操作系统实验报告二
操作系统实验报告二
姓名:许恺
学号:2014011329
日期:10月14日
题目1:编写线程池
关键代码如下:
1.Thread.h #pragma once #ifndef __THREAD_H #define __THREAD_H #include <vector> #include <string> #include <pthread.h> #pragma comment(lib,"x86/pthreadVC2.lib") using namespace std; /** * 执行任务的类,设置任务数据并执行 */ class CTask { protected: string m_strTaskName; /** 任务的名称 */ void* m_ptrData; /** 要执行的任务的具体数据 */ public: CTask() {} CTask(string taskName) //任务类的重载:设置任务名,设置任务内容为空 { m_strTaskName = taskName; m_ptrData = NULL; } virtual int Run() = 0; /*启动任务的虚函数*/ void SetData(void* data); /** 设置任务数据 */ public: virtual ~CTask() {} //虚拟析构函数 }; /** * 线程池管理类的实现 */ class CThreadPool { private: static vector<CTask*> m_vecTaskList; /** 任务列表 */ static bool shutdown; /** 线程退出标志 */ int m_iThreadNum; /** 线程池中启动的线程数 */ pthread_t *pthread_id; static pthread_mutex_t m_pthreadMutex; /** 线程同步锁 */ static pthread_cond_t m_pthreadCond; /** 线程同步的条件变量 */ protected: static void* ThreadFunc(void * threadData); /** 新线程的线程回调函数 */ static int MoveToIdle(pthread_t tid); /** 线程执行结束后,把自己放入到空闲线程中 */ static int MoveToBusy(pthread_t tid); /** 移入到忙碌线程中去 */ int Create(); /** 创建线程池中的线程 */ public: CThreadPool(int threadNum = 10); int AddTask(CTask *task); /** 把任务添加到任务队列中 */ int StopAll(); /** 使线程池中的线程退出 */ int getTaskSize(); /** 获取当前任务队列中的任务数 */ }; #endif 2.Thread.cpp #include "stdafx.h" #include "Thread.h" #include <iostream> void CTask::SetData(void * data) //设置任务的具体内容 { m_ptrData = data; } vector<CTask*> CThreadPool::m_vecTaskList; //任务列表 bool CThreadPool::shutdown = false; //设置关闭为0 pthread_mutex_t CThreadPool::m_pthreadMutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER; //设置变量值 pthread_cond_t CThreadPool::m_pthreadCond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER; /** * 线程池管理类构造函数 */ CThreadPool::CThreadPool(int threadNum) { this->m_iThreadNum = threadNum; //用参数设置线程数量 cout << "I will create " << threadNum << " threads\n" << endl; Create(); //调用创建线程的函数 } /** * 线程回调函数 */ void* CThreadPool::ThreadFunc(void* threadData) { pthread_t tid = pthread_self(); while (1) { pthread_mutex_lock(&m_pthreadMutex); while (m_vecTaskList.size() == 0 && !shutdown) //没有任务就挂起等待 { pthread_cond_wait(&m_pthreadCond, &m_pthreadMutex); } if (shutdown) //如果是关闭的就解锁退出线程 { pthread_mutex_unlock(&m_pthreadMutex); printf("thread %lu will exit\n", pthread_self()); pthread_exit(NULL); } printf("tid %lu run\n", tid); vector<CTask*>::iterator iter = m_vecTaskList.begin(); //添加迭代器从任务列表开头 /** * 取出一个任务并处理之 */ CTask* task = *iter; if (iter != m_vecTaskList.end()) { task = *iter; m_vecTaskList.erase(iter); } pthread_mutex_unlock(&m_pthreadMutex); task->Run(); /** 执行任务 */ printf("tid:%lu idle\n", tid); } return (void*)0; } int CThreadPool::MoveToIdle(pthread_t tid) { return 0; } int CThreadPool::MoveToBusy(pthread_t tid) { return 0; } /** * 往任务队列里边添加任务并发出线程同步信号 */ int CThreadPool::AddTask(CTask *task) { pthread_mutex_lock(&m_pthreadMutex); this->m_vecTaskList.push_back(task); pthread_mutex_unlock(&m_pthreadMutex); pthread_cond_signal(&m_pthreadCond); return 0; } /** * 创建线程 */ int CThreadPool::Create() { pthread_id = (pthread_t*)malloc(sizeof(pthread_t) * m_iThreadNum); for (int i = 0; i < m_iThreadNum; i++) { pthread_create(&pthread_id[i], NULL, ThreadFunc, NULL); } return 0; } /** * 停止所有线程 */ int CThreadPool::StopAll() { /** 避免重复调用 */ if (shutdown) { return -1; } printf("Now I will end all threads!!\n"); /** 唤醒所有等待线程,线程池要销毁了 */ shutdown = true; pthread_cond_broadcast(&m_pthreadCond); /** 阻塞等待线程退出,否则就成僵尸了 */ for (int i = 0; i < m_iThreadNum; i++) { pthread_join(pthread_id[i], NULL); } free(pthread_id); pthread_id = NULL; /** 销毁条件变量和互斥体 */ pthread_mutex_destroy(&m_pthreadMutex); pthread_cond_destroy(&m_pthreadCond); return 0; } /** * 获取当前队列中任务数 */ int CThreadPool::getTaskSize() { return m_vecTaskList.size(); } 3.webServer2.cpp // webServer2.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 // #include "stdafx.h" #include "Thread.h" #include <iostream> #include <windows.h> class CMyTask : public CTask { public: CMyTask() {} inline int Run() { printf("%s\n", (char*)this->m_ptrData); Sleep(10); return 0; } }; int main() { CMyTask taskObj; char szTmp[] = "this is the first thread running\n"; //任务内容 taskObj.SetData((void*)szTmp); //将任务内容设到对象里 CThreadPool threadPool(10); for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { threadPool.AddTask(&taskObj); //将任务对象添加到线程池的任务队列 } while (1)//检查任务完成情况,看是否退出 { printf("there are still %d tasks need to handle\n", threadPool.getTaskSize()); if (threadPool.getTaskSize() == 0) { if (threadPool.StopAll() == -1) //如果没剩就退出 { printf("Now I will exit from main\n"); exit(0); } } Sleep(10); //给予任务执行时间 } return 0; }
题目2:将Web服务器接收功能加入到此线程池中,让线程池中的线程完成信号接收功能、文件读取和发送
程序代码以及运行贴图:
1.webServer2.cpp // webServer2.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 // #include "stdafx.h" #include <iostream> #include <Winsock2.h> #include <windows.h> #include <string> #include <fstream> #pragma comment(lib, "ws2_32.lib") using namespace std; SOCKET socketconn; static string dir = "D:\\xukai\\学习\\操作系统实验\\webServer1\\webServer\\Debug\\";//文件路径 #include "Thread.h" #include "CMyTask.h" void main(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { CMyTask taskObj; CThreadPool threadPool(10); //初始化WinSock库 WORD wVersionRequested; WSADATA wsaData; cout << "初始化库成功" << endl; wVersionRequested = MAKEWORD(2, 2); int wsaret = WSAStartup(wVersionRequested, &wsaData); if (wsaret) return; //创建SOCKET SOCKET socketSrv; socketSrv = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0); if (socketSrv == INVALID_SOCKET) return; cout << "创建socket成功" << endl; SOCKADDR_IN addrSrv; addrSrv.sin_addr.S_un.S_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY); addrSrv.sin_family = AF_INET; addrSrv.sin_port = htons(80); //绑定套接字 if (bind(socketSrv, (struct sockaddr*)&addrSrv, sizeof(SOCKADDR))) { //关闭连接 shutdown(socketSrv, 1); closesocket(socketSrv); WSACleanup(); return; } cout << "绑定套接字成功!" << endl; //等待客户端连接 SOCKADDR_IN addrCli; int len = sizeof(SOCKADDR); //监听端口 if (listen(socketSrv, 5) == SOCKET_ERROR) { printf("监听失败!\n"); } while (true) { socketconn = accept(socketSrv, (SOCKADDR*)&addrCli, &len); //接受连接 if (socketconn == SOCKET_ERROR) { printf("接受连接失败!\n"); return; } cout << "连接成功" << endl; taskObj.SetData((void*)0); //将任务内容设到对象里 threadPool.AddTask(&taskObj); //将任务对象添加到线程池的任务队列 CThreadPool::Threadfunction(); } shutdown(socketSrv, 1); closesocket(socketSrv); //关闭连接 WSACleanup(); } 2.Thread.h #pragma once #ifndef __THREAD_H #define __THREAD_H #include <vector> #include <string> #include <pthread.h> #pragma comment(lib,"x86/pthreadVC2.lib") using namespace std; /** * 执行任务的类,设置任务数据并执行 */ class CTask { protected: string m_strTaskName; /** 任务的名称 */ void* m_ptrData; /** 要执行的任务的具体数据 */ public: CTask() {} CTask(string taskName) //任务类的重载:设置任务名,设置任务内容为空 { m_strTaskName = taskName; m_ptrData = NULL; } virtual int Run() = 0; /*启动任务的虚函数*/ void SetData(void* data); /** 设置任务数据 */ public: virtual ~CTask() {} //虚拟析构函数 }; /** * 线程池管理类的实现 */ class CThreadPool { private: static vector<CTask*> m_vecTaskList; /** 任务列表 */ static bool shutdown; /** 线程退出标志 */ int m_iThreadNum; /** 线程池中启动的线程数 */ pthread_t *pthread_id; static pthread_mutex_t m_pthreadMutex; /** 线程同步锁 */ static pthread_cond_t m_pthreadCond; /** 线程同步的条件变量 */ protected: static int MoveToIdle(pthread_t tid); /** 线程执行结束后,把自己放入到空闲线程中 */ static int MoveToBusy(pthread_t tid); /** 移入到忙碌线程中去 */ static void* ThreadFunc(void*); /** 新线程的线程回调函数 */ int Create(); /** 创建线程池中的线程 */ public: static void Threadfunction(); //在主函数中调用的任务函数 CThreadPool(int threadNum = 10); int AddTask(CTask *task); /** 把任务添加到任务队列中 */ int StopAll(); /** 使线程池中的线程退出 */ int getTaskSize(); /** 获取当前任务队列中的任务数 */ }; #endif 3.Thread.cpp #include "stdafx.h" #include "Thread.h" #include <iostream> void CTask::SetData(void * data) //设置任务的具体内容 { m_ptrData = data; } vector<CTask*> CThreadPool::m_vecTaskList; //任务列表 bool CThreadPool::shutdown = false; //设置关闭为0 pthread_mutex_t CThreadPool::m_pthreadMutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER; //设置变量值 pthread_cond_t CThreadPool::m_pthreadCond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER; /** * 线程池管理类构造函数 */ CThreadPool::CThreadPool(int threadNum) { this->m_iThreadNum = threadNum; //用参数设置线程数量 cout << "I will create " << threadNum << " threads\n" << endl; Create(); //调用创建线程的函数 } /** * 线程回调函数 */ void* CThreadPool::ThreadFunc(void*) { return (void*)1; } void CThreadPool::Threadfunction() { pthread_t tid = pthread_self(); printf("tid %lu run\n", tid); vector<CTask*>::iterator iter = m_vecTaskList.begin(); //添加迭代器从任务列表开头 /** * 取出一个任务并处理之 */ CTask* task = *iter; if (iter != m_vecTaskList.end()) { task = *iter; m_vecTaskList.erase(iter); } pthread_mutex_unlock(&m_pthreadMutex); task->Run(); /** 执行任务 */ printf("tid:%lu idle\n", tid); } int CThreadPool::MoveToIdle(pthread_t tid) { return 0; } int CThreadPool::MoveToBusy(pthread_t tid) { return 0; } /** * 往任务队列里边添加任务并发出线程同步信号 */ int CThreadPool::AddTask(CTask *task) { pthread_mutex_lock(&m_pthreadMutex); this->m_vecTaskList.push_back(task); pthread_mutex_unlock(&m_pthreadMutex); pthread_cond_signal(&m_pthreadCond); return 0; } /** * 创建线程 */ int CThreadPool::Create() { pthread_id = (pthread_t*)malloc(sizeof(pthread_t) * m_iThreadNum); for (int i = 0; i < m_iThreadNum; i++) { pthread_create(&pthread_id[i], NULL,ThreadFunc, NULL); } return 0; } /** * 停止所有线程 */ int CThreadPool::StopAll() { /** 避免重复调用 */ if (shutdown) { return -1; } printf("Now I will end all threads!!\n"); /** 唤醒所有等待线程,线程池要销毁了 */ shutdown = true; pthread_cond_broadcast(&m_pthreadCond); /** 阻塞等待线程退出,否则就成僵尸了 */ for (int i = 0; i < m_iThreadNum; i++) { pthread_join(pthread_id[i], NULL); } free(pthread_id); pthread_id = NULL; /** 销毁条件变量和互斥体 */ pthread_mutex_destroy(&m_pthreadMutex); pthread_cond_destroy(&m_pthreadCond); return 0; } /** * 获取当前队列中任务数 */ int CThreadPool::getTaskSize() { return m_vecTaskList.size(); } 4.CMyTask.h #pragma once #include "Thread.h" #include "windows.h" class CMyTask : public CTask { public: CMyTask() {} inline int Run() { printf("Process startup!\n"); //init WORD wVersionRequested; WSADATA wsaData; wVersionRequested = MAKEWORD(2, 2); WSAStartup(wVersionRequested, &wsaData); DWORD pid = ::GetCurrentProcessId(); sockaddr_in sa; int add_len = sizeof(sa); if (socketconn != INVALID_SOCKET) { getpeername(socketconn, (struct sockaddr *)&sa, &add_len); //while (1) //{ //连接成功后与客户端进行会话 char recvBuff[10000]; string sendBuf; string locDir; ifstream fp; //接收请求 if (recv(socketconn, recvBuff, 10000, 0) == SOCKET_ERROR) { printf("%d\n", socketconn); printf("error!"); getchar(); return 0; } //读取http请求头 string recvBuffer = recvBuff; int posGet = recvBuffer.find("GET", 0); int posHttp = recvBuffer.find("HTTP", 0); //截取html文件路径 for (int pos = posGet + 4; pos < posHttp; pos++) { if (recvBuffer[pos] == '/') { locDir.push_back('\\'); continue; } locDir.push_back(recvBuffer[pos]); } locDir = dir + locDir; //打开http请求文件进行读取 fp.open(locDir.c_str(), std::ios::binary); //打开文件失败 if (!fp.is_open()) { cout << "请求文件" << locDir.c_str() << "不存在" << endl; } else//打开文件成功并读取 { char buffer[1024]; while (fp.good() && !fp.eof()) { fp.getline(buffer, 1024); //将读取的内容追加入sendBuf中 sendBuf.append(buffer); buffer[0] = '\0'; } } fp.close(); //响应请求,将页面信息发送到客户端 if (send(socketconn, sendBuf.c_str(), sendBuf.length(), 0) == SOCKET_ERROR) { return 0; } shutdown(socketconn, 1); //关闭连接 closesocket(socketconn); } else { printf("[%d]fail accept:%d\n", pid, ::WSAGetLastError()); } return 0; } };
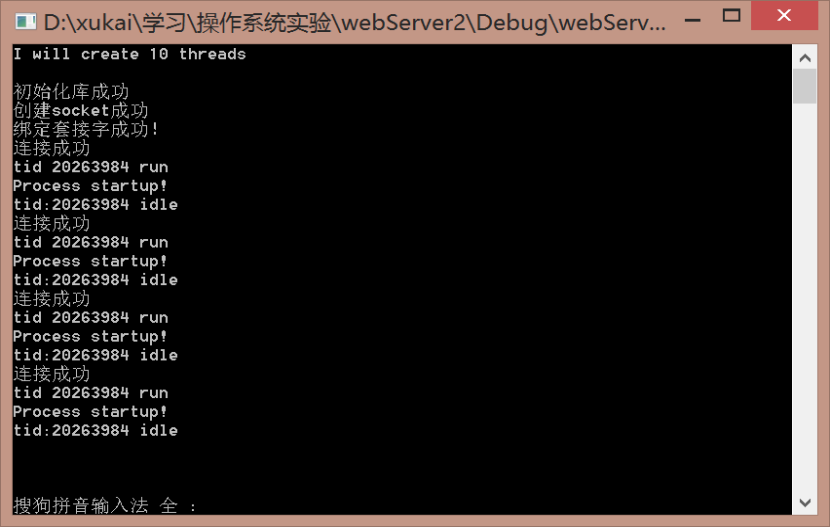

题目3:Web服务器对所有的Web页面请求进行计数,并能够对每个线程处理页面请求时间计时,每分钟报告一次服务器的状态:状态服务器需打印出当前时间,一共处理了多少请求链接,本分钟处理了多少链接请求,每次链接请求的时间是多少?
结论:
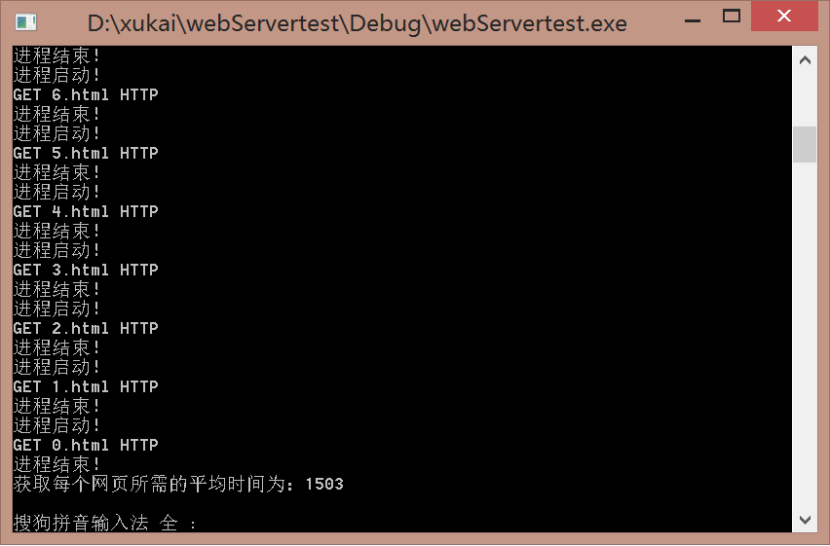
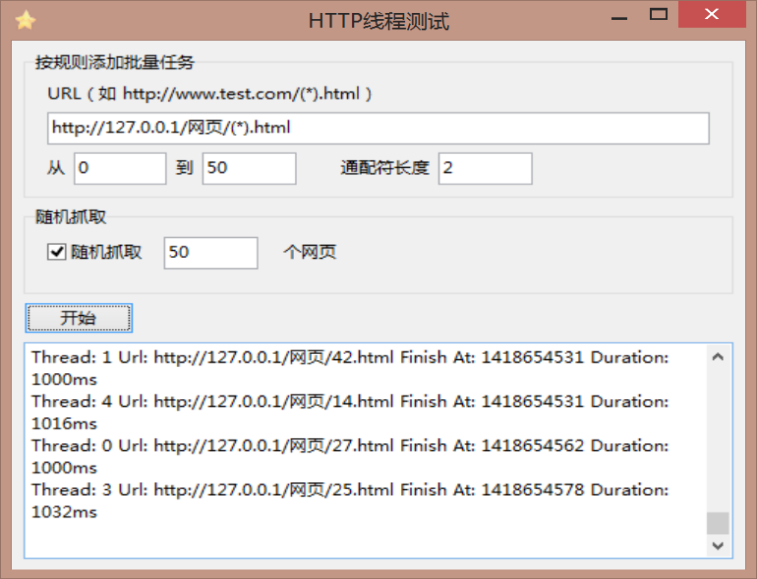
进程的网页测试在实验一的基础上进行,多线程的直接使用了老师给的工具,这里偷了个小懒。经过程序计算,多线程方法显然比进程的要快一些,是因为它不用一遍一遍去创建和释放进程,有线程池循环调用,在互斥锁的功能下也不会出现阻塞。因为不同的程序进行计算时间在细节上会有一定偏差但是差别不大,在这里我们忽略不记。
结果如图:
进程:
线程:
参考资料如下:
1.线程池代码来源:http://blog.csdn.net/rain_qingtian/article/details/12559073 感谢博主帮助。
2.在Windows下的pthread.h怎么用:
http://blog.csdn.net/qianchenglenger/article/details/16907821
3.还有修改阅读过的N个线程池代码:
http://www.oschina.net/code/snippet_256947_46521
http://blog.csdn.net/ithzhang/article/details/9020283
http://www.jb51.net/article/54827.htm
http://www.cnblogs.com/lidabo/p/3328402.html
......
4.pthread_cond_wait是什么:http://baike.baidu.com/link?url=TntmcKnSMIsUSSn2o_V1F2hEdaCw8UAxIJgkZcjK9StSRLB7MXRfFeZA1TaDnUlSLNUGRhy1xS7x7jlPfzCWiK
5.VS无法打开pdb文件的解决方法:
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_96d4636a0102vknm.html
6.createthread函数使用方法:
http://www.doc88.com/p-415724533553.html
7._sprintf_s函数使用方法:
http://blog.163.com/ka_ciky/blog/static/1359004362011711102457625/
8.c++下int和char*和string的转换(网上到处都是就不贴网站了)




