【LeetCode题解】160_相交链表
160_相交链表
描述
编写一个程序,找到两个单链表相交的起始节点。
例如,下面的两个链表:
A: a1 → a2
↘
c1 → c2 → c3
↗
B: b1 → b2 → b3
在节点 c1 开始相交。
注意:
- 如果两个链表没有交点,返回
null. - 在返回结果后,两个链表仍须保持原有的结构。
- 可假定整个链表结构中没有循环。
- 程序尽量满足 O(n) 时间复杂度,且仅用 O(1) 内存。
致谢:
特别感谢 @stellari 添加此问题并创建所有测试用例。
解法一:哈希表
思路
首先遍历链表 A 的所有节点,并将每个节点的引用存入哈希表中。接着,遍历链表 B 的每个节点,如果某个节点的引用在哈希表中存在,返回该节点的引用;如果遍历完链表 B 的所有节点没有发现这样一个节点,则返回 null。
Java 实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null) {
return null;
}
Set<ListNode> nodes = new HashSet<>();
ListNode temp = headA;
while (temp != null) {
nodes.add(temp);
temp = temp.next;
}
temp = headB;
while (temp != null) {
if (nodes.contains(temp)) {
return temp;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
return null;
}
}
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:\(O(m+n)\),其中,\(m\) 表示链表 A 的节点数,\(n\) 表示链表 B 的节点数,最坏的情况下,需要遍历两个链表的所有节点
- 空间复杂度:\(O(m)\) 或者 \(O(n)\)
Python 实现
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution(object):
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA, headB):
"""
:type head1, head1: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
if not headA or not headB:
return None
nodesA = set()
curr = headA
while curr:
nodesA.add(curr)
curr = curr.next
curr = headB
while curr:
if curr in nodesA:
return curr
curr = curr.next
return None
复杂度分析同上。
解法二:双指针(推荐)
思路
双指针解法顾名思义需要两个指针,假设指针 pA 和 pB 分别指向链表 A 和链表 B 的头结点,之后两个指针分别以步幅为 1 的速度向链表的尾部遍历,当指针 pA 遍历到链表 A 的尾节点时,将指针 pA 指向链表 B 的头部。同样地,当指针 pB 遍历到链表 B 的尾节点时,将指针 pB 指向链表 A 的头部。当两个指针相遇时,指针 pA 或者 pB 所指向的节点就是两个链表的相交节点。
为了说明双指针的求解思路,假设链表 A 和链表 B 的结构如下图所示,
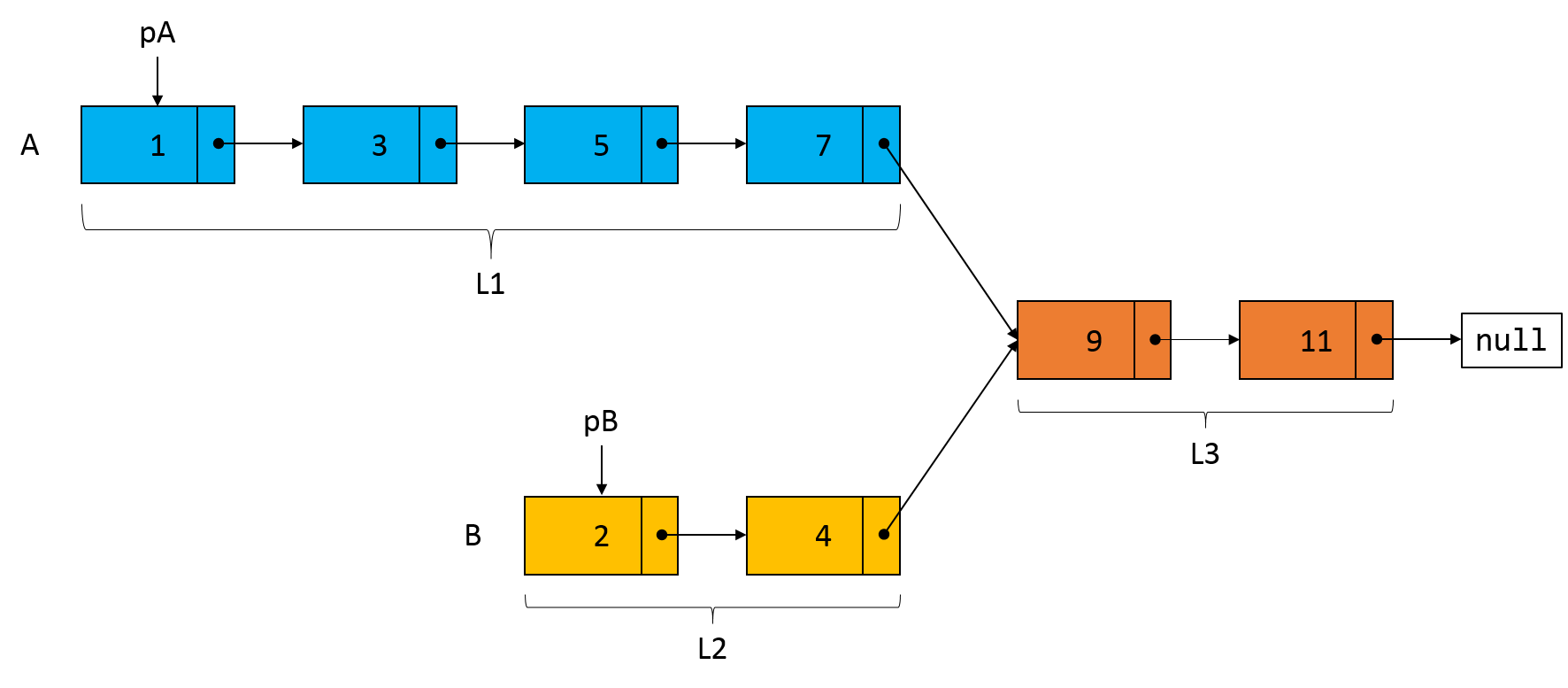
其中,链表 A 包含 6 个节点,节点的值分别为 1、3、5、7、9 和 11;链表 B 包含 4 个节点,节点的值分别为 2、4、9 和 11,因此,两个链表的相交节点为 9。设链表 A 中不相交的部分(即蓝色部分的节点)长度为 \(L1\),链表 B 中不相交的部分(即黄色部分的节点)长度为 \(L2\),两个链表相交的部分(即红色部分的节点)长度为 \(L3\)。
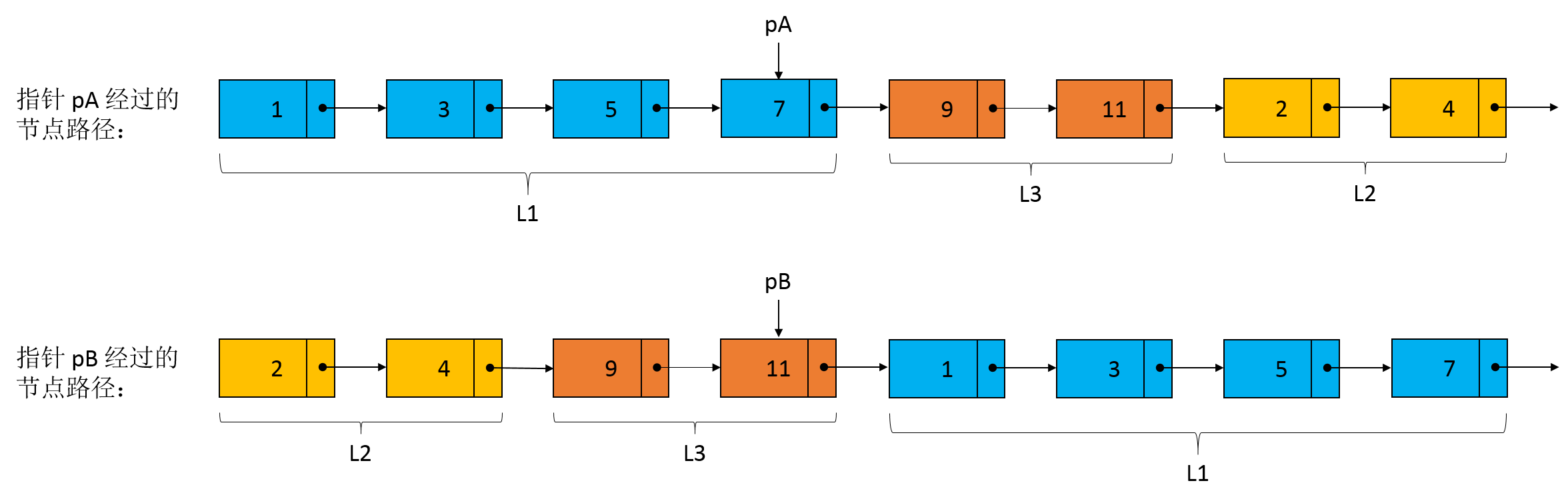
如下图所示,当指针 pB 遍历到链表 B 的尾节点 11 时,指针 pA 遍历到链表 A 中节点 7 的位置,下一次遍历指针 pB 将处于链表 A 的节点 1 的位置。
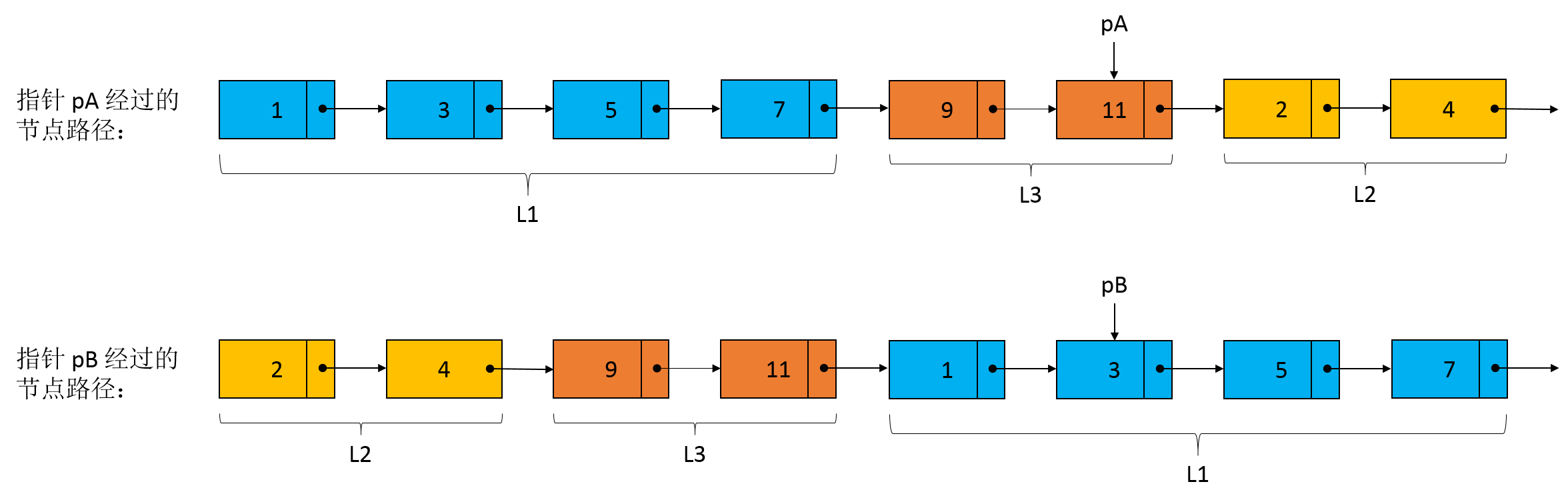
同理,当指针 pA 遍历到链表 A 的尾节点 11 时,此时指针 pB 处于链表 A 中节点 3 的位置,下一次遍历指针 pA 将处于链表 B 的节点 2 位置。
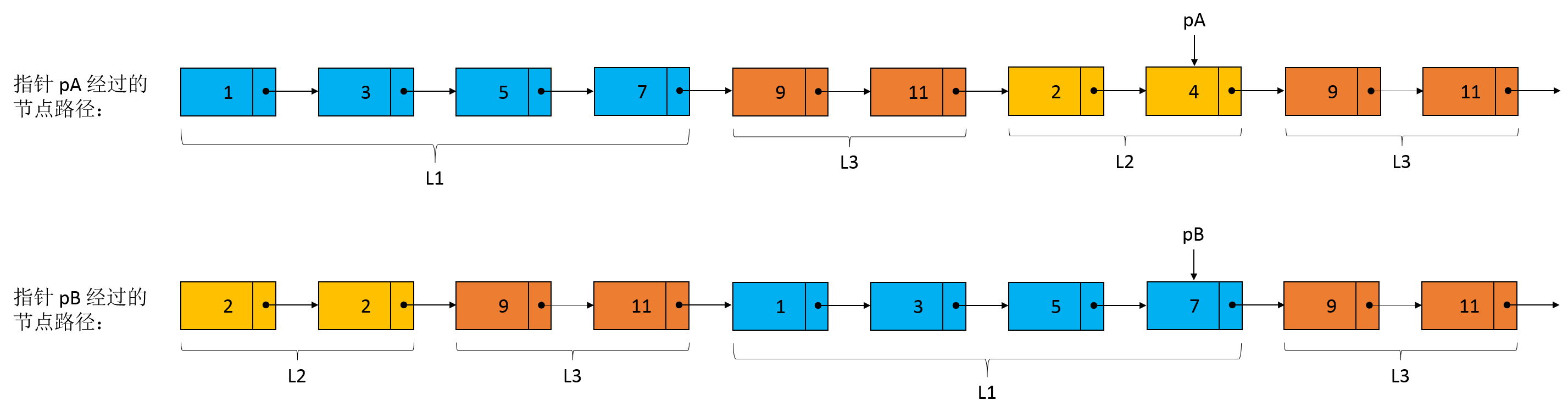
再经过两次遍历后,指针 pA 将位于链表 B 中节点 4 的位置,而指针 pB 也将到达链表 A 的节点 4 的位置,下一次遍历两个指针将在节点 9(即相交节点)相遇。此时,两个指针走过的长度都为 \(L1 + L2 + L3\)。究其原因,可以将两个指针走过的“路程”看成 3 个部分,即蓝色部分、红色部分以及橙色部分,只是两个指针走过 3 个部分的顺序是不同的,指针 pA 先走蓝色部分而指针 pB 先走橙色部分,但是经过前 3 个部分后,两个指针走过的长度一定是相同的,因此在下一次遍历的时候两个指针一定会相遇。
Java 实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode pA = headA;
ListNode pB = headB;
while (pA != pB) {
pA = pA == null ? headB : pA.next;
pB = pB == null ? headA : pB.next;
}
return pA;
}
}
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:\(O(L1 + L2 + L3) = O(n)\),如果两个链表存在相交节点,则经过 \(L1 + L2 + L3\) 的“长度”后,两个指针一定会相遇
- 空间复杂度:\(O(1)\),只需要保存两个引用
Python 实现
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution(object):
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA, headB):
"""
:type head1, head1: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
if not headA or not headB:
return None
p_a, p_b = headA, headB
while p_a != p_b:
if p_a:
p_a = p_a.next
else:
p_a = headB
if p_b:
p_b = p_b.next
else:
p_b = headA
return p_a
复杂度分析同上。



