext.getMappedUpdate(entity); Document filter = updateContext.getMappedQuery(entity); // ... collectionToUse.replaceOne(filter, replacement, new ReplaceOptions().upsert(true)); } return mapped.getId(); }); }
说明:在执行 saveDocument 方法前,在 writeInternal 方法中,如果发现有 _id 字段,但是值为空,会从 document 中剔除_id字段。
insert 方法:
protected Object insertDocument(String collectionName, Document document, Class<?> entityClass) { return execute(collectionName, collection -> { MongoAction mongoAction = new MongoAction(writeConcern, MongoActionOperation.INSERT, collectionName, entityClass, document, null); WriteConcern writeConcernToUse = prepareWriteConcern(mongoAction); if (writeConcernToUse == null) { collection.insertOne(document); } else { collection.withWriteConcern(writeConcernToUse).insertOne(document); } return operations.forEntity(document).getId(); }); }
回写主键ID
调用save方法时,成功保存后,会将主键ID回写到入参对象中
1、在执行完saveDocument或者insertDocument后,会返回一个主键ID,然后立马执行下面的方法:
protected <T> T populateIdIfNecessary(T savedObject, Object id) { return operations.forEntity(savedObject, mongoConverter.getConversionService()) // .populateIdIfNecessary(id); }
2、最终又会执行:
public T populateIdIfNecessary(@Nullable Object id) { if (id == null) { return propertyAccessor.getBean(); } MongoPersistentProperty idProperty = entity.getIdProperty(); if (idProperty == null) { return propertyAccessor.getBean(); } if (identifierAccessor.getIdentifier() != null) { return propertyAccessor.getBean(); } // 将id回写到入参对象中 propertyAccessor.setProperty(idProperty, id); return propertyAccessor.getBean(); }
批量保存
批量保存时,如果出现唯一键索引重复,是否继续执行取决于 ordered 字段(对应 MongoTemplate 中的 BulkOperations):
- ordered:true:默认设置。插入多个文档时,会按插入顺序逐个处理文档,并在遇到的第一个错误时停止插入,已经成功插入的会保留到集合中
- ordered:false:插入多个文档时,发生错误也会继续处理剩下的文档,不会中断


db.runCommand({ insert: "app_ids_element", "$db": "tenant_e95dd4a454e6c86412ca", "ordered": false, "documents": [{ "element_id": "xwj1", "agent_id": "a1", "detail": { "decode_cmd": "abc1", "_class": "com.qt4.ids.dal.model.element.ElementProcess" }, "_class": "com.qt4.ids.dal.model.element.ElementDO" }, { "element_id": "xwj2", "agent_id": "a2", "_class": "com.qt4.ids.dal.model.element.ElementDO" }, { "element_id": "xwj3", "agent_id": "a3", "_class": "com.qt4.ids.dal.model.element.ElementDO" }] })
app_ids_element 表中的 element_id为唯一索引,当表中存在 xwj1 的数据时,执行以上命令还是会成功插入 xwj2 和 xwj3。执行结果如下:
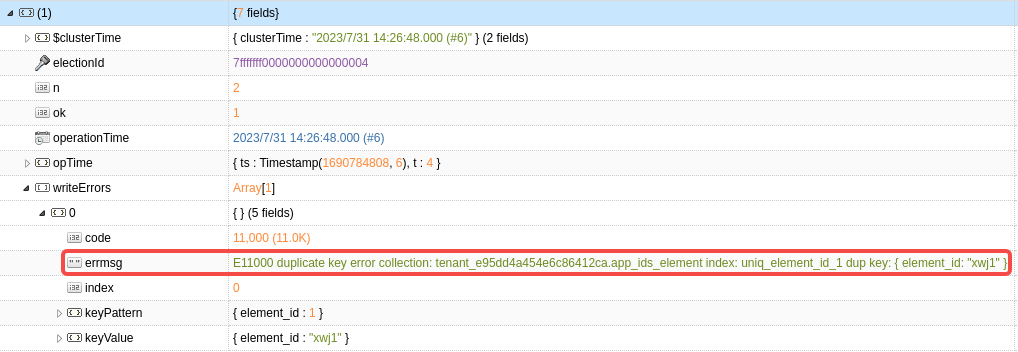
说明:通过 errmsg 可以看出插入失败的原因。如果全部插入成功,是没有 writeErrors 的。







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了