第10次全天课笔记 20180916 字符串
1、将"gloryroad"按照如下规则进行加密:
字母对应的asscii码值进行加密,并且在码值前面加上码值长度
如g对应的码值为ord("g")=103,则字母g加密结果为3103
3是ascii的长度。
“gloryroad”正确输出加密结果为:
"31033108311131143121311431112973100"
def encode_str(s):
encoded_str = ""
for i in s:
encoded_str+= str(len(str(ord(i))))+str(ord(i))
return encoded_str
2、将上题中的加密字符串进行解密
方法有2种:
方法:1 种用while循环,观察加密后的规律,想办法遍历所有的内容
方法2: 递归实现
方法1:
def decode_str(s):
index = 0
decoded_str = ""
while index < len(s):
decoded_str+= chr(int(s[(index+1):(index+int(s[index])+1)]))
index = index+int(s[index])+1
return decoded_str
方法2:
decrypt_result=""
def get_data(data):
global decrypt_result
if len(data)==0:
print("解密结果为:"+decrypt_result)
else:
num=int(data[0])
decrypt_result+=chr(int(data[1:(num+1)]))
get_data(data[(num+1):])
递归:
自己调用自己的逻辑写清楚
要有结束递归的条件
字符串:
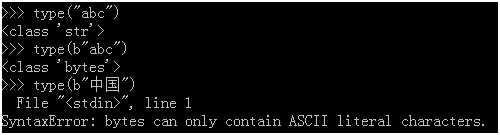

只要不在内存中使用的,全部都是bytes类型。(用str不行)
Windows 的换行符

Linux 和 Mac的换行符
>>> import os
>>> os.linesep
'\n'
是 “\n”

字符串不能被改变

字符串值一样的,在内存中保存的地址是一个


>>> "abc{1}{0}".format("ddd","e")
'abceddd'
>>> "".join(["1","2"])
'12'
>>> "%s = %s" %(1,2)
'1 = 2'
>>> "%d = %d" %(1,2)
'1 = 2'
>>> "%.2f = %.2f" %(1.999,2.555) #有四舍五入
'2.00 = 2.56'


>>> a[5:] #切片不会报错,取不到值为空
''
>>> a[5]
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
IndexError: string index out of range
小练习:
s = "I am a boy!"
统计 一下首字母为'a'的单词
result =0
for word in s.split():
if word[0]=="a":
result+=1
print (result)
将字符串反转
方法1:
s = "I am a boy!"
print(s[::-1])
方法2:
s = "I am a boy!"
result =[]
for word in s.split()[::-1]:
result.append(word[::-1])
print (" ".join(result))
一句话做出:
>>> " ".join(list(map(lambda x:x[::-1],s.split()[::-1])))
'!yob a ma I'
name = 'ruby'
#格式化字符串
print ("My name is %s and weight is %d kg" %(name, 21))


>>> from string import Template
>>> s=Template("There are ${key1} ${key2}")
>>> print(s.substitute(key2="python",key1=3))
There are 3 python
Strip() 去除开头结尾的字符
>>> " abc ".strip()
'abc'
>>> "*###abc ".strip("#*")
'abc '
>>> "*###ab###c ".strip("#*")
'ab###c '
>>> "##**addd#**".lstrip("#*") #去除左边的
'addd#**'
>>> "##**addd#**".rstrip("#*") #去除右边的
'##**addd'
生成所有的小写字母
>>> "".join(list(map(lambda x:chr(x),range(97,122))))
'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxy'
生成所有的大小写字母
>>> import string
>>> string.ascii_letters
'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ'
变换大小写
>>> "abc".upper()
'ABC'
>>> "ABC".lower()
'abc'
首字母大写
>>> "abc".capitalize()
'Abc'
大小写转换
>>> "ahhHHH".swapcase()
'AHHhhh'
所有首字母变成大写
>>> string.capwords("aaa nnn ddd")
'Aaa Nnn Ddd'
>>> "aaa nnn ddd".title()
'Aaa Nnn Ddd'
补齐(左,右,中间)
>>> "abc".ljust(10)
'abc '
>>> "abc".ljust(10,"$")
'abc$$$$$$$'
>>> "abc".rjust(10,"$")
'$$$$$$$abc'
>>> "abc".center(10,"$")
'$$$abc$$$$'
Str和string的区别,str是一个类,string是一个模块
>>> str
<class 'str'>
>>> type(string)
<class 'module'>
>>> string.punctuation
'!"#$%&\'()*+,-./:;<=>?@[\\]^_`{|}~'
Zfill 补充0
>>> "111".zfill(10)
'0000000111'
查找 find 和index,find找不到返回-1,index 找不到抛异常
>>> "abc".find("b")
1
>>> "abc".find("f")
-1
>>> "a111111z".find("z",7,8)
7
>>> "abcda".rfind("a")
4
>>> "abcda".rfind("x")
-1
查找多个,使用正则
>>> import re
>>> re.findall(r"ab","ab ab ab")
['ab', 'ab', 'ab']
>>> "abc".index("b")
1
>>> "abc".index("f")
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
ValueError: substring not found
练习:"abbaaba" 查找出ab
方法1:
result = []
s="abbaaba"
for i in range(len(s)):
if s[i:i+2] == "ab":
result.append(i)
print (result)
方法2:
result = []
s="ababab"
index =0
while 1:
position = s.find("ab",index)
if position != -1:
result.append(position)
index =position+2
else:
break
print (result)
提升开发质量的做法:
1.最重要的是开发人员的素质和敬业程度,招聘提升质量 1个大神顶20个开发
2.流程:不断优化,敏捷。小步快跑,只做明确的需求,不追求过度的文档,强调人和人的沟通,通过自动化测试,实现代码的高效重构。
3.需求明确:1 文档 2 人沟通 3 文档+人
所有的评审,所有的人都在。开发讲需求,测试讲需求,产品不断确认(敏捷方式)
4.技术评审:
架构评审。概要设计的评审
5. 开发自测:覆盖率要求,单元测试来实现。
强制要求:开发代码和你单元测试的代码一起提交
代码评审,开发规范
开发工具、静态代码扫描工具(findbugs)、白盒测试工具
(星云测试:运行产品的时候,你做测试的操作,他会帮你统计代码覆盖率。)
安全扫描工具(外企:)
培训一下如何做单元测试(代码大全2,单元测试的艺术)
上线:通过系统来部署到开发环境、测试环境,预发布环境、生产环境。 Devops,testops
大公司:持续集成(5万行代码,每周改500行),大量的自动化回归(可测试性、自动化测试))
对代码质量提升最多的其实是单元测试 微软70%代码覆盖率
预评审:1 下发冒烟测试用例 2 你测试一遍主要流程
全员质量负责职责:鼓励开发独立负责。
环境的搭建成本的投入,测试模型的建立
测试:
测试人员:有技术的测试
功能:
三剑客---:功能测试框架、bug预防机制、探索式测试
工具测试:功能、安全、性能、抓包、日志分析
项目经验教训的总结。
质量有评估体系:
利益驱动质量:质量变差就对开发人员的绩效有影响。
Replace 用法
>>> "abca".replace("a","xx")
'xxbcxx'
>>> "abca".replace("a","xx",1)
'xxbca'
>>> "a ddd fdsf fsd ".replace(" ","")
'adddfdsffsd'
将tab替换成几个空格
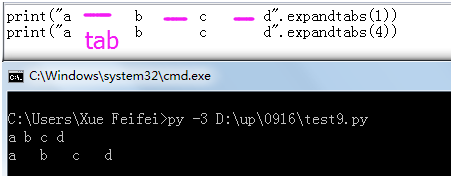
>>> "a\nb\tc\rd e".split() #默认是空白切,包括空格\n,\t,\r等
['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']
>>> "a*b*c".split("*",1) #切几次
['a', 'b*c']
Splitlines 按照回车换行符切割,写1 是保留回车换行符
>>> s = "1\n2\n"
>>> print(s.splitlines())
['1', '2']
>>> print(s.splitlines(1))
['1\n', '2\n']
Join,应该是str类型,给的是int会报错
>>> "*".join([1,2,3])
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: sequence item 0: expected str instance, int found
使用str类型,list或者tuple
>>> "*".join(["1","2","3"])
'1*2*3'
>>> "*".join(("1","2","3"))
'1*2*3'
如何实现join这个功能:
class huang_str(object):
@classmethod
def join(cls,arr,s):
result =""
for i in arr:
result += str(i) +s
return result.rstrip(s)
print(huang_str.join([1,2,3],"*"))
C:\Users\Xue Feifei>py -3 D:\up\0916\test10.py
1*2*3
以什么开头,以什么结尾
>>> "abc".startswith("a")
True
>>> "abc".startswith("d")
False
>>> "abc".endswith("d")
False
>>> "abc".endswith("c")
True
是字母
>>> "abc".isalpha()
True
>>> "abc1".isalpha()
False
是字母和数字
>>> "abc1".isalnum()
True
是数字
>>> "111".isdigit()
True
>>> "111.33".isdigit()
False
是否是空格
>>> " ".isspace()
True
>>> "ee ".isspace()
False
小练习:
判断一下这句话,有几个数字和几个空白,和几个字母
其他字符有几个
"I am a 12 years old boy! hi,me!"
s = "I am a 12 years old boy! hi,me!"
number_num = 0
letter_num = 0
space_num =0
other_num =0
for i in s:
if i.isdigit():
number_num +=1
elif i.isalpha():
letter_num +=1
elif i.isspace():
space_num +=1
else:
other_num +=1
print("数字有%d个,字母有%d个,空格有%d个,其他有%d个"%(number_num,letter_num,space_num,other_num))
大小写字母
>>> "a".islower()
True
>>> "A".isupper()
True
每个单词首字母
>>> "I Am A Boy".istitle()
True
>>> "I Am A boy".istitle()
False
Maketrans 映射关系
>>> map = str.maketrans("123","abc")
>>> s = "123456"
>>> print(s.translate(map))
abc456
>>> t=bytes.maketrans(b'abc',b'ABC')
>>> print (b'abc132'.translate(t,b"123")) #删除123
b'ABC'
编码解码
>>> "中国".encode("gbk")
b'\xd6\xd0\xb9\xfa'
>>> "中国".encode("gbk").decode("gbk")
'中国'
>>> "中国".encode("gbk").decode("utf-8")
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
UnicodeDecodeError: 'utf-8' codec can't decode byte 0xd6 in position 0: invalid
continuation byte
>>> import chardet
>>> chardet.detect("中国人呼呼呼呼发斯蒂芬斯蒂芬但是水电费呼呼呼呼".encode("gbk"))
{'encoding': 'GB2312', 'confidence': 0.99, 'language': 'Chinese'}
>>>
Base64编码解码
>>> import base64
>>> encodestr = base64.b64encode(b'I love you')
>>> print(encodestr)
b'SSBsb3ZlIHlvdQ=='
>>> print(base64.b64decode(encodestr))
b'I love you'
判断类型
>>> isinstance("a",str)
True
>>> isinstance(b"a",str)
False
>>> isinstance(b"a",bytes)
True
>>> isinstance(b"a",(str,bytes)) #是否是类的实例
True
Ord 和 Chr
>>> ord("问")
38382
>>> chr(38382)
'问'
Count
>>> "aaa".count("a")
3
>>> "aaa".count("a",2)
1
>>> "aaa".count("a",1,2)
1


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号