C++ 赎罪之路
实践目标: 1.c++ 类的定义
2.数据变量的定义
3.成员函数的声明以及定义
实例: 平年闰年的判断:
(相关注意点都在程序的注释当中)

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 /* 5 类的数据变量,以及类的成员函数的申明 6 */ 7 class TDate { 8 public: 9 void SetDate(int y, int m, int d); 10 int isLeapYear(); 11 void Print(); 12 private: 13 int year,day,month; 14 }; //类定义完成后加分号 15 16 /* 17 定义类的成员函数,且必须在程序中实现 18 */ 19 void TDate :: SetDate(int y, int m, int d) { 20 year = y ; 21 month = m ; 22 day = d ; 23 } 24 25 int TDate :: isLeapYear() { 26 return (year%4==0 && year%100 != 0) || (year%400 == 0); 27 } 28 void TDate :: Print() { 29 cout<<year<<"."<<month<<"."<<day<<endl ; 30 } 31 32 int main(){ 33 TDate td1 ; 34 td1.SetDate(2009,5,10); 35 int flag = td1.isLeapYear(); 36 td1.Print(); 37 if(flag == 1) 38 cout<<"是闰年"<<endl ; 39 else 40 cout<<"是平年!"<<endl ; 41 return 0; 42 }
8月29日晚上
饭后看了几个知识点,总结下(倒序):
点击http://www.runoob.com/cplusplus/cpp-class-access-modifiers.html看一下继承的权限问题,讲的比较清楚!
1. 派生类:单一继承、多继承、权限问题、消除二义性、作用域分辨、

1 /* 2 * 派生类:(java中类的继承) 3 */ 4 #include <iostream> 5 using namespace std; 6 7 //默认为private A 8 class A { 9 private: 10 int a; 11 public: 12 A(int a){cout<<"this is A.a = "<<a<<endl;} 13 ~A(){cout<<"dele A"<<endl;} 14 }; 15 16 class B { 17 private: 18 int y ; 19 public: 20 B(int y) {cout<<"this is B.y = "<<y<<endl;} 21 ~B() {cout<<"dele B"<<endl;} 22 }; 23 24 /* 25 * C 类继承A and B 26 * 格式: class 派生类名 : 访问控制 基类名 {访问控制:成员声明列表}; 27 * 多继承:class 派生类名 : 访问控制 基类名, 访问控制 基类名, ...{...}; 28 */ 29 class C :public A,public B { 30 private: 31 int c ; 32 public: 33 //构造函数初始化列表 java:C(){super.A()} 34 C(int c, int x, int y):A(x),B(y) { 35 cout<<"this is C.c = "<<c<<endl; 36 } 37 38 //析构函数 39 ~C() {cout<<"dele C"<<endl;} 40 }; 41 42 int main() { 43 C c1(1, 2, 3); 44 return 0; 45 }
权限、二义性、作用域分辨相关示例代码:

1 /* 2 * 派生类:(java中类的继承) 3 */ 4 #include <iostream> 5 using namespace std; 6 7 //默认为private A 8 class A { 9 private: 10 int a; 11 public: 12 A(int a){cout<<"this is A.a = "<<a<<endl;} 13 ~A(){cout<<"dele A"<<endl;} 14 15 void getA() { 16 cout<<"getA()"<<endl; 17 } 18 }; 19 20 class B { 21 private: 22 int y ; 23 public: 24 B(int y) {cout<<"this is B.y = "<<y<<endl;} 25 ~B() {cout<<"dele B"<<endl;} 26 27 void getB(){ 28 cout<<"getB()"<<endl; 29 } 30 }; 31 32 /* 33 * C 类继承A and B 34 * 格式: class 派生类名 : 访问控制 基类名 {访问控制:成员声明列表}; 35 * 多继承:class 派生类名 : 访问控制 基类名, 访问控制 基类名, ...{...}; 36 */ 37 class C :public A,public B { 38 private: 39 int c ; 40 public: 41 //构造函数初始化列表 java:C(){super.A()} 42 C(int c, int x, int y):A(x),B(y) { 43 cout<<"this is C.c = "<<c<<endl; 44 } 45 46 //析构函数 47 ~C() {cout<<"dele C"<<endl;} 48 49 void getC() { 50 cout<<"getC()"<<endl; 51 } 52 void getB() { 53 B::getB(); //作用域分辨 54 } 55 }; 56 57 int main() { 58 C c1(1, 2, 3); 59 cout<<endl<<endl; 60 c1.getA(); 61 cout<<"error:c1.getB()"<<endl; 62 63 /* 64 * 消除二义性,使程序能够找到名字相同的成员函数不同作用域的实现 65 */ 66 c1.getB(); 67 c1.getC(); 68 c1.B::getB(); //当继承B为private时 该句为错误,其他都能正常运行 69 return 0; 70 } 71 ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- 72 运行结果: 73 this is A.a = 2 74 this is B.y = 3 75 this is C.c = 1 76 77 78 getA() 79 error:c1.getB() 80 getB() 81 getC() 82 getB() 83 dele C 84 dele B 85 dele A
2. 静态成员(比较好理解,和可以借助java的静态成员作为理解,毕竟java是儿子)
9月3号 早上
指针:是一个变量,其值为另一个变量的地址,即,内存位置的直接地址。就像其他变量或常量一样,您必须在使用指针存储其他变量地址之前,对其进行声明。
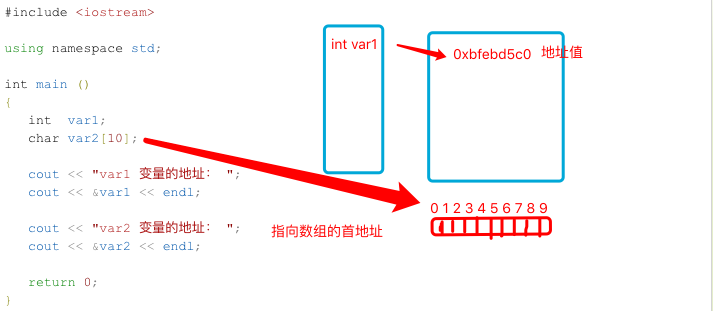
例子2:

在指针中值得注意的是:可以进行比较;(感觉像是在地址进行再比较,其实是地址上的值进行比较,和java上的有些区别)
其他的运算时按照地址上的值进行运算的,都是通过指针的自增或自减实现指针向前、向后移动找到位置上的值来实现运算。

#include <iostream> using namespace std; const int MAX = 3; int main () { int var[MAX] = {10, 100, 200}; int *ptr; // 指针中第一个元素的地址 ptr = var; int i = 0; while ( ptr <= &var[MAX - 1] ) { cout << "Address of var[" << i << "] = "; cout << ptr << endl; cout << "Value of var[" << i << "] = "; cout << *ptr << endl; // 指向上一个位置 ptr++; i++; } return 0; } --------------------------------------------------------------------------执行结果: Address of var[0] = 0xbfce42d0 Value of var[0] = 10 Address of var[1] = 0xbfce42d4 Value of var[1] = 100 Address of var[2] = 0xbfce42d8 Value of var[2] = 200
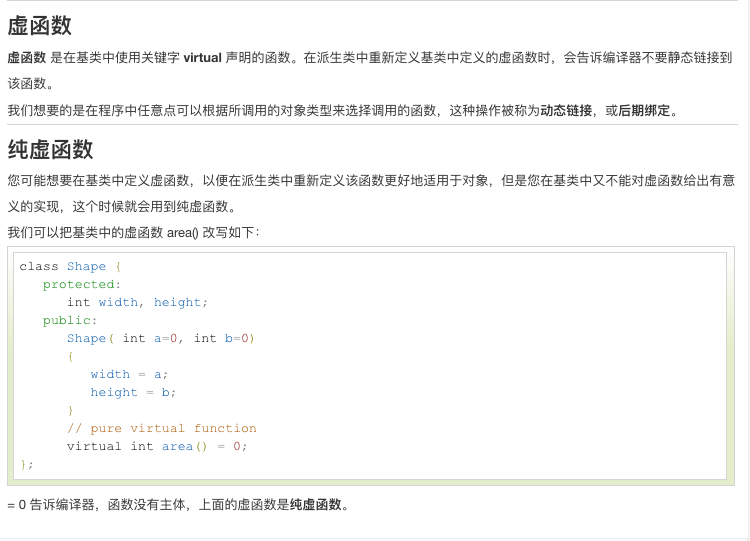
多态:基类指向子类的方法,子类重写基类的方法。

#include <iostream> using namespace std; class Shape { protected: int width, height; public: Shape( int a=0, int b=0) { width = a; height = b; } virtual int area() //virtual修饰后能够动态的绑定到子类的方法 { cout << "Parent class area :" <<endl; return 0; } }; class Rectangle: public Shape{ public: Rectangle( int a=0, int b=0):Shape(a, b) { } int area () { cout << "Rectangle class area :" <<endl; return (width * height); } }; class Triangle: public Shape{ public: Triangle( int a=0, int b=0):Shape(a, b) { } int area () { cout << "Triangle class area :" <<endl; return (width * height / 2); } }; // 程序的主函数 int main( ) { Shape *shape; Rectangle rec(10,7); Triangle tri(10,5); // 存储矩形的地址 shape = &rec; // Shape shape = new Rectangle(); // 调用矩形的求面积函数 area shape->area(); //shape.area(); // 存储三角形的地址 shape = &tri; // 调用三角形的求面积函数 area shape->area(); return 0; }
c++的数据封装
所谓的数据封装就是一个类的属性私有化,然后通过公共的方法(接口)让其对象进行调用,达到对属性的操作的目的;
接口(抽象类):
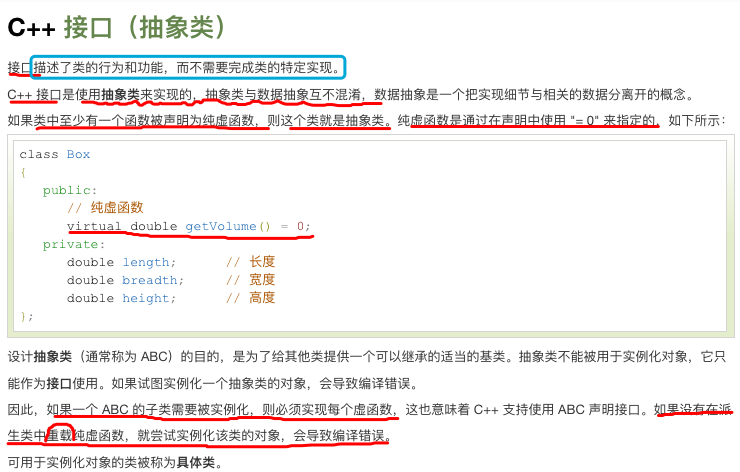

#include <iostream> using namespace std; // 基类 class Shape { public: // 提供接口框架的纯虚函数 virtual int getArea() = 0; void setWidth(int w) { width = w; } void setHeight(int h) { height = h; } protected: int width; int height; }; // 派生类 class Rectangle: public Shape { public: int getArea() { return (width * height); } }; class Triangle: public Shape { public: int getArea() { return (width * height)/2; } }; int main(void) { Rectangle Rect; Triangle Tri; Rect.setWidth(5); Rect.setHeight(7); // 输出对象的面积 cout << "Total Rectangle area: " << Rect.getArea() << endl; Tri.setWidth(5); Tri.setHeight(7); // 输出对象的面积 cout << "Total Triangle area: " << Tri.getArea() << endl; return 0; } -------------------------------------------------------------------------- 运行结果: Total Rectangle area: 35 Total Triangle area: 17 注意:在c++中没有重写的概念,只能是重载;接口就是一个公共的方法,但是是一个纯虚函数



