Python----朴素贝叶斯
1、朴素贝叶斯
朴素贝叶斯是使用概率论来分类的算法。其中朴素:各特征条件独立;贝叶斯:根据贝叶斯定理。
根据贝叶斯定理,对一个分类问题,给定样本特征B,样本属于类别A的概率是:![]()
2、算法特点
优点: 在数据较少的情况下仍然有效,可以处理多类别问题。
缺点: 对于输入数据的准备方式较为敏感。
适用数据类型: 标称型数据。
3、实例

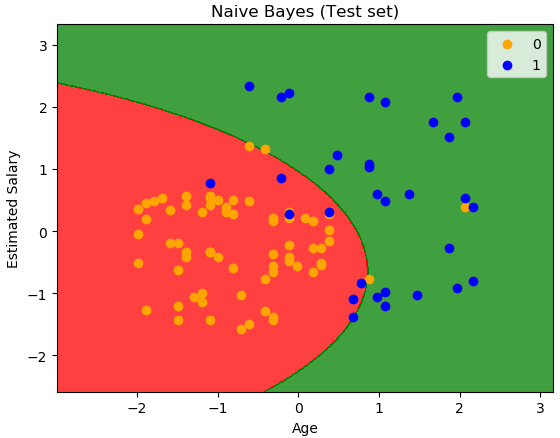
# Importing the libraries import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import pandas as pd # Importing the dataset dataset = pd.read_csv('Social_Network_Ads.csv') X = dataset.iloc[:, [2,3]].values y = dataset.iloc[:, 4].values # Splitting the dataset into the Training set and Test set from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size = 0.25, random_state = 0) # Feature Scaling from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler sc_X = StandardScaler() X_train = sc_X.fit_transform(X_train) X_test = sc_X.transform(X_test) # Fitting Logistic Regression to the Training set #从模型的标准库中导入需要的类 from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB #创建分类器 classifier = GaussianNB() #运用训练集拟合分类器 classifier.fit(X_train, y_train) # Predicting the Test set results #运用拟合好的分类器预测测试集的结果情况 #创建变量(包含预测出的结果) y_pred = classifier.predict(X_test) # Making the Confusion Matrix #通过测试的结果评估分类器的性能 #用混淆矩阵,评估性能 #65,24对应着正确的预测个数;8,3对应错误预测个数;拟合好的分类器正确率:(65+24)/100 from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred) # Visualising the Training set results #在图像看分类结果 from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap #创建变量 X_set, y_set = X_train, y_train #x1,x2对应图中的像素;最小值-1,最大值+1,-1和+1是为了让图的边缘留白,像素之间的距离0.01;第一行年龄,第二行年收入 X1, X2 = np.meshgrid(np.arange(start = X_set[:, 0].min() - 1, stop = X_set[:, 0].max() + 1, step = 0.01), np.arange(start = X_set[:, 1].min() - 1, stop = X_set[:, 1].max() + 1, step = 0.01)) #将不同像素点涂色,用拟合好的分类器预测每个点所属的分类并且根据分类值涂色 plt.contourf(X1, X2, classifier.predict(np.array([X1.ravel(), X2.ravel()]).T).reshape(X1.shape), alpha = 0.75, cmap = ListedColormap(('red', 'green'))) #标注最大值及最小值 plt.xlim(X1.min(), X1.max()) plt.ylim(X2.min(), X2.max()) #为了滑出实际观测的点(黄、蓝) for i, j in enumerate(np.unique(y_set)): plt.scatter(X_set[y_set == j, 0], X_set[y_set == j, 1], c = ListedColormap(('orange', 'blue'))(i), label = j) plt.title('Naive Bayes (Training set)') plt.xlabel('Age') plt.ylabel('Estimated Salary') #显示不同的点对应的值 plt.legend() #生成图像 plt.show() # Visualising the Test set results from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap X_set, y_set = X_test, y_test X1, X2 = np.meshgrid(np.arange(start = X_set[:, 0].min() - 1, stop = X_set[:, 0].max() + 1, step = 0.01), np.arange(start = X_set[:, 1].min() - 1, stop = X_set[:, 1].max() + 1, step = 0.01)) plt.contourf(X1, X2, classifier.predict(np.array([X1.ravel(), X2.ravel()]).T).reshape(X1.shape), alpha = 0.75, cmap = ListedColormap(('red', 'green'))) plt.xlim(X1.min(), X1.max()) plt.ylim(X2.min(), X2.max()) for i, j in enumerate(np.unique(y_set)): plt.scatter(X_set[y_set == j, 0], X_set[y_set == j, 1], c = ListedColormap(('orange', 'blue'))(i), label = j) plt.title('Naive Bayes (Test set)') plt.xlabel('Age') plt.ylabel('Estimated Salary') plt.legend() plt.show()
训练集图像显示结果:
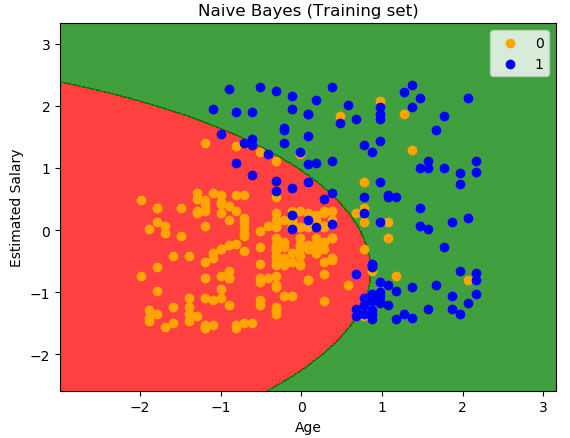
测试集图像显示结果: