JDK Timer的使用方法、原理与使用场景
在使用JDK Timer的时候主要有两个类TimerTask和Timer.
可以这样理解他们的:
- TimerTask是需要被执行的任务
- Timer是执行任务Scheduler
JDK Timer的使用方法
执行一次性任务:
Timer仅执行TimerTask一次
@Test
public void scheduleTaskOnce() throws InterruptedException {
log.info("{},create once schedule task", Thread.currentThread().getName());
TimerTask task = new TimerTask() {
public void run() {
log.info("run scheduleTaskOnce(), thread:{}, time:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName(), sdf.format(new Date()));
}
};
// name==task执行线程名称
Timer timer = new Timer("Timer");
long delay = 1000L;
timer.schedule(task, delay);
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2l);
}
执行周期性任务:
Timer每隔period执行TimerTask一次
@Test
public void fixRateTask() throws InterruptedException {
TimerTask repeatedTask = new TimerTask() {
public void run() {
log.info("run scheduleTaskOnce(), thread:{}, time:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName(), sdf.format(new Date()));
}
};
Timer timer = new Timer("Timer");
long delay = 0l;
long period = 1000L;
// 如果当前Task执行延时,超出下一次任务执行的起始时间,那么当前任务执行结束后,下一次任务将立即开始。
timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(repeatedTask, delay, period);
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10l);
}
取消任务:
取消任务的方式有两种一种是inner另一种是outside
@Test
public void cancelTask() throws InterruptedException {
TimerTask task = new TimerTask() {
public void run() {
System.out.println("Task performed on " + new Date());
// inner cancel
// cancel();
}
};
Timer timer = new Timer("Timer");
timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(task, 1000L, 1000L);
// outside cancel
// timer.cancel();
Thread.sleep(1000L * 2);
}
JDK Timer工作原理
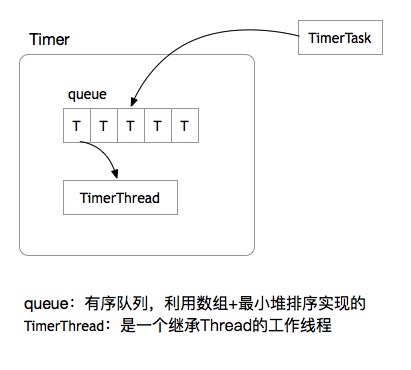
JDK Timer的主要由有序队列和工作线程组成,通过scheduleAtFixedRate 和schedule方法加入将任务添加至有序队列,然后TimmerThread消息队列中Task。
下面我们通过TimerThread.mainLoop()源码看看执行Task的主要逻辑:
private void mainLoop() {
while (true) {
try {
TimerTask task;
boolean taskFired;
// 利用synchronized锁住任务队列
synchronized(queue) {
// 如果队列为空,并且newTasksMayBeScheduled,当前线程挂起等待,直到有queue被notify
// 变量newTasksMayBeScheduled,被用于优化关闭工作线程
while (queue.isEmpty() && newTasksMayBeScheduled)
queue.wait();
if (queue.isEmpty())
break; // Queue is empty and will forever remain; die
// Queue nonempty; look at first evt and do the right thing
long currentTime, executionTime;
task = queue.getMin();
// 获取队列中最小的task,并开始处理
synchronized(task.lock) {
if (task.state == TimerTask.CANCELLED) {
queue.removeMin();
continue; // No action required, poll queue again
}
currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
executionTime = task.nextExecutionTime;
// 这里就是周期执行任务的逻辑处理过程
if (taskFired = (executionTime<=currentTime)) {
// 如果不在有下次执行周期,则从queue中remove此次任务
if (task.period == 0) { // Non-repeating, remove
queue.removeMin();
task.state = TimerTask.EXECUTED;
} else { // Repeating task, reschedule
// 如果有下次执行周期,并下次执行周期已经过时,则重新schdule
queue.rescheduleMin(
task.period<0 ? currentTime - task.period
: executionTime + task.period);
}
}
}
// 如果task还未到执行时间,则等待
if (!taskFired) // Task hasn't yet fired; wait
queue.wait(executionTime - currentTime);
}
if (taskFired) // Task fired; run it, holding no locks
// 执行任务
task.run();
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
}
}
}
JDK Timer的使用场景
1: Timer运行在单线程中,无法满足多个任务同时执行,如果需要被执行的任务存在量大,耗时的话,可能导致业务延迟执行。
2:Timer会被任务异常中断停止,业务逻辑执行过程中,如果抛出了异常,会被捕获并且任务将停止执行,如果不希望任务被异常打断则需要自己在业务方法内部catch主所有异常。
posted on 2020-02-02 17:24 yipianlarou 阅读(341) 评论(0) 收藏 举报


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号