Runtime-iOS运行时应用篇
一、动态方法交换:Method Swizzling
实现动态方法交换(Method Swizzling )是Runtime中最具盛名的应用场景,其原理是:通过Runtime获取到方法实现的地址,进而动态交换两个方法的功能。使用到关键方法如下:
//获取类方法的Mthod
Method _Nullable class_getClassMethod(Class _Nullable cls, SEL _Nonnull name)
//获取实例对象方法的Mthod
Method _Nullable class_getInstanceMethod(Class _Nullable cls, SEL _Nonnull name)
//交换两个方法的实现
void method_exchangeImplementations(Method _Nonnull m1, Method _Nonnull m2)
1.动态方法交换示例
现在演示一个代码示例:在视图控制中,定义两个实例方法printA与printB,然后执行交换
- (void)printA{
NSLog(@"打印A......");
}
- (void)printB{
NSLog(@"打印B......");
}
//交换方法的实现,并测试打印
Method methodA = class_getInstanceMethod([self class], @selector(printA));
Method methodB = class_getInstanceMethod([self class], @selector(printB));
method_exchangeImplementations(methodA, methodB);
[self printA]; //打印B......
[self printB]; //打印A......
2.拦截并替换系统方法
Runtime动态方法交换更多的是应用于系统类库和第三方框架的方法替换。在不可见源码的情况下,我们可以借助Rutime交换方法实现,为原有方法添加额外功能,这在实际开发中具有十分重要的意义。
下面将展示一个拦截并替换系统方法的示例:为了实现不同机型上的字体都按照比例适配,我们可以拦截系统UIFont的systemFontOfSize方法,具体操作如下:
步骤1:在当前工程中添加UIFont的分类:UIFont +Adapt,并在其中添用以替换的方法。
+ (UIFont *)zs_systemFontOfSize:(CGFloat)fontSize{
//获取设备屏幕宽度,并计算出比例scale
CGFloat width = [[UIScreen mainScreen] bounds].size.width;
CGFloat scale = width/375.0;
//注意:由于方法交换,系统的方法名已变成了自定义的方法名,所以这里使用了
//自定义的方法名来获取UIFont
return [UIFont zs_systemFontOfSize:fontSize * scale];
}
步骤2:在UIFont的分类中拦截系统方法,将其替换为我们自定义的方法,代码如下:
//load方法不需要手动调用,iOS会在应用程序启动的时候自动调起load方法,而且执行时间较早,所以在此方法中执行交换操作比较合适。
+ (void)load{
//获取系统方法地址
Method sytemMethod = class_getClassMethod([UIFont class], @selector(systemFontOfSize:));
//获取自定义方法地址
Method customMethod = class_getClassMethod([UIFont class], @selector(zs_systemFontOfSize:));
//交换两个方法的实现
method_exchangeImplementations(sytemMethod, customMethod);
}
添加一段测试代码,切换不同的模拟器,观察在不同机型上文字的大小:
UILabel *label = [[UILabel alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(0, 100, 300, 50)];
label.text = @"测试Runtime拦截方法";
label.font = [UIFont systemFontOfSize:20];
[self.view addSubview:label];
二、实现分类添加新属性
我们在开发中常常使用类目Category为一些已有的类扩展功能。虽然继承也能够为已有类增加新的方法,而且相比类目更是具有增加属性的优势,但是继承毕竟是一个重量级的操作,添加不必要的继承关系无疑增加了代码的复杂度。
遗憾的是,OC的类目并不支持直接添加属性,如果我们直接在分类的声明中写入Property属性,那么只能为其生成set与get方法声明,却不能生成成员变量,直接调用这些属性还会造成崩溃。
所以为了实现给分类添加属性,我们还需借助Runtime的关联对象(Associated Objects)特性,它能够帮助我们在运行阶段将任意的属性关联到一个对象上,下面是相关的三个方法:
/**
1.给对象设置关联属性
@param object 需要设置关联属性的对象,即给哪个对象关联属性
@param key 关联属性对应的key,可通过key获取这个属性,
@param value 给关联属性设置的值
@param policy 关联属性的存储策略(对应Property属性中的assign,copy,retain等)
OBJC_ASSOCIATION_ASSIGN @property(assign)。
OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC @property(strong, nonatomic)。
OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY_NONATOMIC @property(copy, nonatomic)。
OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN @property(strong,atomic)。
OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY @property(copy, atomic)。
*/
void objc_setAssociatedObject(id _Nonnull object,
const void * _Nonnull key,
id _Nullable value,
objc_AssociationPolicy policy)
/**
2.通过key获取关联的属性
@param object 从哪个对象中获取关联属性
@param key 关联属性对应的key
@return 返回关联属性的值
*/
id _Nullable objc_getAssociatedObject(id _Nonnull object,
const void * _Nonnull key)
/**
3.移除对象所关联的属性
@param object 移除某个对象的所有关联属性
*/
void objc_removeAssociatedObjects(id _Nonnull object)
注意:key与关联属性一一对应,我们必须确保其全局唯一性,常用我们使用@selector(methodName)作为key。
现在演示一个代码示例:为UIImage增加一个分类:UIImage+Tools,并为其设置关联属性urlString(图片网络链接属性),相关代码如下:
//UIImage+Tools.h文件中
UIImage+Tools.m
@interface UIImage (Tools)
//添加一个新属性:图片网络链接
@property(nonatomic,copy)NSString *urlString;
@end
//UIImage+Tools.m文件中
#import "UIImage+Tools.h"
#import <objc/runtime.h>
@implementation UIImage (Tools)
//set方法
- (void)setUrlString:(NSString *)urlString{
objc_setAssociatedObject(self,
@selector(urlString),
urlString,
OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC);
}
//get方法
- (NSString *)urlString{
return objc_getAssociatedObject(self,
@selector(urlString));
}
//添加一个自定义方法,用于清除所有关联属性
- (void)clearAssociatedObjcet{
objc_removeAssociatedObjects(self);
}
@end
测试文件中:
UIImage *image = [[UIImage alloc] init];
image.urlString = @"http://www.image.png";
NSLog(@"获取关联属性:%@",image.urlString);
[image clearAssociatedObjcet];
NSLog(@"获取关联属性:%@",image.urlString);
//打印:
//获取关联属性:http://www.image.png
// 获取关联属性:(null)
三、获取类的详细信息
1.获取属性列表
unsigned int count;
objc_property_t *propertyList = class_copyPropertyList([self class], &count);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i<count; i++) {
const char *propertyName = property_getName(propertyList[i]);
NSLog(@"PropertyName(%d): %@",i,[NSString stringWithUTF8String:propertyName]);
}
free(propertyList);
2.获取所有成员变量
Ivar *ivarList = class_copyIvarList([self class], &count);
for (int i= 0; i<count; i++) {
Ivar ivar = ivarList[i];
const char *ivarName = ivar_getName(ivar);
NSLog(@"Ivar(%d): %@", i, [NSString stringWithUTF8String:ivarName]);
}
free(ivarList);
3.获取所有方法
Method *methodList = class_copyMethodList([self class], &count);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i<count; i++) {
Method method = methodList[i];
SEL mthodName = method_getName(method);
NSLog(@"MethodName(%d): %@",i,NSStringFromSelector(mthodName));
}
free(methodList);
4.获取当前遵循的所有协议
__unsafe_unretained Protocol **protocolList = class_copyProtocolList([self class], &count);
for (int i=0; i<count; i++) {
Protocol *protocal = protocolList[i];
const char *protocolName = protocol_getName(protocal);
NSLog(@"protocol(%d): %@",i, [NSString stringWithUTF8String:protocolName]);
}
free(propertyList);
注意:C语言中使用Copy操作的方法,要注意释放指针,防止内存泄漏
四、解决同一方法高频率调用的效率问题
Runtime源码中的IMP作为函数指针,指向方法的实现。通过它,我们可以绕开发送消息的过程来提高函数调用的效率。当我们需要持续大量重复调用某个方法的时候,会十分有用,具体代码示例如下:
void (*setter)(id, SEL, BOOL);
int i;
setter = (void (*)(id, SEL, BOOL))[target methodForSelector:@selector(setFilled:)];
for ( i = 0 ; i < 1000 ; i++ )
setter(targetList[i], @selector(setFilled:), YES);
五、方法动态解析与消息转发
其实该部分可以参考基础篇中内容,这里不再重复赘述,只是大概做出一些总结。
1.动态方法解析:动态添加方法
Runtime足够强大,能够让我们在运行时动态添加一个未实现的方法,这个功能主要有两个应用场景:
场景1:动态添加未实现方法,解决代码中因为方法未找到而报错的问题;
场景2:利用懒加载思路,若一个类有很多个方法,同时加载到内存中会耗费资源,可以使用动态解析添加方法。方法动态解析主要用到的方法如下:
//OC方法:
//类方法未找到时调起,可于此添加类方法实现
+ (BOOL)resolveClassMethod:(SEL)sel
//实例方法未找到时调起,可于此添加实例方法实现
+ (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel
//Runtime方法:
/**
运行时方法:向指定类中添加特定方法实现的操作
@param cls 被添加方法的类
@param name selector方法名
@param imp 指向实现方法的函数指针
@param types imp函数实现的返回值与参数类型
@return 添加方法是否成功
*/
BOOL class_addMethod(Class _Nullable cls,
SEL _Nonnull name,
IMP _Nonnull imp,
const char * _Nullable types)
2.解决方法无响应崩溃问题
执行OC方法其实就是一个发送消息的过程,若方法未实现,我们可以利用方法动态解析与消息转发来避免程序崩溃,这主要涉及下面一个处理未实现消息的过程:

除了上述的方法动态解析,还使用到的相关方法如下:
消息接收者重定向
//重定向类方法的消息接收者,返回一个类
- (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector
//重定向实例方法的消息接受者,返回一个实例对象
- (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector
消息重定向
- (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation;
- (NSMethodSignature*)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)aSelector;
六、动态操作属性
1.动态修改属性变量
现在假设这样一个情况:我们使用第三方框架里的Person类,在特殊需求下想要更改其私有属性nickName,这样的操作我们就可以使用Runtime可以动态修改对象属性。
基本思路:首先使用Runtime获取Peson对象的所有属性,找到nickName,然后使用ivar的方法修改其值。具体的代码示例如下:
Person *ps = [[Person alloc] init];
NSLog(@"ps-nickName: %@",[ps valueForKey:@"nickName"]); //null
//第一步:遍历对象的所有属性
unsigned int count;
Ivar *ivarList = class_copyIvarList([ps class], &count);
for (int i= 0; i<count; i++) {
//第二步:获取每个属性名
Ivar ivar = ivarList[i];
const char *ivarName = ivar_getName(ivar);
NSString *propertyName = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:ivarName];
if ([propertyName isEqualToString:@"_nickName"]) {
//第三步:匹配到对应的属性,然后修改;注意属性带有下划线
object_setIvar(ps, ivar, @"梧雨北辰");
}
}
NSLog(@"ps-nickName: %@",[ps valueForKey:@"nickName"]); //梧雨北辰
总结:此过程类似KVC的取值和赋值
2.实现 NSCoding 的自动归档和解档
归档是一种常用的轻量型文件存储方式,但是它有个弊端:在归档过程中,若一个Model有多个属性,我们不得不对每个属性进行处理,非常繁琐。
归档操作主要涉及两个方法:encodeObject 和 decodeObjectForKey,现在,我们可以利用Runtime来改进它们,关键的代码示例如下:
//原理:使用Runtime动态获取所有属性
//解档操作
- (instancetype)initWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aDecoder{
self = [super init];
if (self) {
unsigned int count = 0;
Ivar *ivarList = class_copyIvarList([self class], &count);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
Ivar ivar = ivarList[i];
const char *ivarName = ivar_getName(ivar);
NSString *key = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:ivarName];
id value = [aDecoder decodeObjectForKey:key];
[self setValue:value forKey:key];
}
free(ivarList); //释放指针
}
return self;
}
//归档操作
- (void)encodeWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aCoder{
unsigned int count = 0;
Ivar *ivarList = class_copyIvarList([self class], &count);
for (NSInteger i = 0; i < count; i++) {
Ivar ivar = ivarList[i];
NSString *key = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:ivar_getName(ivar)];
id value = [self valueForKey:key];
[aCoder encodeObject:value forKey:key];
}
free(ivarList); //释放指针
}
下面是有关归档的测试代码:
//--测试归档
Person *ps = [[Person alloc] init];
ps.name = @"梧雨北辰";
ps.age = 18;
NSString *temp = NSTemporaryDirectory();
NSString *fileTemp = [temp stringByAppendingString:@"person.archive"];
[NSKeyedArchiver archiveRootObject:ps toFile:fileTemp];
//--测试解档
NSString *temp = NSTemporaryDirectory();
NSString *fileTemp = [temp stringByAppendingString:@"person.henry"];
Person *person = [NSKeyedUnarchiver unarchiveObjectWithFile:fileTemp];
NSLog(@"person-name:%@,person-age:%ld",person.name,person.age);
//person-name:梧雨北辰,person-age:18
3.实现字典与模型的转换
字典数据转模型的操作在项目开发中很常见,通常我们会选择第三方如YYModel;其实我们也可以自己来实现这一功能,主要的思路有两种:KVC、Runtime,总结字典转化模型过程中需要解决的问题如下:
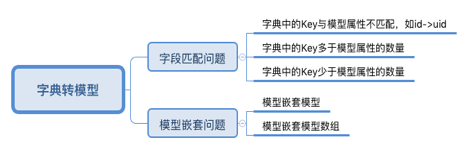
现在,我们使用Runtime来实现字典转模型的操作,大致的思路是这样:
借助Runtime可以动态获取成员列表的特性,遍历模型中所有属性,然后以获取到的属性名为key,在JSON字典中寻找对应的值value;再将每一个对应Value赋值给模型,就完成了字典转模型的目的。
首先准备下面的JSON数据用于测试:
{
"id":"2462079046",
"name": "梧雨北辰",
"age":"18",
"weight":140,
"address":{
"country":"中国",
"province": "河南"
},
"courses":[{
"name":"Chinese",
"desc":"语文课"
},{
"name":"Math",
"desc":"数学课"
},{
"name":"English",
"desc":"英语课"
}
]
}
具体的代码实现流程如下:
步骤1:创建NSObject的类目NSObject+ZSModel,用于实现字典转模型
@interface NSObject (ZSModel)
+ (instancetype)zs_modelWithDictionary:(NSDictionary *)dictionary;
@end
//ZSModel协议,协议方法可以返回一个字典,表明特殊字段的处理规则
@protocol ZSModel<NSObject>
@optional
+ (nullable NSDictionary<NSString *, id> *)modelContainerPropertyGenericClass;
@end;
#import "NSObject+ZSModel.h"
#import <objc/runtime.h>
@implementation NSObject (ZSModel)
+ (instancetype)zs_modelWithDictionary:(NSDictionary *)dictionary{
//创建当前模型对象
id object = [[self alloc] init];
//1.获取当前对象的成员变量列表
unsigned int count = 0;
Ivar *ivarList = class_copyIvarList([self class], &count);
//2.遍历ivarList中所有成员变量,以其属性名为key,在字典中查找Value
for (int i= 0; i<count; i++) {
//2.1获取成员属性
Ivar ivar = ivarList[i];
NSString *ivarName = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:ivar_getName(ivar)] ;
//2.2截取成员变量名:去掉成员变量前面的"_"号
NSString *propertyName = [ivarName substringFromIndex:1];
//2.3以属性名为key,在字典中查找value
id value = dictionary[propertyName];
//3.获取成员变量类型, 因为ivar_getTypeEncoding获取的类型是"@\"NSString\""的形式
//所以我们要做以下的替换
NSString *ivarType = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:ivar_getTypeEncoding(ivar)];// 替换:
//3.1去除转义字符:@\"name\" -> @"name"
ivarType = [ivarType stringByReplacingOccurrencesOfString:@"\"" withString:@""];
//3.2去除@符号
ivarType = [ivarType stringByReplacingOccurrencesOfString:@"@" withString:@""];
//4.对特殊成员变量进行处理:
//判断当前类是否实现了协议方法,获取协议方法中规定的特殊变量的处理方式
NSDictionary *perpertyTypeDic;
if([self respondsToSelector:@selector(modelContainerPropertyGenericClass)]){
perpertyTypeDic = [self performSelector:@selector(modelContainerPropertyGenericClass) withObject:nil];
}
//4.1处理:字典的key与模型属性不匹配的问题,如id->uid
id anotherName = perpertyTypeDic[propertyName];
if(anotherName && [anotherName isKindOfClass:[NSString class]]){
value = dictionary[anotherName];
}
//4.2.处理:模型嵌套模型
if ([value isKindOfClass:[NSDictionary class]] && ![ivarType hasPrefix:@"NS"]) {
Class modelClass = NSClassFromString(ivarType);
if (modelClass != nil) {
//将被嵌套字典数据也转化成Model
value = [modelClass zs_modelWithDictionary:value];
}
}
//4.3处理:模型嵌套模型数组
//判断当前Vaue是一个数组,而且存在协议方法返回了perpertyTypeDic
if ([value isKindOfClass:[NSArray class]] && perpertyTypeDic) {
Class itemModelClass = perpertyTypeDic[propertyName];
//封装数组:将每一个子数据转化为Model
NSMutableArray *itemArray = @[].mutableCopy;
for (NSDictionary *itemDic in value) {
id model = [itemModelClass zs_modelWithDictionary:itemDic];
[itemArray addObject:model];
}
value = itemArray;
}
//5.使用KVC方法将Vlue更新到object中
if (value != nil) {
[object setValue:value forKey:propertyName];
}
}
free(ivarList); //释放C指针
return object;
}
@end
步骤2:分别创建各个数据模型Student、Address、Course
Student类:
//Student.h文件
#import "NSObject+ZSModel.h"
#import "AddressModel.h"
#import "CourseModel.h"
@interface StudentModel : NSObject<ZSModel> //遵循协议
//普通属性
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *uid;
@property(nonatomic,copy)NSString *name;
@property (nonatomic, assign) NSInteger age;
//嵌套模型
@property (nonatomic, strong) AddressModel *address;
//嵌套模型数组
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSArray *courses;
@end
#import "StudentModel.h"
@implementation StudentModel
+ (NSDictionary *)modelContainerPropertyGenericClass {
//需要特别处理的属性
return @{@"courses" : [CourseModel class],@"uid":@"id"};
}
@end
Address类:
//AddressModel.h文件
@interface AddressModel : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *country; //国籍
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *province; //省份
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *city; //城市
@end
//-----------------优美的分割线------------------------
//AddressModel.m文件
#import "AddressModel.h"
@implementation AddressModel
@end
Course类:
//读取JSON数据
NSDictionary *jsonData = [FileTools getDictionaryFromJsonFile:@"Student"];
NSLog(@"%@",jsonData);
//字典转模型
StudentModel *student = [StudentModel zs_modelWithDictionary:jsonData];
CourseModel *courseModel = student.courses[0];
NSLog(@"%@",courseModel.name);
步骤4:测试字典转模型操作
//读取JSON数据
NSDictionary *jsonData = [FileTools getDictionaryFromJsonFile:@"Student"];
NSLog(@"%@",jsonData);
//字典转模型
StudentModel *student = [StudentModel zs_modelWithDictionary:jsonData];
CourseModel *courseModel = student.courses[0];
NSLog(@"%@",courseModel.name);
效果如下:

最后总结
以上就是我们在实际开发中常用的Runtime的操作了,Runtime的强大作用远不止如此。深入的了解和学习Runtime,不仅仅有助于iOS开发,而且对于理解编程语言的底层原理也十分有用,Keep Learning!~
posted on 2019-07-09 06:58 东方🐺 阅读(279) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报



