Proj THUDBFuzz Paper Reading: SoK: The Progress, Challenges, and Perspectives of Directed Greybox Fuzzing
Abstract
背景: Coverage-based Greybox Fuzzing很有用,但是并非全部增长的coverage都和bug直接相关。
Directed Fuzzer将时间直接花费在到达程序的确定位置上,非常适宜于patch testing, bug reproduction, special bug hunting等任务
本文调研了28个fuzzers,基于Directed Greybox Fuzzing从15个角度对这些fuzzers做出了评估。
此外,还对该领域的挑战和前景做出了一定总结和推测。
1. Intro
P1: 灰盒测试受欢迎;常与演化算法一同使用;可用在测试libraries, protocaols, kernels, smart contracts, 多线程程序等上。
P2: 引入directed greybox fuzzing的必要性
P3: 传统上directed fuzzers常用符号执行实现,将可达性转化为迭代的满足constraint问题,但在规模和兼容性上都有问题
P4:
- 2017, Bohme等: Directed Greybox Fuzzing;
- 基本思路: 指定待测程序中一些目标位点,利用轻量级编译插桩
- 基本步骤:
- 计算seed和target之间的距离
- 给距离target更近的seed更高的变异机会
- 将可达性转化为一个优化问题
- 效果:
- 能够工作在更大的规模上,还能够提升effciency好几倍
- 能够在20min内重现heartbleed bug,而基于符号执行的工具KATCH则需要超过24h才能重现
- DGF现在已经不再仅仅使用人工标记的Target site和基于距离的度量,而是利用到了以下信息:
- target sequence
- semantic information
- parser
- typestate
- sanitizer checks
- memory usage
- vulnerable probability
- DGF能够测到更多复杂的行为,比如以下Bugs:
- use-after-free bugs
- memory consumption bugs
- memory violation bugs
- algorithmic complexity vulnerabilities
- input validation bugs in robotic vehicles
- deep stateful bugs
II. Background
A. Terminology
介绍了Fuzzing, Testcase, Seed, Seed Prioritization, Power Schedule, Fuzzing Cylce
B. Coverage-guide Greybox Fuzzing
以AFL为例,介绍了其Edge coverage, Seed prioritization(为每个edge保存效果最好的seed),Mutation Strategies(deterministic stage和non-determinisitic stage(havoc, splice)),Power Schedule(偏好覆盖路径更多,执行速度更快,发现时间更晚的)
C. Directed Greybox Fuzzing
2017年Bohme提出了DGF的概念,并且完成了名为AFLGo的工具。本节以AFLGo为例。
- 在编译阶段,不只做插桩,还计算输入和pre-defined targets之间的距离
- 距离是种子执行trace中到target basic blocks权重的平均值
- 权重由call graph中的边数决定
- 执行距离优先的变异
- 将灰盒fuzzing视作马尔科夫链,以power schedule来驱动
The exploration-exploitation problem
DGF将fuzzing过程划分为两个阶段: 1. exploration phase 2. exploitation phase。平衡exploration phase和exploitation phase就成为了可以研究的问题
- exploration phase: 尽可能多覆盖路径
- exploitation phase: 让引擎尽可能接近target code areas
- DGF中是使用让更靠近Target code area的种子可变异次数更高来做的
- 因为从直觉上来说当前种子执行的path如果接近任何能够达到target code area的expected paths,那么给这个种子更多的变异机会很可能产生满足要求的代码
D. Difference between CGF and DGF
Seed Priorization
CGF主要集中于扩大path coverage,只要能覆盖更多的新路径种子权重就更高。DGF则是会根据distance, coverage,path,或者到达指定区域的概率
Target Involvement
CGF可以认为是untargeted,DGF却可以用人力或者自动化的目标来定制fuzzing的方向。比如,可以在malloc()或者strcpy()等函数调用的critical sites上加重变异次数,以此引发memory corruption bugs
Exploration-Exploitation
greybox fuzzing可以被建模为multi-armed bandit problem,将每个seed作为一个arm来考虑。
E. Application of DGF
Patch Testing
- 补丁可能只修复了一部分会引起这个bug的输入对应的崩溃
- 补丁可能会造成新bug
Bug reproduction
- 重现bug
- 生成PoC
Knowledge boost
- Man-in-the-loop, 或者人工识别提供一些元信息
- symbolic execution
- taint analysis
- static analysis
- 机器学习
Energy Saving
例如为了测试IoT装置,只在关键区域测试
Special bug hunting
- 使用memory usage作为优先级来找memory consumption bugs
- 使用typestate violation来做use-after-free bug
III Assessment of the-state-of-the-art Works
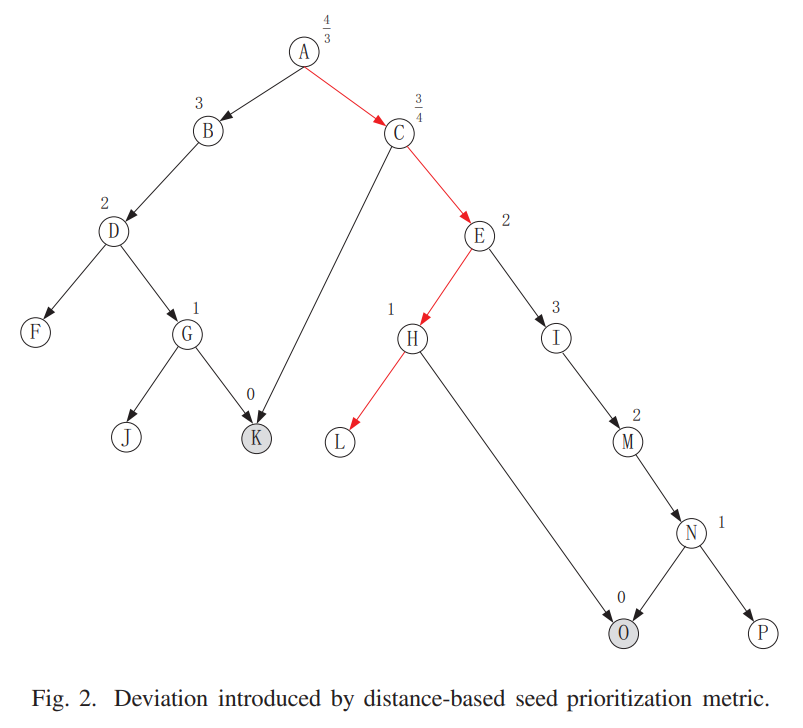
A. Directed Type
- AFLGo和Hawkeye: 人工标记需要覆盖的位置
- UAFuzz, UAFL, LOLLY: 都使用target sequences来找到必须由多个statements同时导致的bugs
- 比如为了引发use-after-free的操作,就一定要有分配memory, 使用memory这样的顺序
- Berry: 当遇到复杂路径时,使用符号执行
- Memlock: 以memory usage为指引,寻找uncontrolled memory & consumption bugs
- V-Fuzz: 利用深度学习模型来预测可能会产生bug的代码区域,用vulnerable prob来指导覆盖
- SemFuzz和DrillerGo: 利用CVE描述和git logs中的语义信息来指引directed fuzzing,生成PoC exploits
- IDVUL:用影响了原本数据流或者控制流的补丁相关的branches来发现1-day漏洞
- SAVIOR, Parmesan: 由Sanitizer提供信息指引
- IJON: 使用人类专家标注的annotation来指引
- RVFUZZER: 用机动车上的无法控制来引导
- PFUZZER: 显式由input parser指导
B. Input Optimization
- SeededFuzz: 使用dynamic taint analysis来标记受影响的bytes,只对这些受影响的bytes做变异
- FuzzGuard: 使用深度学习,将程序输入视为一种模式,学习目标是预测可达性。使用前一次执行标记了可达性的大量inputs来训练模型,然后只执行可达的输入
- TOFU: 从已知的输入结构中生成valid inputs。TOFU的fuzzing过程分为语法fuzzing和语义Fuzzing两部分。不过其input language grammar的实现可能要花费一定时间
C. Seed Prioritization
选择种子优先级的metrics:
- Distance
- AFLGo, ParmeSan, IDVUL: the number of edges in the call graphs and control-flow graphs
- TOFU: the number of correct branching decisions needed to reach the target.
- RDFuzz: Combines distance with frequency, 将code areas划分为high/low freq和high/low distance共四种类型。在exploration阶段,使用low-frequency seeds,在exploitation阶段,使用low distance seeds
- UAFuzz: 专注于use-after-free, use a distance metric of call chains learning to target functions that are more likely to include both allocation and free functions
- Wuestholz等用静态分析先分析不可能到达target location的所有path prefix
- 缺点:当到达target的路有多条时,会忽略更长的那一条和相关options的构建
- Similarity & Coverage:
- Hawkeye: 静态分析, basic block trace distance + covered function similarity for the seed prioritization and power scheduling.
- LOLLY: target user-specified program statement sequence, 使用sequence coverage作为度量
- UAFL: uses the operation sequence coverage that is likely to trigger use-after-free vulnerabilities.
- UAFuzz: 使用带有序列花特征的相似性度量来测试当前种子执行轨迹和目标bug轨迹。(a sequenceness-aware target similarity metric to measure the similarity between the execution of a seed and the target UAF bug trace)
- Berry: 考虑目标执行轨迹和经过调整的target sequence之间的相似度
- SAVIOR: 使用UBSan预测的labels coverage来衡量seed的潜力
- TortoiseFuzz: 基于对三种粒度的内存操作:function, loop, basic blocks的覆盖率和安全影响的衡量来给种子赋予优先级。
- 概率(可能到达目标状态的概率)
- V-Fuzz, SUZZER: 使用deep learning来给每个basic block一个vulnerable prob static score
- SAVIOR: 利用UBSan来标记code areas
- TAFL: 使用静态语义metrics,包括sensitive, complex, deep and rare-to-reach regions来标记vulnerable regions
D. Power Assignment
都是模拟退火,用来在exploration阶段保留向外探索,不被困在局部极小值的能力
- AFLGO: a simulated annealing-based power schedule,用来避免陷入局部极小值
- Hawkeye: simulated annealing with added prioritization
- LOLLY: optimized simulated annealing targeted for sequence coverage
E. Mutator Scheduling
多数采取了粒度相关的mutation策略
- Hawkeye: adaptive mutation strategy, 将mutators分类为粗粒度和细粒度。
- 粗粒度更改bulks of bytes
- 细粒度只修改几个byte
- 到达目标函数的概率越高,越倾向于细粒度
- V-Fuzz: 将mutations分为 slight mutation, heavy mutation
- 根据实际的fuzzing状态设置一个threshold
- SemFuzz: resemble classification, based on syscall
- coarse mutation: 用于找到能够更靠近vulnerable functions的syscall sequence
- fine-grained mutation: 用来检测关键变量
- TAFL:
- coarse-grained mutators outperform fine-grained mutators on path growth
- 联合使用多类mutators常比只用单类效果更好
- ProFuzzer: input type probing
- 根据input field types采取不同的策略。
F. Data-flow Analysis
- RDFuzz: a disturb-and-check method来识别和保护对距离敏感的内容
- UAFL: information flow analysis between the input and the program variables in the conditional statement. 为更可能改变结果的bytes赋予更高的strength
- SemFuzz: backward data-flow analysis,跟踪关键变量依赖的kernel function parameters
- PFUZZER: dynamic tainting
- TIFF: 通过in-memory data-structure identification and dynamic taint analysis来infers input type
IV. Challenges and Solutions
A. Binary Code Support
背景
- 基于AFL则多半需要源码来插桩
挑战
- heavy runtime overhead: 使用QEMU等emulator来获取信息,非常慢
- difficulty in collecting target information: 只能从bug traces来获取信息,不能使用code changes, CVE descriptions, 人工标注重点区域等方法
- difficulty in labeling the targets: 难以标注PUT,往往需要借助逆向工程将二进制转化为源码之后再进行理解标注
Mitigations:
- hardware support: Intel PT, Intel Last Branch Record(只能将输出存在register中)
- automatically identify the vulnerable code
B. Automatic target identification
- AFLGO, Hawkeye等:需要已知目标位点的line number或者virtual memory address等信息
- git commit logs, bug traces, CVE descriptions,
- static analysis tools
- compiler sanitizer passes: e.g: UBSan
- 1DVUL: patch-related target branch: 使用Bindiff来做对比
- attack surface identification component
C. Differentiated weight metric
e.g: 使用transitions among basic blocks来衡量种子到target的距离
实际上忽略了不同的branch jumps有不同的概率这一问题。
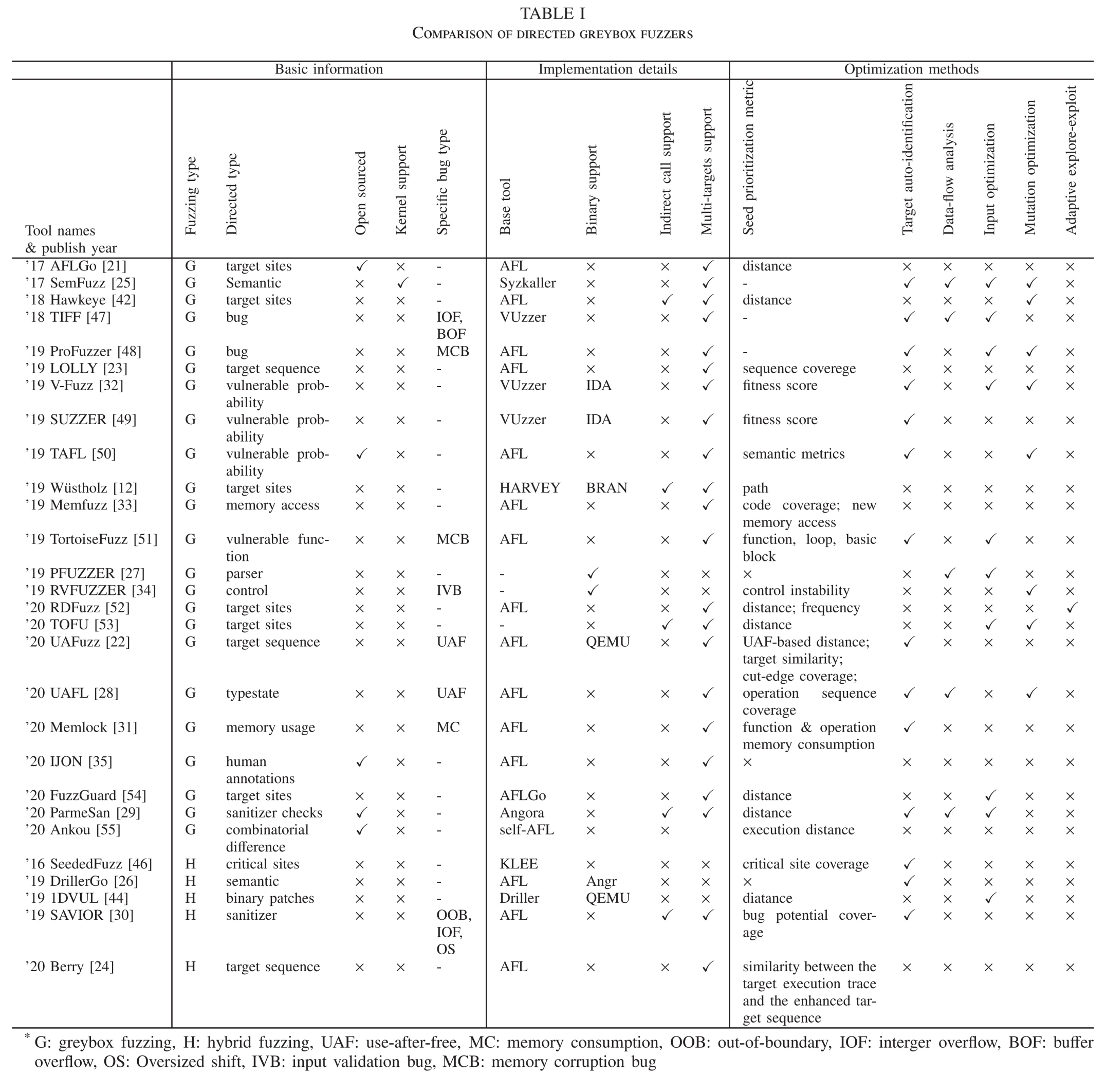
例如:图1中的路径A到G的概率其实大约是0.3,与到E的概率是差不多的。但是如果只看transition数目,则路径A到G的距离是3,A到E为2,多半会保留并使用到E的结果。
解决方案
- 考虑跳转概率:常与马尔科夫链以及蒙特卡洛方法连用
- 缺点:runtime overhead
- Mitigations:
- interval sampling
- accelerate the computation, usually optimizing the store and access of metadata. 例如:介于邻接链表和邻接矩阵之间的某种数据结构
- Mitigations:
D. Global Optimum Deviation
multi-targets
- 使用最短路算法:缺点:miss the local optimum seed that is closest to a certain target.
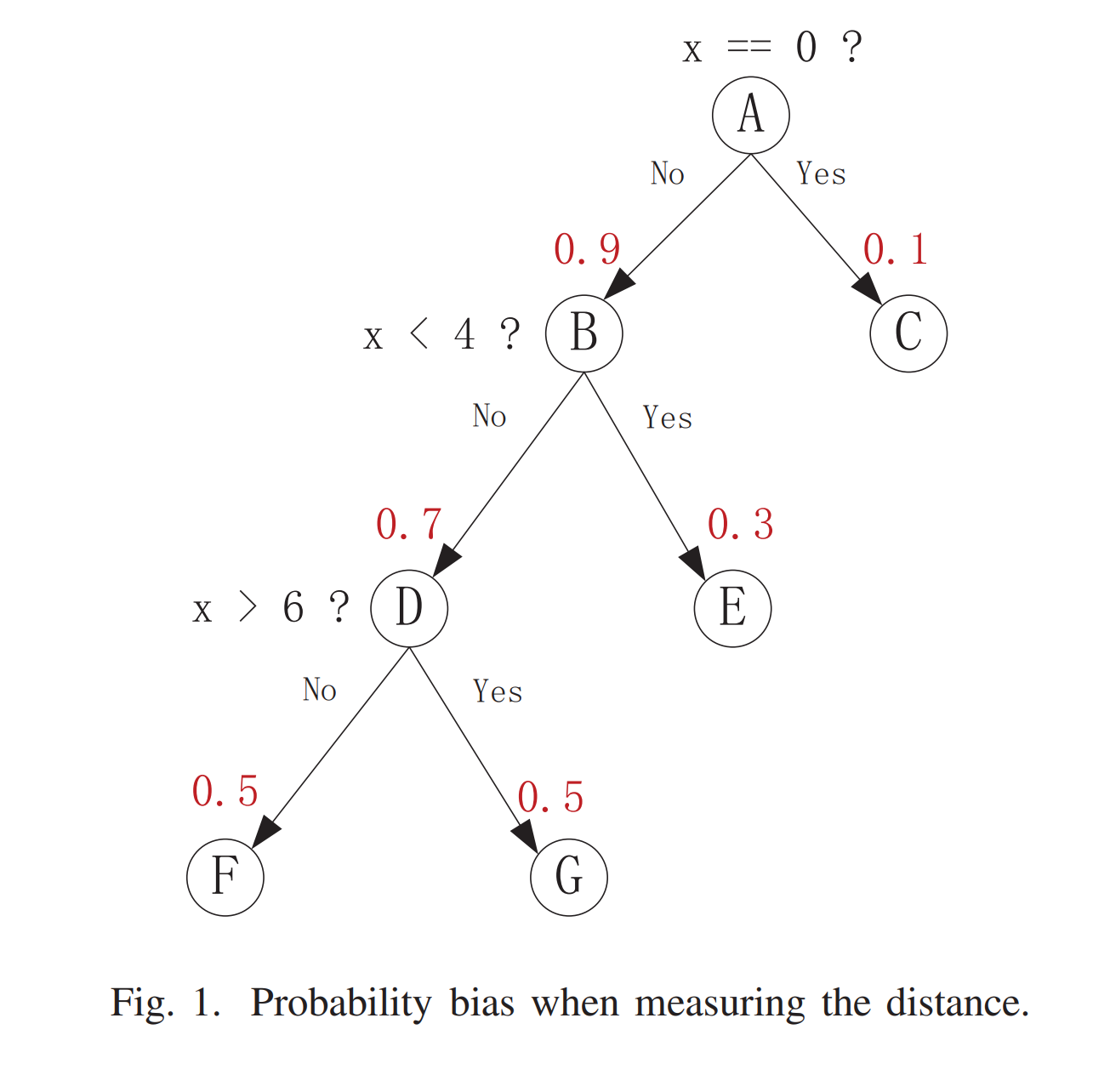
- 例子:Fig2, 每条路径的距离被算作每个节点的距离(已经标在节点上)的平均值。考虑到K, O是targets,ABDGK和ACEIMNO这两个已经到达targets的序列明显是更好的,但是算出来就是会取ACEHL
- dABDGK = (4/3 + 3 + 2 + 1 + 0)/5 ≈ 1.47,
- dACEIMNO = (4/3 + 3/4+ 2 + 3 + 2 + 1 + 0)/7 ≈ 1.44
- dACEHL = (4/3 + 3/4 + 2 + 1)/4 ≈ 1.27.
- 考虑所有potential paths
- Hawkeye: adjacent-function distance augmentation + lightweight static analysis, considers the patterns of the (immediate) call relation based on the generated call graph.
- separating the targets: 对不同的目标,选择不同的seed优先





