高级语言程序设计课程第十次个人作业
这个作业属于哪个课程:https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/fzu/2024C
这个作业要求在哪里:https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/fzu/2024C/homework/13314
学号:102300108
姓名:陈茜蕾
1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#pragma warning(disable:4996)
void copy(FILE* p1, FILE* p2) {
char line[20]; // 假设每行至多20个字符
while (fgets(line, sizeof(line), p1) != NULL) {
fputs(line, p2); // 完成复制
}
}
int main() {
// 打开文件用于写入内容
FILE* p1 = fopen("test1.txt", "w");
if (p1 == NULL) {
printf("无法打开 test1.txt 文件!\n");
return 1;
}
FILE* p2 = fopen("test2.txt", "w");
if (p2 == NULL) {
printf("无法打开 test2.txt 文件!\n");
fclose(p1);
return 1;
}
// 向 test1.txt 写入内容
fputs("hello\nworld\n!", p1);
// 关闭 p1,以便下文使用
fclose(p1);
// 重新打开 p1 用于读取,p2 用于写入复制内容
p1 = fopen("test1.txt", "r");
if (p1 == NULL) {
printf("无法重新打开 test1.txt 文件!\n");
fclose(p2);
return 1;
}
p2 = fopen("test2.txt", "w"); // 清空 test2.txt 文件
if (p2 == NULL) {
printf("无法重新打开 test2.txt 文件!\n");
fclose(p1);
return 1;
}
// 复制内容
copy(p1, p2);
// 关闭文件
fclose(p1);
fclose(p2);
// 打开文件以打印验证内容
p1 = fopen("test1.txt", "r");
p2 = fopen("test2.txt", "r");
if (p1 == NULL || p2 == NULL) {
printf("无法打开文件以验证内容!\n");
return 1;
}
char line[20];
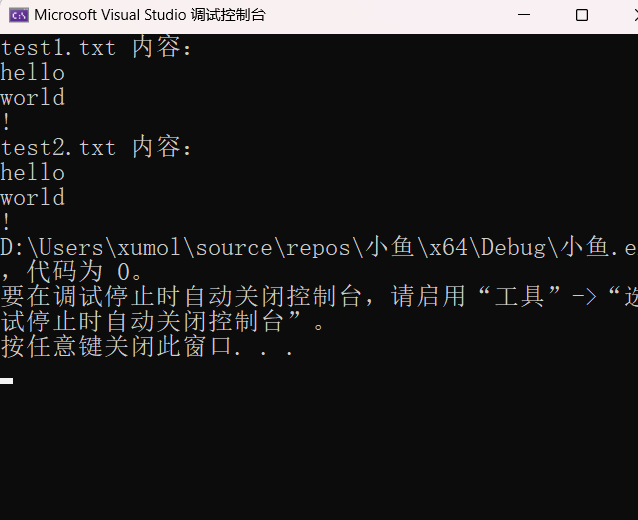
printf("test1.txt 内容:\n");
while (fgets(line, sizeof(line), p1) != NULL) {
printf("%s", line);
}
printf("\ntest2.txt 内容:\n");
while (fgets(line, sizeof(line), p2) != NULL) {
printf("%s", line);
}
// 关闭文件
fclose(p1);
fclose(p2);
return 0;
}
2
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#pragma warning(disable:4996)
int caculate(FILE* p1) {
int count = 0;
while (fgetc(p1)!=EOF) {
count++;
}
return count;
}
int main() {
// 打开文件用于写入内容
FILE* p1 = fopen("test1.txt", "w");
if (p1 == NULL) {
printf("无法打开 test1.txt 文件!\n");
return 1;
}
// 向 test1.txt 写入内容
fputs("hello\nworld\n!", p1);
// 关闭 p1,以便下文使用
fclose(p1);
// 重新打开 p1 用于读取
p1 = fopen("test1.txt", "r");
if (p1 == NULL) {
printf("无法重新打开 test1.txt 文件!\n");
return 1;
}
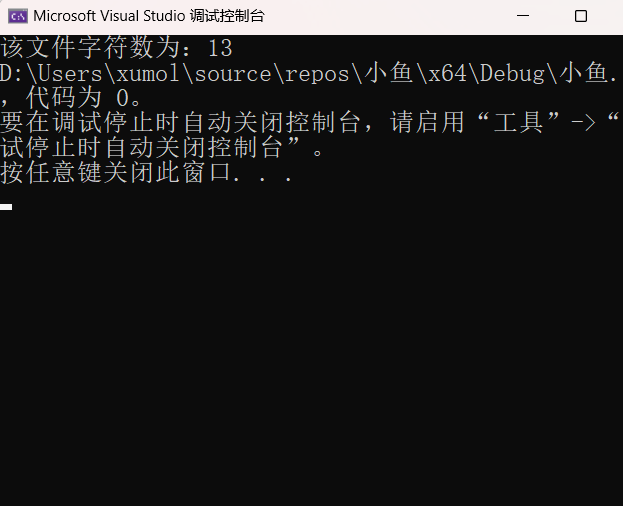
int cnt = caculate(p1);
// 关闭文件
fclose(p1);
printf("该文件字符数为:%d", cnt);
return 0;
}
3
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#pragma warning(disable:4996)
void print(FILE* p1) {
char c;
while ((c = fgetc(p1)) != EOF) {
printf("%c", c);
}
}
int main() {
// 打开文件用于写入内容
FILE* p1 = fopen("test1.txt", "w");
if (p1 == NULL) {
printf("无法打开 test1.txt 文件!\n");
return 1;
}
// 向 test1.txt 写入内容
fputs("hello\nworld\n!", p1);
// 关闭 p1,以便下文使用
fclose(p1);
// 重新打开 p1 用于读取
p1 = fopen("test1.txt", "r");
if (p1 == NULL) {
printf("无法重新打开 test1.txt 文件!\n");
return 1;
}
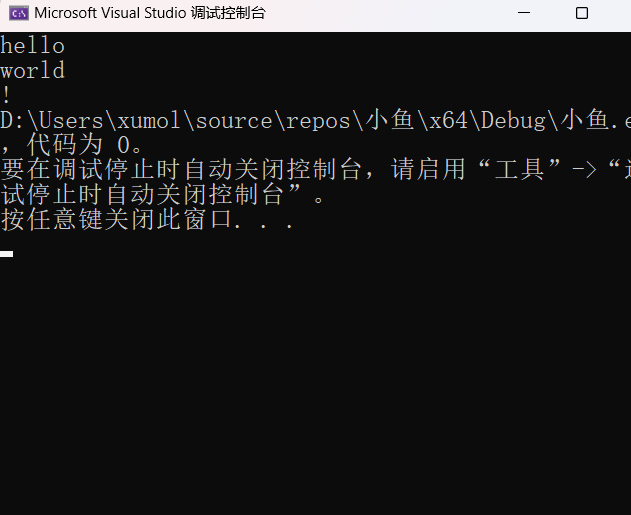
print(p1);
fclose(p1);
return 0;
}
4
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#pragma warning(disable:4996)
void print(FILE* p1) {
char c;
while ((c = fgetc(p1)) != EOF) {
printf("%c", c);
}
}
int main() {
// 打开文件用于写入内容
FILE* p1 = fopen("test1.txt", "w");
if (p1 == NULL) {
printf("无法打开 test1.txt 文件!\n");
return 1;
}
// 向 test1.txt 写入内容
fputs("hello\nworld\n!\n", p1);
// 关闭 p1,以便下文使用
fclose(p1);
// 重新打开 p1 用于追加
p1 = fopen("test1.txt", "a");
if (p1 == NULL) {
printf("无法重新打开 test1.txt 文件!\n");
return 1;
}
fputs("ooooooo!\n", p1);
fclose(p1);
p1 = fopen("test1.txt", "r");
print(p1);
fclose(p1);
return 0;
}

5
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#pragma warning(disable:4996)
void print(FILE* p1) {
char c;
while ((c = fgetc(p1)) != EOF) {
printf("%c", c);
}
}
int main() {
// 打开文件用于写入内容
FILE* p1 = fopen("test1.txt", "w");
FILE* p2 = fopen("test2.txt", "w");
if (p1 == NULL) {
printf("无法打开 test1.txt 文件!\n");
return 1;
}
if (p2 == NULL) {
printf("无法打开 test2.txt 文件!\n");
fclose(p1);
return 1;
}
// 向 test1.txt 写入内容
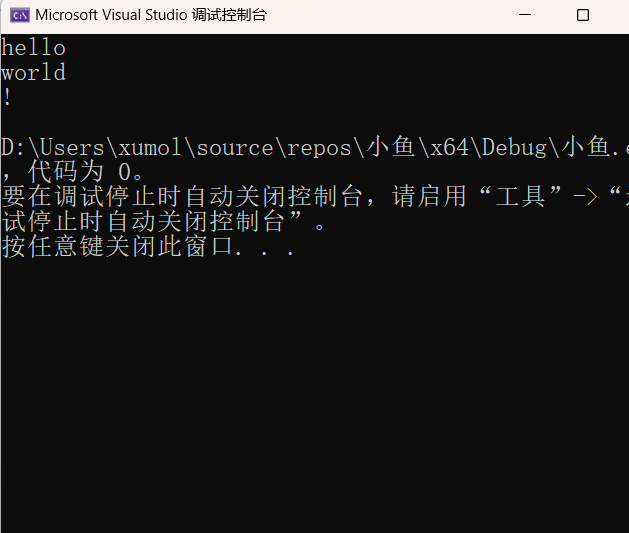
fputs("hello\nworld\n!\n", p1);
fputs("I like apples.\n", p1);
// 关闭 p1,以便下文使用
fclose(p1);
// 重新打开 p1 用于读取
p1 = fopen("test1.txt", "r");
char line[20];
while (fgets(line, 20, p1)) {
//指定查找apples
if (strstr(line, "apples")==NULL) {
fputs(line, p2);
}
}
fclose(p1);
fclose(p2);
p2 = fopen("test2.txt", "r");
print(p2);
fclose(p2);
return 0;
}
6
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#pragma warning(disable:4996)
int main() {
// 打开文件用于写入内容
FILE* p1 = fopen("test1.txt", "w");
if (p1 == NULL) {
printf("无法打开 test1.txt 文件!\n");
return 1;
}
// 向 test1.txt 写入内容
fputs("hello\nworld\n!\n", p1);
fputs("I like apples.\n", p1);
fclose(p1);
p1 = fopen("test1.txt", "r");
if (p1 == NULL) {
printf("无法打开 test1.txt 文件!\n");
return 1;
}
fseek(p1, 0, SEEK_END);
printf("%d\n", ftell(p1));
fclose(p1);
return 0;
}

7
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#pragma warning(disable:4996)
void print(FILE* p1) {
char c;
while ((c = fgetc(p1)) != EOF) {
printf("%c", c);
}
}
int main() {
// 打开文件用于写入内容
FILE* p1 = fopen("student.txt", "w");
if (p1 == NULL) {
printf("无法打开 student.txt 文件!\n");
return 1;
}
char name[5][20];
int grade1[5] = { 0 };
int grade2[5] = { 0 };
int grade3[5] = { 0 };
double average[5] = { 0 };
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
scanf("%s %d %d %d", &name[i], &grade1[i], &grade2[i], &grade3[i]);
average[i] += (grade1[i] + grade2[i] + grade3[i]) / 3.0;
fprintf(p1, "%s %d %d %d %lf\n", name[i], grade1[i], grade2[i], grade3[i], average[i]);
}
fclose(p1);
p1 = fopen("student.txt", "r");
if (p1 == NULL) {
printf("无法打开 student.txt 文件!\n");
return 1;
}
print(p1);
fclose(p1);
return 0;
}
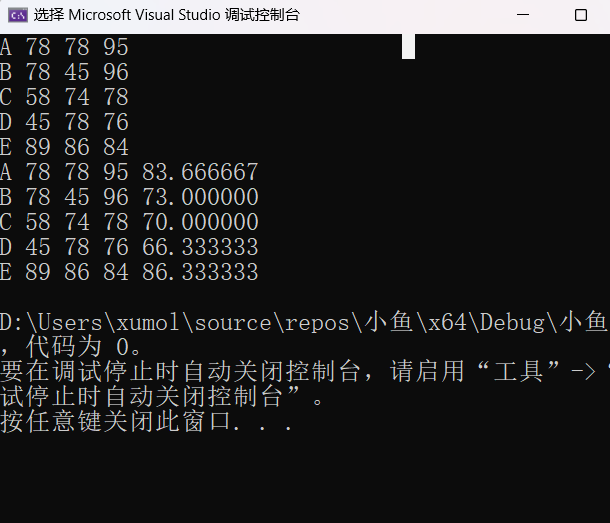
总结
没什么大问题但会忘记关文件和检查文件是否为空orz





