Proj THUDBFuzz Paper Reading: AFL++: Combining incremental steps of fuzzing research
github
https://github.com/AFLplusplus
Abstract
本文: AFL++
特点: community-driven open-source tool
方法: 例如提供了Custom Mutator API
本文其它贡献: 对一些现有的fuzzing方法做了探究,发现这些技术往往能为一些类型的目标程序带来收益,同时在另外一些上效率降低
1. Intro
P1: fuzzing的好处;symbolically-assisted fuzzing带来的好处
P2: fuzzing技术常常是正交的和相互独立的,所以能够集成在一起;因为fuzzing技术发展很快,所以选择何种fuzzing技术也会带来困扰;
P3: 通过提供可拓展的API来提高标准并解决这个问题;未来的研究可以使用AFL++作为新的基准;AFL++和AFL的关系(重新设计)
P4: 为甚么要选取afl当作base-因为18个月没有维护了
P5: afl++发展历程
2. State-of-the-Art
2.1 American Fuzzy Lop
2.1.1 Coverage Guided Feedback
何为interesting input:引发新edge的覆盖或者edge执行次数落在某个未触发的整数区间;
hash碰撞的风险
AFL用weighted minimium set cover来维护一个favored test set
AFL会做trimming
2.1.2 Mutations
两阶段: deterministic, havoc
- deterministic: 在测试样例上做单次确定性的mutation,比如bit flips, additions, substitution等
- havoc: 随机选取多次mutations
- splicing: 将两个样例合为一个
2.1.3 Forkserver
为了避免execve()带来的消耗,AFL将forkserver注入目标程序,然后用IPC来控制forkserver。当AFL需要执行一个test case的时候,它只需要通知目标程序来fork自身,产生的子进程会执行这个test case。这样,fuzzer就不需要每次都做昂贵的初始化或者startup了。
2.1.4 Persistent Mode
在Persistent Mode中,目标程序并不为每个testcase做fork()操作以节约时间。目标程序应当满足足够稳定,而且状态变化不至于影响下一次执行
2.2 Smart Scheduling
2.2.1 AFLFast
更倾向于被覆盖频率更低的分支
提出了两个问题
- In which order should the fuzzer pick the seeds, in order to stress low-frequency paths?
- 提出了新的搜索策略
- Can we tune the amount of generated inputs from each seed (the energy)?
- 提出了6种power scheduling strategies
2.2.2 MOpt
引入了mutation scheduling,具体来说是给不同的变异算子分配概率。
使用粒子群优化算法来做mutation scheduling
将变异过程分为两个stages:
- Pilot: evalutes the operators
- Code: generates mutations
2.3 Bypassing Roadblocks
2.3.1 LAF-Intel
目标: 绕过困难的多bytes比较
方法: 将整数和字符串比较拆分
具体:
- 将>=(或者<=)拆分为>和==
- 将有符号整数拆分为正负性比较和无符号整数比较
- 将所有宽度为64,32,16的无符号整数比较拆分为8bit多重比较
2.3.2 RedQueen
主要聚焦于和输入有关的比较操作(Input-to-state comparison)。
- 先用随机bytes来标记输入
- 定位Input-to-state comparision在输入种对应的位置
- 用I2S修复新生成的有趣输入的checksum,如果失败,则将对应的testcase删除
2.4 Mutate Structured Inputs
2.4.1 AFLSmart
使用PEACH pits作为输入模型格式(这样可以复用为peach写的协议规范)
AFL在第一次从queue中取到某个testcase时对其进行解析。由于解析延迟计算的,所以如果不用结构变异,AFLSmart就相当于是AFL本身
3. A New Baseline for Fuzzing
3.1 Seed Scheduling
主要依据以下变量进行调度
- 第i号种子从queue中被选上的次数
- 与第i号种子覆盖的路径相同的inputs的数目
- the average number of generated inputs exercising a path./The average number of generated test cases with the same coverage in general;
6种AFLFast scheduling strategies:
- fast
- coe
- explore(default)
- quad
- lin
- exploit
AFL++: - mmopt: 偏袒最新的种子
- rare: 忽略seed的实际选取次数,转而偏袒能够覆盖低丰度branch的种子
| AFL flag | Power Schedule |
|---|---|
-p explore |
|
-p fast (default) |
|
-p coe |
|
-p quad |
|
-p lin |
|
-p exploit (AFL) |
|
-p mmopt |
Experimental: explore with no weighting to runtime and increased weighting on the last 5 queue entries |
-p rare |
Experimental: rare puts focus on queue entries that hit rare edges |
-p seek |
Experimental: seek is EXPLORE but ignoring the runtime of the queue input and less focus on the size |
| where α(i) is the performance score that AFL uses to compute for the seed input i, β(i)>1 is a constant, s(i) is the number of times that seed i has been chosen from the queue, f(i) is the number of generated inputs that exercise the same path as seed i, and μ is the average number of generated inputs exercising a path. |
3.2 Mutators
3.2.1 Custom Mutator API
AFL++允许其他fuzzing reseach在AFL++的基础上做scheduling, mutation和trimming而无需修改太多。这点实际上最初在Holler's AFL fork中实现,但是AFL++做了更多
afl_custom_(de)init: 初始化或取消初始化。自定义变量器应确保给定相同随机种子时,模糊结果是可重现的。
afl_custom_queue_get 是否应该对当前entry做fuzzing
afl_custom_fuzz 自定义突变
afl_custom_havoc_mutation 做单次custom mutation
afl_custom_havoc_mutation_probability 调用自定义突变的概率
afl_custom_post_process 进行格式转换或者checksums, sizes等
afl_custom_queue_new_entry store metadata on disk
afl_custom_init_trim
afl_custom_trim
afl_custom_post_trim
3.2.2 Input-To-State Mutator
基于REDQUEEN实现了I2S Mutator
优化:
- 染色操作会很慢,为此,当coverage bitmap hash值不变时或者执行速度超过原种子执行速度2倍时,突变区域就保持不变
- 每次比较都带有概率,具体来说,如果在某次试图绕过某个比较的时候失败了,这个comparision分配到的概率就会降低
CmpLog插桩
不像原始REDQUEEN那样用断点来记录比较操作,而是使用Fioraldi等人为WEIZZ设计的shared table
该表为256MB,在fuzzer和目标程序中共享。
每个比较操作都会将自己的最后256次执行记录在这张表中,如果一个比较操作没有执行就不会记录在这张表中。
这张表的第一部分是每个比较操作的metadata。
CmpLog已经支持了LLVM mode和QEMU mode
3.2.3 MOpt Mutator
重新实现了MOpt
3.3 Instrumentations
支持多种插桩backends,如LLVM, GCC, QEMU, Unicorn和QBDI。此外,还提供一个proxy module用于传递信息(forward test cases to targets and give any kind of coverage to afl-fuzz, even remote and non-coverage, such as ampere consumption or branch addresses of JTAG)
NeverZero
用于插桩的后台。为AFL的hitcount机制做优化。
解决问题:当某条边执行256次时,对应该边hitcount的byte会变为0
NeverZero 策略:将进位添加到bitmap中
Saturated Counters 策略: 计数器到达255就冻结计数器
我们观察到NeverZero非常有效,并且在覆盖率和速度方面都提高了AFL(现在的种子选择考虑了以前隐藏的边缘)。在大多数可用的仪器上,我们选择将NeverZero设置为AFL ++的默认值。
3.3.1 LLVM
支持LLVM11, edge coverage, Context-sensitive Edge Coverage(xor the ID of the callee), Ngram(考虑目标block和前面N-1个blocks), LAF-INTEL passes(还尝试了分割浮点数的比较,增加了字符串比较的支持),CmpLog passes,允许指定插桩的modules,INSTRIM patches(用dominator tree来避免无意义的插桩)
3.3.2 GCC
gcc plugin, support deferred initialization + persistent mode
3.3.3 QEMU
- QEMU 3.1.1; support binary-only instrumentations, retrowrite based on binary patching, 2. 现在,当在QEMU中选择一个块时,不再在模拟器的上下文中记录基本的块转换,而是使用帮助程序内联了对记录例程的调用(The basic blocks transitions are now not anymore logged in the context of the emulator when slecting a block in QEMU but the call to the logging routine is in-lined using a helper)。 这样,我们可以重新启用链接AFL禁用的块(首先由[8]显示为线程不安全的方式)(we can re-enable the blocks linking that AFL disabled)
- QEMU模式由Fioraldi和QAsan [16]进行了扩展,以结合基于AddressSanitizer的基于动态二进制翻译的实现来支持针对堆违规的清理
- 也支持LAF-intel, 但方法略有不同,是用了一个不同的bitmap,此外没有直接更改比较指令
- the code is not modified, but all comparisons are hooked and each byte of each operand is compared, increasing a different bitmap entry if equal
- Q: 此指令插入与LIBFUZZER基于popcnt的指令插入类似,但是在字节级别,产生的输入非常少,以避免路径爆炸,这一问题使得LIBFUZZER的值配置文件模式在某些目标上不如普通模式有效。它可以配置为只拆分与立即数操作数的整数比较、所有整数比较或所有整数和浮点比较
- supports persistent mode
- 两种方法1. 用户自己写一个loop 2. 用户指定入口点和出口点,QEMU会生成loop
3.3.4 Unicornafl
afl++集成了Nathan Voss的afl-unicorn。
- AFL++添加了一些简单的C, Rust和python bindings,以支持unicornafl
- unicorn本身就有一些set page mappings, read/write memory and registers, add hoosks, start/stop execution with different conditions的APIs
- AFL++额外添加了允许在任何时间推出fast persistent mode的API,以及设置多个exits的API,还有多重post-fuzzing handlers来方便探测crashes
afl-unicorn将目标程序的firmware与父进程的状态相关联- forkserver中有根据Unicorn的JIT(inspired by AFL QEMU mode)的caching mechanism
- unicornafl将插桩直接放入translated blocks,这样就减少了需要间接跳转的需求,同时重新激活了optimized blocks
uc_afl_forkserver_start: kick off the fork server at a certain point in time, ef-fectively freezing the current state prior to a fuzzing run and telling AFL++ to start generating inputs
uc_afl_fuzzdirectly reading input for each test case
3.3.5 QBDI
支持android native libraries的动态茶庄。
3.4 Platform Support
Besides GNU/Linux, the fuzzer runs on Android, iOS, macOS, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD and is packaged in several popular distributions like De-bian, Ubuntu, NixOS, Arch Linux, FreeBSD, Kali Linux and more.
AFL++ ’s QEMU [7] mode, has a Wine [1] mode, that can fuzz compatible Win32 binaries on GNU/Linux.
3.5 Snapshot LKM
内接一个Linux Kernel Module(inspired by Perffuzz by Xu),以解决fork()带来的性能瓶颈。
Perffuzz实现了一个创建/还原snapshot的轻量级机制,这能为测试带来2倍的性能提升
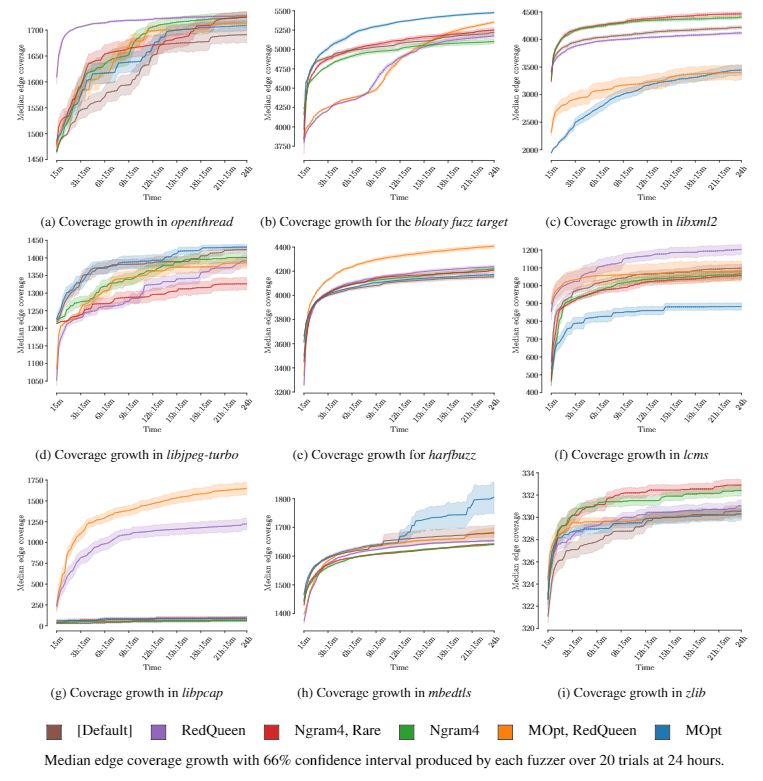
4 Evaluation Use Cases
实验:
竞品对象: AFL的6种设置
- default
- MOpt
- Ngram4
- RedQueen
- Ngram4, Rare
- MOpt, RedQueen
数据集: FuzzBench
实验数据使用FuzzBench Service收集
这里FuzzBench在21个选定的目标程序上运行24/23小时。每个run都会重复20次来获得edge coverage中位数。
P: 为何选择这些目标程序展示;为何技术具有正交性;集成技术的好处;每个目标程序上哪种配置更好,为甚么;分析每种配置的特点
4.1 AFL++ Optimal
针对给定目标执行了AFL ++的设置调参,称为AFL ++ Optimal
5 Future Work
5.1 Scaling
AFL++ ’s scaling to multiple threads is less than ideal,原因是用文件系统来传递Test case
探索:Linux Kernel Mode for snapshots



