PgSQL · 源码分析 · PG优化器浅析
在使用PostgreSQL数据库过程中,对SQL调优最常用的手段是使用explain查看执行计划,很多时候我们只关注了执行计划的结果而未深入了解执行计划是如何生成的。优化器作为数据库核心功能之一,也是数据库的“大脑”,理解优化器将有助于我们更好地优化SQL,下面将会为大家解开PostgreSQL优化器神秘的面纱。
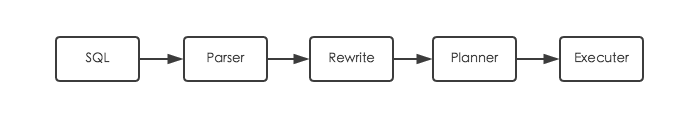
SQL执行过程
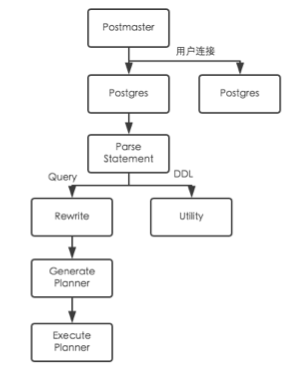
在PG数据库中,对于DDL语句无需进行优化,到utility模块处理,对于DML语句需要到优化器中处理,一个用户连接从接收SQL到执行的流程如下:
查询重写
主要目的是为了消除view、rule等,如下示例,视图v_t_1_2在执行计划里面已经被t1、t2替换。
create view v_t_1_2 as SELECT t1.a1, t1.b1, t2.a2, t2.b2 FROM t1, t2;
postgres=> explain select * from v_t_1_2, t1 where v_t_1_2.a1 = 10 and t1.b1 = 20; QUERY PLAN
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Nested Loop (cost=0.55..41.59 rows=1000 width=24)
-> Nested Loop (cost=0.55..16.60 rows=1 width=16)
-> Index Scan using t1_a1_key on t1 t1_1 (cost=0.28..8.29 rows=1 width=8)
Index Cond: (a1 = 10)
-> Index Scan using b1_1 on t1 (cost=0.28..8.29 rows=1 width=8)
Index Cond: (b1 = 20)
-> Seq Scan on t2 (cost=0.00..15.00 rows=1000 width=8)
(7 rows)
提升子链
目标是将IN和exists子句递归提升。 select * from t1 where t1.a1 in (select t2.a2 from t2 where t2.b2 = 10); 假设t2.a2为unique 转化为: select t1.a1,t1,a2 from t1 join t2 where t1.a1=t2.a2 and t2.b2 = 10;
in子链接执行计划如下:
postgres=> explain select * from t1 where t1.a1 in (select t2.a2 from t2 where t2.b2 = 10);
QUERY PLAN
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
Nested Loop (cost=0.28..25.80 rows=1 width=8)
-> Seq Scan on t2 (cost=0.00..17.50 rows=1 width=4)
Filter: (b2 = 10)
-> Index Scan using t1_a1_key on t1 (cost=0.28..8.29 rows=1 width=8)
Index Cond: (a1 = t2.a2)
explain select * from t1 where exists (select t2.a2 from t2 where t2.a2 = t1.a1) ; 假设t2.a2为unique 转化为: select t1.a1, t1.b1 from t1, t2 where t1.a1=t2.a1;
exists子链接执行计划如下:
postgres=> explain select * from t1 where exists (select t2.a2 from t2 where t2.a2 = t1.a1) ;
QUERY PLAN
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Hash Join (cost=26.42..54.69 rows=952 width=8)
Hash Cond: (t2.a2 = t1.a1)
-> Seq Scan on t2 (cost=0.00..15.00 rows=1000 width=4)
-> Hash (cost=14.52..14.52 rows=952 width=8)
-> Seq Scan on t1 (cost=0.00..14.52 rows=952 width=8)
(5 rows)
提升子查询
子查询和子链接区别:子查询不在表达式中子句,子链接在in/exists表达式中的子句。 select * from t1, (select * from t2) as c where t1.a1 = c.a2; 转化为: select * from t1, t2 where t1.a1 = t2.a2;
postgres=> explain select * from t1, (select * from t2) as c where t1.a1 = c.a2;
QUERY PLAN
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Hash Join (cost=26.42..54.69 rows=952 width=16)
Hash Cond: (t2.a2 = t1.a1)
-> Seq Scan on t2 (cost=0.00..15.00 rows=1000 width=8)
-> Hash (cost=14.52..14.52 rows=952 width=8)
-> Seq Scan on t1 (cost=0.00..14.52 rows=952 width=8)
(5 rows)
并不是所有的子查询都能提升,含有集合操作、聚合操作、sort/limit/with/group、易失函数、from为空等是不支持提升的。 如下:
postgres=> explain select t1.a1 from t1, (select a2 from t2 limit 1) as c where c.a2 = 10;
QUERY PLAN
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Nested Loop (cost=0.00..24.07 rows=952 width=4)
-> Subquery Scan on c (cost=0.00..0.03 rows=1 width=0)
Filter: (c.a2 = 10)
-> Limit (cost=0.00..0.01 rows=1 width=4)
-> Seq Scan on t2 (cost=0.00..15.00 rows=1000 width=4)
-> Seq Scan on t1 (cost=0.00..14.52 rows=952 width=4)
(6 rows)
化简条件
包含逻辑推理、表达式计算等
外连接消除(left/right/full join)
以left join为例,left join(左连接) 返回包括左表中的所有记录和右表中连接字段相等的记录 ,如果右表没有匹配的记录,那么右表将会以NULL值代替,例如:
A表 B表
ID1 ID2
1 1
2
select * from A left join B on A.id1 = B.id2;
结果如下:
ID1 ID2
1 1
2 NULL
存在外连接left join
postgres=> explain select * from t1 left join t2 on true;
QUERY PLAN
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Nested Loop Left Join (cost=0.00..11932.02 rows=952000 width=16)
-> Seq Scan on t1 (cost=0.00..14.52 rows=952 width=8)
-> Materialize (cost=0.00..20.00 rows=1000 width=8)
-> Seq Scan on t2 (cost=0.00..15.00 rows=1000 width=8)
(4 rows)
消除外连接需要where和join条件保证右表不会有NULL值的行产生。
postgres=> explain select * from t1 left join t2 on t1.b1 = t2.b2 where t2.b2 is not NULL;
QUERY PLAN
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Nested Loop (cost=0.28..23.30 rows=1 width=16)
-> Seq Scan on t2 (cost=0.00..15.00 rows=1 width=8)
Filter: (b2 IS NOT NULL)
-> Index Scan using b1_1 on t1 (cost=0.28..8.29 rows=1 width=8)
Index Cond: (b1 = t2.b2)
(5 rows)
条件下推
条件下推的目的为了连接前,元组数组尽量少,如下示例,条件已经下推到每个表上面了。
postgres=> explain select * from t1,t2 where t1.a1 < 10 and t2.a2 > 900;
QUERY PLAN
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Nested Loop (cost=0.55..31.20 rows=1000 width=16)
-> Index Scan using t2_a2_key on t2 (cost=0.28..10.03 rows=100 width=8)
Index Cond: (a2 > 900)
-> Materialize (cost=0.28..8.70 rows=10 width=8)
-> Index Scan using t1_a1_key on t1 (cost=0.28..8.65 rows=10 width=8)
Index Cond: (a1 < 10)
语义优化
当表中字段存在约束键时,PostgreSQL将会对其进行语义优化,因为查询条件有可能已经隐含满足或者不满足,例如:
create table tt1(id int not null);
postgres=> explain select * from tt1 where id is null;
QUERY PLAN
--------------------------------------------------------
Seq Scan on tt1 (cost=0.00..15407.02 rows=1 width=15)
Filter: (id IS NULL)
set constraint_exclusion = on;
postgres=> explain select * from tt1 where id is null;
QUERY PLAN
------------------------------------------
Result (cost=0.00..0.01 rows=1 width=0)
One-Time Filter: false
表tt1的id字段已经隐含了不为NULL,所以id=null这种条件可以直接返回false,PostgreSQL数据库默认并没有开启约束优化,需要设置constraint_exclusion这个参数。
MIN/MAX优化
min/max函数在应用的使用中是非常广泛的,数据库有必要对其进行特殊优化,比如索引中已经将数据排好序了,最大最小值可以直接获取到,所以PostgreSQL对min/max函数做了一步转化。 select min(a1) from t1 转化为 select a1 from t1 order by a1 limit 1; 如果a1没有索引,那么将会是顺序扫描,不进行转化。
postgres=> explain select min(a1) from t1;
QUERY PLAN
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Result (cost=0.32..0.33 rows=1 width=0)
InitPlan 1 (returns $0)
-> Limit (cost=0.28..0.32 rows=1 width=4)
-> Index Only Scan using t1_a1_key on t1 (cost=0.28..45.09 rows=952 width=4)
Index Cond: (a1 IS NOT NULL)
group by优化
如果不对group by优化,那么将会需要对结果进行Sort或者Hash,但是如果表中数据已经是排序好的,那么将可以对其进行优化。
create index tt1_id_key on tt1 using btree ( id);
postgres=> explain select id from tt1 group by id;
QUERY PLAN
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Group (cost=0.42..33891.21 rows=1000102 width=4)
Group Key: id
-> Index Only Scan using tt1_id_key on tt1 (cost=0.42..31390.96 rows=1000102 width=4)
postgres=> explain select name from tt1 group by name;
QUERY PLAN
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
Group (cost=132169.76..137170.27 rows=1000102 width=11)
Group Key: name
-> Sort (cost=132169.76..134670.02 rows=1000102 width=11)
Sort Key: name
-> Seq Scan on tt1 (cost=0.00..15407.02 rows=1000102 width=11)
order by优化
1. 利用索引消除order by
postgres=> explain select * from t1 order by a1;
QUERY PLAN
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
Index Scan using t1_a1_key on t1 (cost=0.28..42.71 rows=952 width=8)
(1 row)
2. order by下推,利用merge join实现更快的连接
postgres=> explain select * from t1,t2 where t1.b1=t2.b2 order by b1;
QUERY PLAN
------------------------------------------------------------------
Merge Join (cost=126.45..136.22 rows=1 width=16)
Merge Cond: (t1.b1 = t2.b2)
-> Sort (cost=61.62..64.00 rows=952 width=8)
Sort Key: t1.b1
-> Seq Scan on t1 (cost=0.00..14.52 rows=952 width=8)
-> Sort (cost=64.83..67.33 rows=1000 width=8)
Sort Key: t2.b2
-> Seq Scan on t2 (cost=0.00..15.00 rows=1000 width=8)
(8 rows)
distinct优化
类似于group by优化,distinct将会从Sort和Hash中选择最优的,如果字段中有索引,Sort代价可能会更低。
postgres=> explain select distinct(a1) from t1;
QUERY PLAN
-----------------------------------------------------------
HashAggregate (cost=16.90..26.42 rows=952 width=4)
Group Key: a1
-> Seq Scan on t1 (cost=0.00..14.52 rows=952 width=4)
(3 rows)
postgres=> explain select distinct(name) from tt1;
QUERY PLAN
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
Unique (cost=132169.76..137170.27 rows=1000102 width=11)
-> Sort (cost=132169.76..134670.02 rows=1000102 width=11)
Sort Key: name
-> Seq Scan on tt1 (cost=0.00..15407.02 rows=1000102 width=11)
集合操作优化
集合操作union被转换成Append方式。
postgres=> explain select a1 from t1 where a1 < 10 union select a2 from t2;
QUERY PLAN
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
HashAggregate (cost=36.28..46.38 rows=1010 width=4)
Group Key: t1.a1
-> Append (cost=0.28..33.75 rows=1010 width=4)
-> Index Only Scan using t1_a1_key on t1 (cost=0.28..8.65 rows=10 width=4)
Index Cond: (a1 < 10)
-> Seq Scan on t2 (cost=0.00..15.00 rows=1000 width=4)
postgres=> explain select a1 from t1 where a1 < 10 union all select a2 from t2;
QUERY PLAN
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Append (cost=0.28..23.75 rows=1010 width=4)
-> Index Only Scan using t1_a1_key on t1 (cost=0.28..8.65 rows=10 width=4)
Index Cond: (a1 < 10)
-> Seq Scan on t2 (cost=0.00..15.00 rows=1000 width=4)
总结
以上介绍了几种常见的PostgreSQL优化器对SQL优化的方法,这些方法更着重于SQL逻辑优化,也就是尽量对SQL进行等价或者推倒变换,以达到更有效率的执行计划。PostgreSQL优化器原理远不止这些,比如表的扫描方式选择、多表组合方式、多表组合顺序等,这些内容将会在后续的月报中继续呈现。