spring-springmvc源码分析(二)
参考:
http://www.cnblogs.com/leftthen/p/5207787.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/leftthen/p/5208169.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/leftthen/p/5208376.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/leftthen/p/5208404.html
HandlerMapping - SimpleUrlHandlerMapping初始化
摘要:
SimpleUrlHandlerMapping只是参与Handler的注册,请求映射时由AbstractUrlHandlerMapping搞定.
初始化时,通过setMappings(Properties mappings)或者setUrlMap(Map<String, ?> urlMap)设置映射关系,然后通过WebApplicationObjectSupport的initApplicationContext调用registerHandlers进行注册.
覆写initApplicationContext方法时,先调用父类实现,然后才调用registerHandlers进行注册.其中最终的注册registerHandler实现是由AbstractUrlHandlerMapping实现的.
父类AbstractHandlerMapping继承了WebApplicationObjectSupport,所以SimpleUrlHandlerMapping可以通过覆写initApplicationContext注册Handler.
注册Handler前,不忘靠AbstractHandlerMapping来初始化拦截器.
// SimpleUrlHandlerMapping
1 /**
2 * Calls the {@link #registerHandlers} method in addition to the
3 * superclass's initialization.
4 */
5 @Override
6 public void initApplicationContext() throws BeansException {
7 super.initApplicationContext();
8 registerHandlers(this.urlMap);
9 }
initApplicationContext主要是进行拦截器的初始化.
extendInterceptors是留给子类用的扩展接口,暂时没有使用
detectMappedInterceptors是通过BeanFactoryUtils扫描应用下的全部MappedInterceptor类
initInterceptors初始化特定的拦截器,检查MappedInterceptor,在需要时适配adaptor HandlerInterceptor
// AbstractHandlerMapping
1 /**
2 * Initializes the interceptors.
3 * @see #extendInterceptors(java.util.List)
4 * @see #initInterceptors()
5 */
6 @Override
7 protected void initApplicationContext() throws BeansException {
8 extendInterceptors(this.interceptors);
9 detectMappedInterceptors(this.mappedInterceptors);
10 initInterceptors();
11 }
// AbstractHandlerMapping
1 /**
2 * Extension hook that subclasses can override to register additional interceptors,
3 * given the configured interceptors (see {@link #setInterceptors}).
4 * <p>Will be invoked before {@link #initInterceptors()} adapts the specified
5 * interceptors into {@link HandlerInterceptor} instances.
6 * <p>The default implementation is empty.
7 * @param interceptors the configured interceptor List (never {@code null}),
8 * allowing to add further interceptors before as well as after the existing
9 * interceptors
10 */
11 protected void extendInterceptors(List<Object> interceptors) {
12 }
springmvc中经常使用BeanFactoryUtils扫描应用下的类来进行初始化.
// AbstractHandlerMapping
1 /**
2 * Detects beans of type {@link MappedInterceptor} and adds them to the list of mapped interceptors.
3 * This is done in addition to any {@link MappedInterceptor}s that may have been provided via
4 * {@link #setInterceptors(Object[])}. Subclasses can override this method to change that.
5 *
6 * @param mappedInterceptors an empty list to add MappedInterceptor types to
7 */
8 protected void detectMappedInterceptors(List<MappedInterceptor> mappedInterceptors) {
9 mappedInterceptors.addAll(
10 BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(
11 getApplicationContext(),MappedInterceptor.class, true, false).values());
12 }
// AbstractHandlerMapping
1 /**
2 * Initialize the specified interceptors, checking for {@link MappedInterceptor}s and adapting
3 * HandlerInterceptors where necessary.
4 * @see #setInterceptors
5 * @see #adaptInterceptor
6 */
7 protected void initInterceptors() {
8 if (!this.interceptors.isEmpty()) {
9 for (int i = 0; i < this.interceptors.size(); i++) {
10 Object interceptor = this.interceptors.get(i);
11 if (interceptor == null) {
12 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Entry number " + i + " in interceptors array is null");
13 }
14 if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) {
15 mappedInterceptors.add((MappedInterceptor) interceptor);
16 }
17 else {
18 adaptedInterceptors.add(adaptInterceptor(interceptor));
19 }
20 }
21 }
22 }
适配HandlerInterceptor和WebRequestHandlerInterceptorAdapter(什么是WebRequestHandlerInterceptorAdapter,晚点再说吧,具体看到时候拦截器部分的分析)
// AbstractHandlerMapping
1 /**
2 * Adapt the given interceptor object to the HandlerInterceptor interface.
3 * <p>Supported interceptor types are HandlerInterceptor and WebRequestInterceptor.
4 * Each given WebRequestInterceptor will be wrapped in a WebRequestHandlerInterceptorAdapter.
5 * Can be overridden in subclasses.
6 * @param interceptor the specified interceptor object
7 * @return the interceptor wrapped as HandlerInterceptor
8 * @see org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor
9 * @see org.springframework.web.context.request.WebRequestInterceptor
10 * @see WebRequestHandlerInterceptorAdapter
11 */
12 protected HandlerInterceptor adaptInterceptor(Object interceptor) {
13 if (interceptor instanceof HandlerInterceptor) {
14 return (HandlerInterceptor) interceptor;
15 }
16 else if (interceptor instanceof WebRequestInterceptor) {
17 return new WebRequestHandlerInterceptorAdapter((WebRequestInterceptor) interceptor);
18 }
19 else {
20 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Interceptor type not supported: " + interceptor.getClass().getName());
21 }
22 }
这才到SimpleUrlHandlerMapping干活的地方,迭代urlMap调用AbstractUrlHandlerMapping的registerHandler进行注册
(保障url以"/"开头就不多说了)
// SimpleUrlHandlerMapping
1 /**
2 * Register all handlers specified in the URL map for the corresponding paths.
3 * @param urlMap Map with URL paths as keys and handler beans or bean names as values
4 * @throws BeansException if a handler couldn't be registered
5 * @throws IllegalStateException if there is a conflicting handler registered
6 */
7 protected void registerHandlers(Map<String, Object> urlMap) throws BeansException {
8 if (urlMap.isEmpty()) {
9 logger.warn("Neither 'urlMap' nor 'mappings' set on SimpleUrlHandlerMapping");
10 }
11 else {
12 for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : urlMap.entrySet()) {
13 String url = entry.getKey();
14 Object handler = entry.getValue();
15 // Prepend with slash if not already present.
16 if (!url.startsWith("/")) {
17 url = "/" + url;
18 }
19 // Remove whitespace from handler bean name.
20 if (handler instanceof String) {
21 handler = ((String) handler).trim();
22 }
23 registerHandler(url, handler);
24 }
25 }
26 }
// AbstractUrlHandlerMapping
1 /**
2 * Register the specified handler for the given URL path.
3 * @param urlPath the URL the bean should be mapped to
4 * @param handler the handler instance or handler bean name String
5 * (a bean name will automatically be resolved into the corresponding handler bean)
6 * @throws BeansException if the handler couldn't be registered
7 * @throws IllegalStateException if there is a conflicting handler registered
8 */
9 protected void registerHandler(String urlPath, Object handler) throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
10 Assert.notNull(urlPath, "URL path must not be null");
11 Assert.notNull(handler, "Handler object must not be null");
12 Object resolvedHandler = handler;
13
14 // Eagerly resolve handler if referencing singleton via name.不是单例同时不是懒加载
15 if (!this.lazyInitHandlers && handler instanceof String) {
16 String handlerName = (String) handler;
17 if (getApplicationContext().isSingleton(handlerName)) {
18 resolvedHandler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
19 }
20 }
21
22 Object mappedHandler = this.handlerMap.get(urlPath);// 获取之前已经匹配的Handler
23 if (mappedHandler != null) {
24 if (mappedHandler != resolvedHandler) {// 如果新匹配得到的跟之前已解析到的handler不一致,则抛异常
25 throw new IllegalStateException(
26 "Cannot map " + getHandlerDescription(handler) + " to URL path [" + urlPath +
27 "]: There is already " + getHandlerDescription(mappedHandler) + " mapped.");
28 }
29 }
30 else {
31 if (urlPath.equals("/")) {// 设置rootHandler
32 if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
33 logger.info("Root mapping to " + getHandlerDescription(handler));
34 }
35 setRootHandler(resolvedHandler);
36 }
37 else if (urlPath.equals("/*")) {// 设置默认的defaultHandler
38 if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
39 logger.info("Default mapping to " + getHandlerDescription(handler));
40 }
41 setDefaultHandler(resolvedHandler);
42 }
43 else {// 最后才是普通handler的设置
44 this.handlerMap.put(urlPath, resolvedHandler);
45 if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
46 logger.info("Mapped URL path [" + urlPath + "] onto " + getHandlerDescription(handler));
47 }
48 }
49 }
50 }
HandlerMapping - AbstractDetectingUrlHandlerMapping系列初始化
AbstractDetectingUrlHandlerMapping是通过扫描方式注册Handler,收到请求时由AbstractUrlHandlerMapping的getHandlerInternal进行分发.
共有5个子类,一个抽象类.
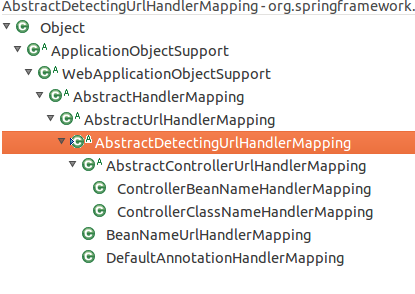
与SimpleUrlHandlerMapping类似,通过覆写initApplicationContext,然后调用detectHandlers进行初始化.
detectHandlers通过BeanFactoryUtils扫描应用下的Object,然后预留determineUrlsForHandler给子类根据Handler生成对应的url.
注册使用的registerHandler依然由AbstractUrlHandlerMapping提供.
// AbstractDetectingUrlHandlerMapping
1 /**
2 * Calls the {@link #detectHandlers()} method in addition to the
3 * superclass's initialization.
4 */
5 @Override
6 public void initApplicationContext() throws ApplicationContextException {
7 super.initApplicationContext();
8 detectHandlers();
9 }
这边一样是调用AbstractHandlerMapping的initApplicationContext初始化拦截器.
主角上场,detectHandlers,扫描Handlers
// AbstractDetectingUrlHandlerMapping
1 /**
2 * Register all handlers found in the current ApplicationContext.
3 * <p>The actual URL determination for a handler is up to the concrete
4 * {@link #determineUrlsForHandler(String)} implementation. A bean for
5 * which no such URLs could be determined is simply not considered a handler.
6 * @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException if the handler couldn't be registered
7 * @see #determineUrlsForHandler(String)
8 */
9 protected void detectHandlers() throws BeansException {
10 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
11 logger.debug("Looking for URL mappings in application context: " + getApplicationContext());
12 }
13 String[] beanNames = (this.detectHandlersInAncestorContexts ?
14 BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(getApplicationContext(), Object.class) :
15 getApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class));
16
17 // Take any bean name that we can determine URLs for.
18 for (String beanName : beanNames) {
19 String[] urls = determineUrlsForHandler(beanName);
20 if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(urls)) {
21 // URL paths found: Let's consider it a handler.
22 registerHandler(urls, beanName);
23 }
24 else {
25 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
26 logger.debug("Rejected bean name '" + beanName + "': no URL paths identified");
27 }
28 }
29 }
30 }
这边预留的模板方法定义如下:
1 /**
2 * Determine the URLs for the given handler bean.
3 * @param beanName the name of the candidate bean
4 * @return the URLs determined for the bean,
5 * or {@code null} or an empty array if none
6 */
7 protected abstract String[] determineUrlsForHandler(String beanName);
我们再来看看模板方法在BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping和AbstractControllerUrlHandlerMapping中的实现吧.
BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping非常简单,就实现了determineUrlsForHandler.
其中的alias应该是应该就是通过beanName在配置文件中配置的.
// BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping
1 /**
2 * Checks name and aliases of the given bean for URLs, starting with "/".
3 */
4 @Override
5 protected String[] determineUrlsForHandler(String beanName) {
6 List<String> urls = new ArrayList<String>();
7 if (beanName.startsWith("/")) {
8 urls.add(beanName);
9 }
10 String[] aliases = getApplicationContext().getAliases(beanName);
11 for (String alias : aliases) {
12 if (alias.startsWith("/")) {
13 urls.add(alias);
14 }
15 }
16 return StringUtils.toStringArray(urls);
17 }
再来看看AbstractControllerUrlHandlerMapping中的实现
isEligibleForMapping判断controller是否被排除在外(通过包package排除或类class排除).
buildUrlsForHandler由子类实现具体的url生成规则
isControllerType判断是否Controller的子类
buildUrlsForHandler预留给子类生产url的模板方法.
// AbstractControllerUrlHandlerMapping
1 /**
2 * This implementation delegates to {@link #buildUrlsForHandler},
3 * provided that {@link #isEligibleForMapping} returns {@code true}.
4 */
5 @Override
6 protected String[] determineUrlsForHandler(String beanName) {
7 Class beanClass = getApplicationContext().getType(beanName);
8 if (isEligibleForMapping(beanName, beanClass)) {
9 return buildUrlsForHandler(beanName, beanClass);
10 }
11 else {
12 return null;
13 }
14 }
// AbstractControllerUrlHandlerMapping
1 /**判断controller是否被排除在外(通过包package排除或类class排除).
2 * Determine whether the specified controller is excluded from this mapping.
3 * @param beanName the name of the controller bean
4 * @param beanClass the concrete class of the controller bean
5 * @return whether the specified class is excluded
6 * @see #setExcludedPackages
7 * @see #setExcludedClasses
8 */
9 protected boolean isEligibleForMapping(String beanName, Class beanClass) {
10 if (beanClass == null) {
11 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
12 logger.debug("Excluding controller bean '" + beanName + "' from class name mapping " +
13 "because its bean type could not be determined");
14 }
15 return false;
16 }
17 if (this.excludedClasses.contains(beanClass)) {
18 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
19 logger.debug("Excluding controller bean '" + beanName + "' from class name mapping " +
20 "because its bean class is explicitly excluded: " + beanClass.getName());
21 }
22 return false;
23 }
24 String beanClassName = beanClass.getName();
25 for (String packageName : this.excludedPackages) {
26 if (beanClassName.startsWith(packageName)) {
27 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
28 logger.debug("Excluding controller bean '" + beanName + "' from class name mapping " +
29 "because its bean class is defined in an excluded package: " + beanClass.getName());
30 }
31 return false;
32 }
33 }
34 return isControllerType(beanClass);
35 }
// AbstractControllerUrlHandlerMapping
1 /**
2 * Determine whether the given bean class indicates a controller type
3 * that is supported by this mapping strategy.
4 * @param beanClass the class to introspect
5 */
6 protected boolean isControllerType(Class beanClass) {
7 return this.predicate.isControllerType(beanClass);
8 }
// ControllerTypePredicate
这边提供2个api,分别判断是Controller的子类还是MultiActionController的子类.
1 /**
2 * Internal helper class that identifies controller types.
3 *
4 * @author Juergen Hoeller
5 * @since 2.5.3
6 */
7 class ControllerTypePredicate {
8
9 public boolean isControllerType(Class beanClass) {
10 return Controller.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass);
11 }
12
13 public boolean isMultiActionControllerType(Class beanClass) {
14 return MultiActionController.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass);
15 }
16
17 }
预留生成url的模板方法
// AbstractControllerUrlHandlerMapping
1 /** 2 * Abstract template method to be implemented by subclasses. 3 * @param beanName the name of the bean 4 * @param beanClass the type of the bean 5 * @return the URLs determined for the bean 6 */ 7 protected abstract String[] buildUrlsForHandler(String beanName, Class beanClass);
再来看看AbstractControllerUrlHandlerMapping的2个实现ControllerBeanNameUrlHandlerMapping和ControllerClassNameUrlHandlerMapping.
其实这两个,很简单,一个是根据beanName来生产url,一个是根据className来生产url.
// ControllerBeanNameUrlHandlerMapping
1 @Override
2 protected String[] buildUrlsForHandler(String beanName, Class beanClass) {
3 List<String> urls = new ArrayList<String>();
4 urls.add(generatePathMapping(beanName));
5 String[] aliases = getApplicationContext().getAliases(beanName);// 也获取配置的别名
6 for (String alias : aliases) {
7 urls.add(generatePathMapping(alias));
8 }
9 return StringUtils.toStringArray(urls);
10 }
// ControllerBeanNameUrlHandlerMapping
1 /**对path添加前后缀,还有/
2 * Prepends a '/' if required and appends the URL suffix to the name.
3 */
4 protected String generatePathMapping(String beanName) {
5 String name = (beanName.startsWith("/") ? beanName : "/" + beanName);
6 StringBuilder path = new StringBuilder();
7 if (!name.startsWith(this.urlPrefix)) {
8 path.append(this.urlPrefix);
9 }
10 path.append(name);
11 if (!name.endsWith(this.urlSuffix)) {
12 path.append(this.urlSuffix);
13 }
14 return path.toString();
15 }
// ControllerClassNameUrlHandlerMapping
直接委托给generatePathMappings实现
1 @Override
2 protected String[] buildUrlsForHandler(String beanName, Class beanClass) {
3 return generatePathMappings(beanClass);
4 }
// ControllerClassNameUrlHandlerMapping
通过buildPathPrefix获取path的前缀
通过ClassUtils获取className,如BookController(不带包名),同时使用cglib代理的问题一并解决
根据大小写是否敏感,转换className(默认caseSensitive = false;)
isMultiActionControllerType判断Controller是否MultiActionController的子类,就是controller是否包含多个handler
1 /**
2 * Generate the actual URL paths for the given controller class.
3 * <p>Subclasses may choose to customize the paths that are generated
4 * by overriding this method.
5 * @param beanClass the controller bean class to generate a mapping for
6 * @return the URL path mappings for the given controller
7 */
8 protected String[] generatePathMappings(Class beanClass) {
9 StringBuilder pathMapping = buildPathPrefix(beanClass);
10 String className = ClassUtils.getShortName(beanClass);
11 String path = (className.endsWith(CONTROLLER_SUFFIX) ?
12 className.substring(0, className.lastIndexOf(CONTROLLER_SUFFIX)) : className);
13 if (path.length() > 0) {
14 if (this.caseSensitive) {
15 pathMapping.append(path.substring(0, 1).toLowerCase()).append(path.substring(1));
16 }
17 else {
18 pathMapping.append(path.toLowerCase());
19 }
20 }
21 if (isMultiActionControllerType(beanClass)) {
22 return new String[] {pathMapping.toString(), pathMapping.toString() + "/*"};
23 }
24 else {
25 return new String[] {pathMapping.toString() + "*"};
26 }
27 }
// ControllerClassNameUrlHandlerMapping
1 /**
2 * Build a path prefix for the given controller bean class.
3 * @param beanClass the controller bean class to generate a mapping for
4 * @return the path prefix, potentially including subpackage names as path elements
5 */
6 private StringBuilder buildPathPrefix(Class beanClass) {
7 StringBuilder pathMapping = new StringBuilder();
8 if (this.pathPrefix != null) {
9 pathMapping.append(this.pathPrefix);
10 pathMapping.append("/");
11 }
12 else {
13 pathMapping.append("/");
14 }
15 if (this.basePackage != null) {
16 String packageName = ClassUtils.getPackageName(beanClass);
17 if (packageName.startsWith(this.basePackage)) {
18 String subPackage = packageName.substring(this.basePackage.length()).replace('.', '/');
19 pathMapping.append(this.caseSensitive ? subPackage : subPackage.toLowerCase());
20 pathMapping.append("/");
21 }
22 }
23 return pathMapping;
24 }
// AbstractControllerUrlHandlerMapping
predicate.isMultiActionControllerType具体实现看上面的ControllerTypePredicate
1 /**
2 * Determine whether the given bean class indicates a controller type
3 * that dispatches to multiple action methods.
4 * @param beanClass the class to introspect
5 */
6 protected boolean isMultiActionControllerType(Class beanClass) {
7 return this.predicate.isMultiActionControllerType(beanClass);
8 }
HandlerMapping - AbstractUrlHandlerMapping系列request分发
AbstractHandlerMapping实现HandlerMapping接口定的getHandler
1. 提供getHandlerInternal模板方法给子类实现
2. 如果没有获取Handler,则使用默认的defaultHandler
3. 如果handler是string类型,从context获取实例
4. 通过getHandlerExecutionChain封装handler,添加interceptor
// AbstractHandlerMapping
1 /**
2 * Look up a handler for the given request, falling back to the default
3 * handler if no specific one is found.
4 * @param request current HTTP request
5 * @return the corresponding handler instance, or the default handler
6 * @see #getHandlerInternal
7 */
8 public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
9 Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
10 if (handler == null) {
11 handler = getDefaultHandler();
12 }
13 if (handler == null) {
14 return null;
15 }
16 // Bean name or resolved handler?
17 if (handler instanceof String) {
18 String handlerName = (String) handler;
19 handler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
20 }
21 return getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
22 }
// AbstractHandlerMapping
1 /**
2 * Build a HandlerExecutionChain for the given handler, including applicable interceptors.
3 * <p>The default implementation simply builds a standard HandlerExecutionChain with
4 * the given handler, the handler mapping's common interceptors, and any {@link MappedInterceptor}s
5 * matching to the current request URL. Subclasses may
6 * override this in order to extend/rearrange the list of interceptors.
7 * <p><b>NOTE:</b> The passed-in handler object may be a raw handler or a pre-built
8 * HandlerExecutionChain. This method should handle those two cases explicitly,
9 * either building a new HandlerExecutionChain or extending the existing chain.
10 * <p>For simply adding an interceptor, consider calling {@code super.getHandlerExecutionChain}
11 * and invoking {@link HandlerExecutionChain#addInterceptor} on the returned chain object.
12 * @param handler the resolved handler instance (never {@code null})
13 * @param request current HTTP request
14 * @return the HandlerExecutionChain (never {@code null})
15 * @see #getAdaptedInterceptors()
16 */
17 protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) {
18 HandlerExecutionChain chain =
19 (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain) ?
20 (HandlerExecutionChain) handler : new HandlerExecutionChain(handler);
21
22 chain.addInterceptors(getAdaptedInterceptors());
23
24 String lookupPath = urlPathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request);
25 for (MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor : mappedInterceptors) {
26 if (mappedInterceptor.matches(lookupPath, pathMatcher)) {
27 chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor());
28 }
29 }
30
31 return chain;
32 }
接下来看看AbstractUrlHandlerMapping实现的getHandlerInternal
// AbstractUrlHandlerMapping
1 /**
2 * Look up a handler for the URL path of the given request.
3 * @param request current HTTP request
4 * @return the handler instance, or {@code null} if none found
5 */
6 @Override
7 protected Object getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
8 // 根据request获取url
9 String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
10 // 根据url查找handler
11 Object handler = lookupHandler(lookupPath, request);
12 if (handler == null) {
13 // 如果没有匹配到handler需要查找默认的,下面需要将PATH_WITHIN_HANDLER_MAPPING_ATTRIBUTE缓存到request
14 // We need to care for the default handler directly, since we need to
15 // expose the PATH_WITHIN_HANDLER_MAPPING_ATTRIBUTE for it as well.
16 Object rawHandler = null;
17 if ("/".equals(lookupPath)) {
18 rawHandler = getRootHandler();
19 }
20 if (rawHandler == null) {
21 rawHandler = getDefaultHandler();
22 }
23 if (rawHandler != null) {
24 // Bean name or resolved handler?
25 if (rawHandler instanceof String) {
26 String handlerName = (String) rawHandler;
27 rawHandler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
28 }
29 // 预留的校验handler模板方法,没有使用
30 validateHandler(rawHandler, request);
31 // 添加expose属性到request的拦截器
32 handler = buildPathExposingHandler(rawHandler, lookupPath, lookupPath, null);
33 }
34 }
35 if (handler != null && logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
36 logger.debug("Mapping [" + lookupPath + "] to " + handler);
37 }
38 else if (handler == null && logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
39 logger.trace("No handler mapping found for [" + lookupPath + "]");
40 }
41 return handler;
42 }
// AbstractUrlHandlerMapping
1 /**
2 * Look up a handler instance for the given URL path.
3 * <p>Supports direct matches, e.g. a registered "/test" matches "/test",
4 * and various Ant-style pattern matches, e.g. a registered "/t*" matches
5 * both "/test" and "/team". For details, see the AntPathMatcher class.
6 * <p>Looks for the most exact pattern, where most exact is defined as
7 * the longest path pattern.
8 * @param urlPath URL the bean is mapped to
9 * @param request current HTTP request (to expose the path within the mapping to)
10 * @return the associated handler instance, or {@code null} if not found
11 * @see #exposePathWithinMapping
12 * @see org.springframework.util.AntPathMatcher
13 */
14 protected Object lookupHandler(String urlPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
15 // Direct match? 直接根据url进行查找handler
16 Object handler = this.handlerMap.get(urlPath);
17 if (handler != null) {
18 // Bean name or resolved handler?
19 if (handler instanceof String) {
20 String handlerName = (String) handler;
21 handler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
22 }
23 validateHandler(handler, request);
24 return buildPathExposingHandler(handler, urlPath, urlPath, null);
25 }
26 // Pattern match? 通过表达式进行匹配具体通过AntPathMatcher实现,具体后面分析
27 List<String> matchingPatterns = new ArrayList<String>();
28 for (String registeredPattern : this.handlerMap.keySet()) {
29 if (getPathMatcher().match(registeredPattern, urlPath)) {
30 matchingPatterns.add(registeredPattern);
31 }
32 }
33 String bestPatternMatch = null;
34 Comparator<String> patternComparator = getPathMatcher().getPatternComparator(urlPath);
35 if (!matchingPatterns.isEmpty()) {
36 Collections.sort(matchingPatterns, patternComparator);
37 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
38 logger.debug("Matching patterns for request [" + urlPath + "] are " + matchingPatterns);
39 }
40 // order序号最小的优先级最高
41 bestPatternMatch = matchingPatterns.get(0);
42 }
43 if (bestPatternMatch != null) {
44 handler = this.handlerMap.get(bestPatternMatch);
45 // Bean name or resolved handler?
46 if (handler instanceof String) {
47 String handlerName = (String) handler;
48 handler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
49 }
50 validateHandler(handler, request);
51 String pathWithinMapping = getPathMatcher().extractPathWithinPattern(bestPatternMatch, urlPath);
52
53 // There might be multiple 'best patterns', let's make sure we have the correct URI template variables
54 // for all of them
55 Map<String, String> uriTemplateVariables = new LinkedHashMap<String, String>();
56 for (String matchingPattern : matchingPatterns) {
57 if (patternComparator.compare(bestPatternMatch, matchingPattern) == 0) {
58 Map<String, String> vars = getPathMatcher().extractUriTemplateVariables(matchingPattern, urlPath);
59 Map<String, String> decodedVars = getUrlPathHelper().decodePathVariables(request, vars);
60 uriTemplateVariables.putAll(decodedVars);
61 }
62 }
63 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
64 logger.debug("URI Template variables for request [" + urlPath + "] are " + uriTemplateVariables);
65 }
66 return buildPathExposingHandler(handler, bestPatternMatch, pathWithinMapping, uriTemplateVariables);
67 }
68 // No handler found...
69 return null;
70 }
设计用于校验Handler,实际什么都没做,包括子类.
1 /**
2 * Validate the given handler against the current request.
3 * <p>The default implementation is empty. Can be overridden in subclasses,
4 * for example to enforce specific preconditions expressed in URL mappings.
5 * @param handler the handler object to validate
6 * @param request current HTTP request
7 * @throws Exception if validation failed
8 */
9 protected void validateHandler(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
10 }
封装handler为HandlerExecutionChain,并添加PathExposingHandlerInterceptor和UriTemplateVariablesHandlerInterceptor拦截器.
1 /**
2 * Build a handler object for the given raw handler, exposing the actual
3 * handler, the {@link #PATH_WITHIN_HANDLER_MAPPING_ATTRIBUTE}, as well as
4 * the {@link #URI_TEMPLATE_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE} before executing the handler.
5 * <p>The default implementation builds a {@link HandlerExecutionChain}
6 * with a special interceptor that exposes the path attribute and uri template variables
7 * @param rawHandler the raw handler to expose
8 * @param pathWithinMapping the path to expose before executing the handler
9 * @param uriTemplateVariables the URI template variables, can be {@code null} if no variables found
10 * @return the final handler object
11 */
12 protected Object buildPathExposingHandler(Object rawHandler, String bestMatchingPattern,
13 String pathWithinMapping, Map<String, String> uriTemplateVariables) {
14
15 HandlerExecutionChain chain = new HandlerExecutionChain(rawHandler);
16 chain.addInterceptor(new PathExposingHandlerInterceptor(bestMatchingPattern, pathWithinMapping));
17 if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(uriTemplateVariables)) {
18 chain.addInterceptor(new UriTemplateVariablesHandlerInterceptor(uriTemplateVariables));
19 }
20 return chain;
21 }
HandlerMapping - RequestMappingHandlerMapping初始化
RequestMappingHandlerMapping ,用于注解@Controller,@RequestMapping来定义controller.
1 @Controller
2 @RequestMapping(value = "books")
3 public class BookController {
4
5 @RequestMapping(value = "/{id}")
6 @ResponseBody
7 public String getBook(@PathVariable("id") String id) {
8 // ...
9 return id;
10 }
11 }

初始化时,3个类的大致分工如下:
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping定义整个算法流程;
RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping提供匹配条件RequestMappingInfo的解析处理;
RequestMappingHandlerMapping根据@RequestMapping注解生成 RequestMappingInfo,同时提供isHandler实现
整个初始化工作由AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的initHandlerMethods主导.
1. 使用BeanFactoryUtils扫描应用下的Object或者直接从容器中获取Object
2. 迭代类,分别判断isHandler判断目标类是否Handler
2.1 RequestMappingHandlerMapping.isHandler根据@Controller或@RequestMapping注解判断(有任意一个)
3. 对handler解析出所有需要分发的方法detectHandlerMethods
3.1 获取原始的Class<?>
3.2 使用HandlerMethodSelector.selectMethods过滤具体handler method,预留getMappingForMethod模板方法给子类
RequestMappingHandlerMapping.getMappingForMethod根据类,方法上的RequestMapping注解生成匹配条件RequestMappingInfo
3.3 对过滤到的每个method进行注册registerHandlerMethod
a, 使用createHandlerMethod封装处理器为HandlerMethod
b, 判断之前是否已经匹配条件对应的处理器是否冲突(相同的匹配条件只能有一个对应的处理器)
c, 设置匹配条件到handler method的映射关系
d, 从匹配条件中解析出url,并注册到urlMap(url到匹配条件的映射),这边由RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping.getMappingPathPatterns实现
4. 对HandlerMethod进行初始化handlerMethodsInitialized,其实现在什么都没做
在讲初始化之前,我们先来聊聊使用到的一些概念
1. 映射关系,url到匹配条件RequestMappingInfo,匹配条件到HandlerMethod
2. 特殊的MultiValueMap,特别在value是个List
3. 使用到注解@Controller,@RequestMapping
4. 封装处理器信息的HandlerMethod
5. 封装各类匹配条件的RequestMappingInfo(诸如pattern,http method,request parameter等)
6. RequestCondition记录匹配条件
1. 进行request分发前,需要在初始化时准备好映射关系,这边AbstractHandlerMethodMapping中有两个属性保存了映射关系
// AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
1 // 匹配条件到HandlerMethod的映射 2 private final Map<T, HandlerMethod> handlerMethods = new LinkedHashMap<T, HandlerMethod>(); 3 // url到匹配条件的映射 4 private final MultiValueMap<String, T> urlMap = new LinkedMultiValueMap<String, T>();
2. 这边的MultiValueMap其实挺简单,就是map的值是个list
1 public interface MultiValueMap<K, V> extends Map<K, List<V>> {
2 // ...
3 }
3. 我们再来看看这边使用到的两个注解:
// @Controller
1 // org.springframework.stereotype.Controller
2 @Target({ElementType.TYPE})
3 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
4 @Documented
5 @Component
6 public @interface Controller {
7
8 /**
9 * The value may indicate a suggestion for a logical component name,
10 * to be turned into a Spring bean in case of an autodetected component.
11 * @return the suggested component name, if any
12 */
13 String value() default "";
14
15 }
// @RequestMapping
1 // org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping
2 @Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
3 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
4 @Documented
5 @Mapping
6 public @interface RequestMapping {
7
8 /**
9 * url路径,如/myPath/*.do
10 */
11 String[] value() default {};
12
13 /**
14 * HTTP request methods 如:GET, POST, HEAD, OPTIONS, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, TRACE.
15 */
16 RequestMethod[] method() default {};
17
18 /**
19 * requeset parameter 有3种匹配方式,是否包含某个参数,参数值相等,参数值不等于某个值,如myParam!=myValue
20 */
21 String[] params() default {};
22
23 /**
24 * request的header
25 */
26 String[] headers() default {};
27
28 /**
29 * request的content type
30 */
31 String[] consumes() default {};
32
33 /**
34 * 返回内容的content type
35 */
36 String[] produces() default {};
37
38 }
39 }
4. HandlerMethod封装了处理器相关的全部信息,如类Object,方法Method,BeanFactory,参数MethodParameter[],原始方法Method
// HandlerMethod
1 // org.springframework.web.method.HandlerMethod 2 private final Object bean;// 因为final不可修改,所以下面每次需要修改信息时,都需要new一个 3 4 private final Method method; 5 6 private final BeanFactory beanFactory; 7 8 private final MethodParameter[] parameters; 9 10 private final Method bridgedMethod;
5. 这边匹配条件的范型只有一个实现,RequestMappingInfo.匹配条件里记录的是RequestCondition子类,用于诸如pattern,http method,request parameter等
// RequestMappingInfo
1 // javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest.RequestMappingInfo
2 public final class RequestMappingInfo implements RequestCondition<RequestMappingInfo> {
3
4 private final PatternsRequestCondition patternsCondition;
5
6 private final RequestMethodsRequestCondition methodsCondition;
7
8 private final ParamsRequestCondition paramsCondition;
9
10 private final HeadersRequestCondition headersCondition;
11
12 private final ConsumesRequestCondition consumesCondition;
13
14 private final ProducesRequestCondition producesCondition;
15
16 private final RequestConditionHolder customConditionHolder;
17 // ...
18
19 }
6. 最后再简单看看RequestCondition ,这边定义了3个方法
1 package org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.condition;
2 public interface RequestCondition<T> {
3 /**
4 * 拼接条件
5 */
6 T combine(T other);
7
8 /**
9 * 查找匹配的条件,并返回
10 */
11 T getMatchingCondition(HttpServletRequest request);
12
13 /**
14 * 用于排序
15 */
16 int compareTo(T other, HttpServletRequest request);
17 }
看看继承体系吧,老套路,定义接口,然后模板方法实现主要逻辑,具体算法留给子类实现,还有正事要做,还是后期再细化吧.
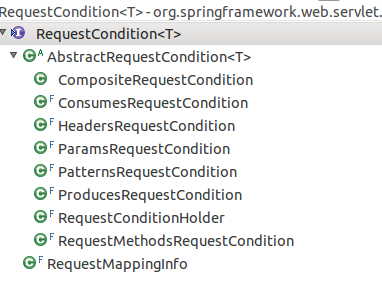
正文
整个初始化工作由AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的initHandlerMethods主导.copy一段,省得回去比对看
1. 使用BeanFactoryUtils扫描应用下的Object或者直接从容器中获取Object
2. 迭代类,分别判断isHandler判断目标类是否Handler
2.1 RequestMappingHandlerMapping.isHandler根据@Controller或@RequestMapping注解判断(有任意一个)
3. 对handler解析出所有需要分发的方法detectHandlerMethods
3.1 获取原始的Class<?>
3.2 使用HandlerMethodSelector.selectMethods过滤具体handler method,预留getMappingForMethod模板方法给子类
RequestMappingHandlerMapping.getMappingForMethod根据类,方法上的RequestMapping注解生成匹配条件RequestMappingInfo
3.3 对过滤到的每个method进行注册registerHandlerMethod
a, 使用createHandlerMethod封装处理器为HandlerMethod
b, 判断之前是否已经匹配条件对应的处理器是否冲突(相同的匹配条件只能有一个对应的处理器)
c, 设置匹配条件到handler method的映射关系
d, 从匹配条件中解析出url,并注册到urlMap(url到匹配条件的映射),这边由RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping.getMappingPathPatterns实现
4. 对HandlerMethod进行初始化handlerMethodsInitialized,其实现在什么都没做
// AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
1 /** 这个方法哪来的,具体看备注的InitializingBean
2 * Detects handler methods at initialization.
3 */
4 public void afterPropertiesSet() {
5 initHandlerMethods();
6 }
7
8 /**扫描ApplicationContext中的bean,然后筛选handler method 并注册
9 * Scan beans in the ApplicationContext, detect and register handler methods.
10 * @see #isHandler(Class)
11 * @see #getMappingForMethod(Method, Class)
12 * @see #handlerMethodsInitialized(Map)
13 */
14 protected void initHandlerMethods() {
15 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
16 logger.debug("Looking for request mappings in application context: " + getApplicationContext());
17 }
18
19 String[] beanNames = (this.detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts ?
20 BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(getApplicationContext(), Object.class) :
21 getApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class));
22
23 for (String beanName : beanNames) {
24 if (isHandler(getApplicationContext().getType(beanName))){
25 detectHandlerMethods(beanName);
26 }
27 }
28 handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods());
29 }
预留给子类实现的判断handler,实际是由RequestMappingHandlerMapping实现
// AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
1 /** 2 * Whether the given type is a handler with handler methods. 3 * @param beanType the type of the bean being checked 4 * @return "true" if this a handler type, "false" otherwise. 5 */ 6 protected abstract boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType);
// RequestMappingHandlerMapping
这边判断的逻辑很简单,类上使用Controller或RequestMapping其中至少一个注解就可以.
1 /**
2 * {@inheritDoc}
3 * Expects a handler to have a type-level @{@link Controller} annotation.
4 */
5 @Override
6 protected boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType) {
7 return ((AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class) != null) ||
8 (AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(beanType, RequestMapping.class) != null));
9 }
// AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
1 /**
2 * Look for handler methods in a handler.
3 * @param handler the bean name of a handler or a handler instance
4 */
5 protected void detectHandlerMethods(final Object handler) {
6 Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String) ?
7 getApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass();
8
9 final Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);
10
11 Set<Method> methods = HandlerMethodSelector.selectMethods(userType, new MethodFilter() {
12 public boolean matches(Method method) {
13 return getMappingForMethod(method, userType) != null;
14 }
15 });
16
17 for (Method method : methods) {
18 T mapping = getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
19 registerHandlerMethod(handler, method, mapping);
20 }
21 }
// AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
这边具体的实现是由RequestMappingHandlerMapping实现,根据注解生产匹配关系,这边实现类是RequestMappingInfo,就是代码有点多,慢慢看
1 /**
2 * Provide the mapping for a handler method. A method for which no
3 * mapping can be provided is not a handler method.
4 * @param method the method to provide a mapping for
5 * @param handlerType the handler type, possibly a sub-type of the method's
6 * declaring class
7 * @return the mapping, or {@code null} if the method is not mapped
8 */
9 protected abstract T getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class<?> handlerType);
// RequestMappingHandlerMapping
1 /**
2 * Uses method and type-level @{@link RequestMapping} annotations to create
3 * the RequestMappingInfo.
4 *
5 * @return the created RequestMappingInfo, or {@code null} if the method
6 * does not have a {@code @RequestMapping} annotation.
7 *
8 * @see #getCustomMethodCondition(Method)
9 * @see #getCustomTypeCondition(Class)
10 */
11 @Override
12 protected RequestMappingInfo getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class<?> handlerType) {
13 RequestMappingInfo info = null;
14 // 读取方法上的RequestMapping注解信息
15 RequestMapping methodAnnotation = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(method, RequestMapping.class);
16 if (methodAnnotation != null) {
17 // 读取自定义的条件,这边没有使用
18 RequestCondition<?> methodCondition = getCustomMethodCondition(method);
19 // 根据方法上的RequsetMapping注解和自定义条件,生成匹配条件.这边的匹配条件包括http method,request parameter,request header等
20 info = createRequestMappingInfo(methodAnnotation, methodCondition);
21 // 读取类上的RequestMapping注解信息
22 RequestMapping typeAnnotation = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(handlerType, RequestMapping.class);
23 if (typeAnnotation != null) {
24 RequestCondition<?> typeCondition = getCustomTypeCondition(handlerType);
25 // 生成类上的匹配条件,并合并方法上的
26 info = createRequestMappingInfo(typeAnnotation, typeCondition).combine(info);
27 }
28 }
29 return info;
30 }
// RequestMappingHandlerMapping
1 /**
2 * Created a RequestMappingInfo from a RequestMapping annotation.
3 */
4 private RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(RequestMapping annotation, RequestCondition<?> customCondition) {
5 String[] patterns = resolveEmbeddedValuesInPatterns(annotation.value());
6 return new RequestMappingInfo(
7 new PatternsRequestCondition(patterns, getUrlPathHelper(), getPathMatcher(),
8 this.useSuffixPatternMatch, this.useTrailingSlashMatch, this.fileExtensions),
9 new RequestMethodsRequestCondition(annotation.method()),
10 new ParamsRequestCondition(annotation.params()),
11 new HeadersRequestCondition(annotation.headers()),
12 new ConsumesRequestCondition(annotation.consumes(), annotation.headers()),
13 new ProducesRequestCondition(annotation.produces(), annotation.headers(), getContentNegotiationManager()),
14 customCondition);
15 }
16
17 /**
18 * Resolve placeholder values in the given array of patterns.
19 * @return a new array with updated patterns
20 */
21 protected String[] resolveEmbeddedValuesInPatterns(String[] patterns) {
22 if (this.embeddedValueResolver == null) {
23 return patterns;
24 }
25 else {
26 String[] resolvedPatterns = new String[patterns.length];
27 for (int i=0; i < patterns.length; i++) {
28 resolvedPatterns[i] = this.embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(patterns[i]);
29 }
30 return resolvedPatterns;
31 }
32 }
// AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
1 /**
2 * Register a handler method and its unique mapping.
3 * @param handler the bean name of the handler or the handler instance
4 * @param method the method to register
5 * @param mapping the mapping conditions associated with the handler method
6 * @throws IllegalStateException if another method was already registered
7 * under the same mapping
8 */
9 protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, T mapping) {
10 HandlerMethod newHandlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method);
11 HandlerMethod oldHandlerMethod = handlerMethods.get(mapping);
12 if (oldHandlerMethod != null && !oldHandlerMethod.equals(newHandlerMethod)) {
13 throw new IllegalStateException("Ambiguous mapping found. Cannot map '" + newHandlerMethod.getBean()
14 + "' bean method \n" + newHandlerMethod + "\nto " + mapping + ": There is already '"
15 + oldHandlerMethod.getBean() + "' bean method\n" + oldHandlerMethod + " mapped.");
16 }
17
18 this.handlerMethods.put(mapping, newHandlerMethod);// 匹配条件requestMappingInfo 到处理器HandlerMethod
19 if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
20 logger.info("Mapped \"" + mapping + "\" onto " + newHandlerMethod);
21 }
22
23 Set<String> patterns = getMappingPathPatterns(mapping);
24 for (String pattern : patterns) {
25 if (!getPathMatcher().isPattern(pattern)) {
26 this.urlMap.add(pattern, mapping);// url到匹配条件RequestMappingInfo
27 }
28 }
29 }
// AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
1 /**
2 * Create the HandlerMethod instance.
3 * @param handler either a bean name or an actual handler instance
4 * @param method the target method
5 * @return the created HandlerMethod
6 */
7 protected HandlerMethod createHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method) {
8 HandlerMethod handlerMethod;
9 if (handler instanceof String) {
10 String beanName = (String) handler;
11 handlerMethod = new HandlerMethod(beanName, getApplicationContext(), method);
12 }
13 else {
14 handlerMethod = new HandlerMethod(handler, method);
15 }
16 return handlerMethod;
17 }
// AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
1 /** 2 * Extract and return the URL paths contained in a mapping. 3 */ 4 protected abstract Set<String> getMappingPathPatterns(T mapping);
RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping会实现这个模板方法
// RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping
1 /**
2 * Get the URL path patterns associated with this {@link RequestMappingInfo}.
3 */
4 @Override
5 protected Set<String> getMappingPathPatterns(RequestMappingInfo info) {
6 return info.getPatternsCondition().getPatterns();
7 }
备注:
1. 这边的afterPropertiesSet是因为实现了InitializingBean接口
// org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean
1 /**
2 * Interface to be implemented by beans that need to react once all their
3 * properties have been set by a BeanFactory: for example, to perform custom
4 * initialization, or merely to check that all mandatory properties have been set.
5 *
6 * <p>An alternative to implementing InitializingBean is specifying a custom
7 * init-method, for example in an XML bean definition.
8 * For a list of all bean lifecycle methods, see the BeanFactory javadocs.
9 *
10 * @author Rod Johnson
11 * @see BeanNameAware
12 * @see BeanFactoryAware
13 * @see BeanFactory
14 * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition#getInitMethodName
15 * @see org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware
16 */
17 public interface InitializingBean {
18
19 /**
20 * Invoked by a BeanFactory after it has set all bean properties supplied
21 * (and satisfied BeanFactoryAware and ApplicationContextAware).
22 * <p>This method allows the bean instance to perform initialization only
23 * possible when all bean properties have been set and to throw an
24 * exception in the event of misconfiguration.
25 * @throws Exception in the event of misconfiguration (such
26 * as failure to set an essential property) or if initialization fails.
27 */
28 void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;
29
30 }
HandlerMapping - RequestMappingHandlerMapping请求分发
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping实现接口getHandlerInternal,定义查找流程
RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping根据RequestMappingInfo,细化匹配条件,并在匹配不到情况下,顽强的使用RequestCondition一再尝试匹配
虽然 RequestMappingHandlerMapping是受益方,但在这边什么都没做(就是在初始化时,根据@Controller,@RequestMapping注解生成RequestMappingInfo;并根据这两个注解判断是否目标Handler 实现isHandler)
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping实现接口getHandlerInternal
1. 使用UrlPathHelper查找request对应的path
2. 查找path对应的HandlerMethod
2.1 从urlMap中直接等值匹配查找匹配条件RequestMappingInfo
2.2 如果等值查找到匹配条件,将其添加到match条件中
2.3 如果没有找到匹配条件,使用所有的handlerMethod的RequestMappingInfo进行匹配
2.4 对匹配到的Match进行排序,取出最高优先级的Match,并核对是否是唯一的最高优先级
2.5 对匹配到条件,没有匹配到条件的两种情况,分别进行封装
3. 封装HandlerMethod,确保bean中存的是实例
// AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
实现接口getHandlerInternal
1 package org.springframework.web.servlet.handler
2 // AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T>
3 /**
4 * Look up a handler method for the given request.
5 */
6 @Override
7 protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
8 // 就是request对应的url
9 String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
10 // 查找到处理器,这边的处理器会封装成HandlerMethod
11 HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
12 // 确保bean中存的是实例
13 return (handlerMethod != null) ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null;
14 }
// AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
package org.springframework.web.servlet.handler;
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
/**
* Look up the best-matching handler method for the current request.
* If multiple matches are found, the best match is selected.
* @param lookupPath mapping lookup path within the current servlet mapping
* @param request the current request
* @return the best-matching handler method, or {@code null} if no match
* @see #handleMatch(Object, String, HttpServletRequest)
* @see #handleNoMatch(Set, String, HttpServletRequest)
*/
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<Match>();
// 从urlMap中直接等值匹配查找匹配条件RequestMappingInfo
List<T> directPathMatches = this.urlMap.get(lookupPath);
if (directPathMatches != null) {
//
addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
}
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
// No choice but to go through all mappings
// 没有匹配的情况下,遍历handlerMethods的全部匹配条件进行查找
addMatchingMappings(this.handlerMethods.keySet(), matches, request);
}
if (!matches.isEmpty()) {
Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request));
Collections.sort(matches, comparator);
Match bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (matches.size() > 1) {
Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1);
if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) {
Method m1 = bestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
Method m2 = secondBestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
// 不能有相同的最优Match
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Ambiguous handler methods mapped for HTTP path '" + request.getRequestURL() + "': {" +
m1 + ", " + m2 + "}");
}
}
// 就是往request域中缓存url中解析出来的参数,mediaType等,这边RequestMappingHandlerMapping也覆写了一下
handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request);
return bestMatch.handlerMethod;
}
else {
// RequestMappingHandlerMapping
return handleNoMatch(handlerMethods.keySet(), lookupPath, request);
}
}
}
// AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
查找具体符合条件的RequestCondition
1 package org.springframework.web.servlet.handler;
2 public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
3
4 private void addMatchingMappings(Collection<T> mappings, List<Match> matches, HttpServletRequest request) {
5 for (T mapping : mappings) {
6 T match = getMatchingMapping(mapping, request);
7 if (match != null) {
8 matches.add(new Match(match, handlerMethods.get(mapping)));
9 }
10 }
11 }
// AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
1 /**
2 * Check if a mapping matches the current request and return a (potentially
3 * new) mapping with conditions relevant to the current request.
4 * @param mapping the mapping to get a match for
5 * @param request the current HTTP servlet request
6 * @return the match, or {@code null} if the mapping doesn't match
7 */
8 protected abstract T getMatchingMapping(T mapping, HttpServletRequest request);
我们来看看RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping中的实现,从RequestMappingInfo中查找符合的RequestCondition
// RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping
1 /**
2 * Check if the given RequestMappingInfo matches the current request and
3 * return a (potentially new) instance with conditions that match the
4 * current request -- for example with a subset of URL patterns.
5 * @return an info in case of a match; or {@code null} otherwise.
6 */
7 @Override
8 protected RequestMappingInfo getMatchingMapping(RequestMappingInfo info, HttpServletRequest request) {
9 return info.getMatchingCondition(request);
10 }
// AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
1 /**
2 * Invoked when a matching mapping is found.
3 * @param mapping the matching mapping
4 * @param lookupPath mapping lookup path within the current servlet mapping
5 * @param request the current request
6 */
7 protected void handleMatch(T mapping, String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) {
8 request.setAttribute(HandlerMapping.PATH_WITHIN_HANDLER_MAPPING_ATTRIBUTE, lookupPath);
9 }
RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping中又对其进行了覆写,具体是干啥用的,等看了HandlerAdaptor再说吧
1 /**
2 * Expose URI template variables, matrix variables, and producible media types in the request.
3 * @see HandlerMapping#URI_TEMPLATE_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE
4 * @see HandlerMapping#MATRIX_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE
5 * @see HandlerMapping#PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE
6 */
7 @Override
8 protected void handleMatch(RequestMappingInfo info, String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) {
9 super.handleMatch(info, lookupPath, request);
10
11 Set<String> patterns = info.getPatternsCondition().getPatterns();
12 String bestPattern = patterns.isEmpty() ? lookupPath : patterns.iterator().next();
13 request.setAttribute(BEST_MATCHING_PATTERN_ATTRIBUTE, bestPattern);
14
15 Map<String, String> uriVariables = getPathMatcher().extractUriTemplateVariables(bestPattern, lookupPath);
16 Map<String, String> decodedUriVariables = getUrlPathHelper().decodePathVariables(request, uriVariables);
17 request.setAttribute(HandlerMapping.URI_TEMPLATE_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE, decodedUriVariables);
18
19 if (isMatrixVariableContentAvailable()) {
20 request.setAttribute(HandlerMapping.MATRIX_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE, extractMatrixVariables(request, uriVariables));
21 }
22
23 if (!info.getProducesCondition().getProducibleMediaTypes().isEmpty()) {
24 Set<MediaType> mediaTypes = info.getProducesCondition().getProducibleMediaTypes();
25 request.setAttribute(PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE, mediaTypes);
26 }
27 }
1 /**
2 * Invoked when no matching mapping is not found.
3 * @param mappings all registered mappings
4 * @param lookupPath mapping lookup path within the current servlet mapping
5 * @param request the current request
6 * @throws ServletException in case of errors
7 */
8 protected HandlerMethod handleNoMatch(Set<T> mappings, String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request)
9 throws Exception {
10
11 return null;
12 }
RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping,覆写,不死心,再匹配一次
// RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping
1 /**
2 * Iterate all RequestMappingInfos once again, look if any match by URL at
3 * least and raise exceptions accordingly.
4 * @throws HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException if there are matches by URL
5 * but not by HTTP method
6 * @throws HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException if there are matches by URL
7 * but not by consumable/producible media types
8 */
9 @Override
10 protected HandlerMethod handleNoMatch(Set<RequestMappingInfo> requestMappingInfos,
11 String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws ServletException {
12
13 Set<String> allowedMethods = new LinkedHashSet<String>(4);
14
15 Set<RequestMappingInfo> patternMatches = new HashSet<RequestMappingInfo>();
16 Set<RequestMappingInfo> patternAndMethodMatches = new HashSet<RequestMappingInfo>();
17
18 for (RequestMappingInfo info : requestMappingInfos) {
19 if (info.getPatternsCondition().getMatchingCondition(request) != null) {
20 patternMatches.add(info);
21 if (info.getMethodsCondition().getMatchingCondition(request) != null) {
22 patternAndMethodMatches.add(info);
23 }
24 else {
25 for (RequestMethod method : info.getMethodsCondition().getMethods()) {
26 allowedMethods.add(method.name());
27 }
28 }
29 }
30 }
31
32 if (patternMatches.isEmpty()) {
33 return null;
34 }
35 else if (patternAndMethodMatches.isEmpty() && !allowedMethods.isEmpty()) {
36 throw new HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException(request.getMethod(), allowedMethods);
37 }
38
39 Set<MediaType> consumableMediaTypes;
40 Set<MediaType> producibleMediaTypes;
41 Set<String> paramConditions;
42
43 if (patternAndMethodMatches.isEmpty()) {
44 consumableMediaTypes = getConsumableMediaTypes(request, patternMatches);
45 producibleMediaTypes = getProducibleMediaTypes(request, patternMatches);
46 paramConditions = getRequestParams(request, patternMatches);
47 }
48 else {
49 consumableMediaTypes = getConsumableMediaTypes(request, patternAndMethodMatches);
50 producibleMediaTypes = getProducibleMediaTypes(request, patternAndMethodMatches);
51 paramConditions = getRequestParams(request, patternAndMethodMatches);
52 }
53
54 if (!consumableMediaTypes.isEmpty()) {
55 MediaType contentType = null;
56 if (StringUtils.hasLength(request.getContentType())) {
57 try {
58 contentType = MediaType.parseMediaType(request.getContentType());
59 }
60 catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
61 throw new HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException(ex.getMessage());
62 }
63 }
64 throw new HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException(contentType, new ArrayList<MediaType>(consumableMediaTypes));
65 }
66 else if (!producibleMediaTypes.isEmpty()) {
67 throw new HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException(new ArrayList<MediaType>(producibleMediaTypes));
68 }
69 else if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(paramConditions)) {
70 String[] params = paramConditions.toArray(new String[paramConditions.size()]);
71 throw new UnsatisfiedServletRequestParameterException(params, request.getParameterMap());
72 }
73 else {
74 return null;
75 }
76 }





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步