第15次全天课笔记 20181104 面向对象编程
全天课笔记 20181104
第一道题,写一个包,里面实现一个模块
模块里面有个类,类有两个实例方法,一个方法可以统计某个路径文件的英文个数,一个是统计空白字符个数,再实现以下调用类的逻辑。
//string_count.py的内容
class Count(object): def __init__(self,file_path): self.file_path =file_path #file_path 是实例变量 def count_letter_num(self): letter_num = 0 try: with open(self.file_path,encoding="utf-8") as fp: for line in fp: for letter in line: if (letter >="a" and letter <="z") or (letter >="A" and letter <="Z"): letter_num +=1 return letter_num except IOError as e: print(e) return None def count_space_num(self): space_num = 0 try: with open(self.file_path,encoding="utf-8") as fp: for line in fp: for letter in line: if letter.isspace(): space_num +=1 return space_num except IOError as e: print(e) return None
调用的实现
//a.py
import count.string_count #包名.模块名
file1 = count.string_count.Count("D:\\up\\0826\\test1.py") #包名.模块名.类名
print(file1.count_letter_num())
print(file1.count_space_num())
第二题: 统计一下两个句子中不重复单词数量,并列出哪些单词出现了重复值
import string s1 = "I am a boy, good boy!" s2 = "I am not a boy, good girl" for i in string.punctuation: s1 = s1.replace(i," ") s2 = s2.replace(i," ") wordlist1 = set(s1.split()) wordlist2 = set(s2.split()) print(wordlist1) print(wordlist2) print(list(wordlist1^wordlist2)) print(len(list(wordlist1^wordlist2))) #使用异或,不相同的 print(list(wordlist1&wordlist2)) #使用并集 print(len(list(wordlist1&wordlist2)))
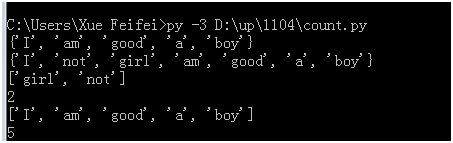
Subscriptable 切片
>>> class P:
... def print_info():pass #实例方法必须有self
... def print_str(self):
... print("P")
...
>>> p=P()
>>> p.print_info()
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: print_info() takes 0 positional arguments but 1 was given #因为self
>>> p.print_str()
P
>>> class P:
... def print_str(self):
... print("P")
... def func(self):
... self.print_str() #实例方法是互相可以调用的
...
>>> p=P()
>>> p.func()
P
实现加减乘除方法
class ComputeTwoNumbers(object): def __init__(self,a,b): self.a = a self.b = b def sum(self): return self.a + self.b def sub(self): return self.a - self.b def mul(self): return self.a * self.b def div(self): return self.a /self.b jisuan = ComputeTwoNumbers(3,5) print(jisuan.sum()) print(jisuan.sub()) print(jisuan.mul()) print(jisuan.div())
类成员
方法:普通方法、类方法、静态方法
类方法
>>> class P:
... @classmethod #装饰器
... def print_str(cls,content): #cls必须的
... print(content)
...
>>> P.print_str("hello") #类直接调用可以
hello
>>> p=P()
>>> p.print_str("hi") #实例化之后调用也可以
hi
面试准备:
1. 功能准备
所有用例的设计方法,测试框架,bug预防,探索式测试
2. 编程
算法:冒泡、快排、二分查找法、链表、二叉树的深度遍历和广度遍历、递归
字符串相关的面试题
3. Http协议
Get和post区别,http和https的区别,http的各种状态码,http请求或者响应包的一些机构:头、body
4. IOS七层模型
Ip tcp http https
操作系统:线程和进程的区别,多进程,多线程,协程
5. 设计模式
单例模式,工厂模式,MVC模式
6. 原理: webdriver的原理,spring boot的原理,spring的原理
Jvm的理解: 内容泄露和内存溢出,垃圾回收,虚拟机的一些区
7.Linux:
常见的30命令,看cpu、内存、IO、日志、看网络
Linux安装软件: rpm和源码
Shell编程,awk,sed
8. 数据库
Sql:多表查询、子查询、更新,索引的知识,慢查询:slow query
执行计划,存储引擎的特点,行锁,表锁
9. 架构
公司的产品架构怎么实现
10.自动化
设计模式:数据驱动,关键字驱动,混合驱动
元素+动作+操作值
11.性能
12.安全
13. 价值和软技能:项目贡献,学习能力,表达能力,主动性,流程的优化和改进,质量度量
静态方法
>>> class P:
... @staticmethod #staticmethod 静态方法
... def print_str(content):
... print(content)
...
>>> P.print_str("hi") #类直接调用
hi
>>> p=P() #实例方法也可以调用
>>> p.print_str("hello")
Hello
普通方法:由对象调用,至少一个self参数,执行时自动将调用该方法的对象赋值给self
类方法:由类调用,至少一个cls参数,执行时自动将调用该方法的类赋值给cls
静态方法:由类调用,无默认参数
class ComputeTwoNumbers(object): count = 0 #类变量 def __init__(self,a,b): #构造函数 self.a = a self.b = b def sum(self): #实例方法 ComputeTwoNumbers.count+=1 return self.a + self.b @classmethod def sub(cls,a,b): #类方法 ComputeTwoNumbers.count+=1 return a-b @staticmethod #静态方法 def mul(a,b): ComputeTwoNumbers.count+=1 return a*b def div(self): ComputeTwoNumbers.count+=1 return self.a /self.b jisuan = ComputeTwoNumbers(3,5) print(jisuan.sum()) print(jisuan.div()) #print(jisuan.sub(5,2)) print(ComputeTwoNumbers.sub(5,2)) print(jisuan.mul(5,5)) print(ComputeTwoNumbers.mul(5,5)) print(ComputeTwoNumbers.count)
@property 的使用
class Foo:
def __init__(self,value):
self.value = value
def func(self):
print("func!")
@property
def prop(self):
return self.value*123
foo_obj = Foo(100)
foo_obj.func()
print(foo_obj.prop) #调用属性,不用加括号
C:\Users\Xue Feifei>py -3 D:\up\1104\a.py
func!
12300
class Goods(object):
def __init__(self):
self.value = 1
@property #动态生成属性值
def price(self):
print("######@property")
return self.value
@price.setter #设定赋值的规则
def price(self,value):
self.value = value
print("@price.setter")
@price.deleter #做清理
def price(self):
del self.value
print("@price.deleter")
obj = Goods()
print(obj.price)
obj.price = 123
print(obj.price)
del obj.price
print(obj.price)
私有变量 __value 加两个下划线
使用函数添加、删除、修改、访问类属性
可以使用以下函数来操作对象的属性:
1、getattr(obj, name[, default]) : 访问对象的属性,如果存在返回对象属性的值,
否则抛出AttributeError异常。
2、hasattr(obj,name) : 检查是否存在某个属性,存在返回True,否则返回False。
3、setattr(obj,name,value) : 设置一个属性。如果属性不存在,会创建一个新属
性,该函数无返回值。若存在则更新这个值
4、delattr(obj, name) : 删除属性,如果属性不存在则抛出AttributeError异常,
该函数也无返回值。
>>> class P:
... def __init__(self,gender):
... self.gender = gender
... def get_gender(self):
... print(self.gender)
...
>>> p=P("Female")
>>> p.gender #获取属性值
'Female'
>>> getattr(p,"gender") #获取属性值
'Female'
>>> getattr(p,"gender1") #当属性值没有的时候,抛出AttributeError异常
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
AttributeError: 'P' object has no attribute 'gender1'
>>> getattr(p,"gender1","hello") #可以返回一个默认值,并不是赋值
'hello'
>>> setattr(p,"salary",100) #设置属性
>>> getattr(p,"salary")
100
>>> delattr(p,"salary")
>>> p.salary
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
AttributeError: 'P' object has no attribute 'salary'
Python内置类属性
Python有如下内置的类属性:
__dict__ : 类的属性(包含一个字典,由类的数据属性组成)
__doc__ :类的文档字符串,也就是类的帮助信息。
__name__: 类名
__module__: 类定义所在的模块(类的全名是’__main__’,如果类位于一个
导入模块mymod中,那么className.__module__ 等于 mymod)
__bases__ : 类的所有父类(包含了所有父类组成的元组)
>>> class P:
... a=100
... def __init__(self,value):
... self.value = value
... def print_str(self):
... print(self.value)
...
>>> p =P(30)
>>> P.__dict__ #类
mappingproxy({'__module__': '__main__', 'a': 100, '__init__': <function P.__init
__ at 0x00000000024DA9D8>, 'print_str': <function P.print_str at 0x00000000024DA
AE8>, '__dict__': <attribute '__dict__' of 'P' objects>, '__weakref__': <attribu
te '__weakref__' of 'P' objects>, '__doc__': None})
>>> p.__dict__ #实例对象
{'value': 30}
>>> P.__name__
'P'
>>> P.__module__
'__main__'
>>> import os
>>> os.getcwd() #获取当前工作路径
'C:\\Users\\Xue Feifei'
>>> P.__base__
<class 'object'>
类的私有属性
class Person(object):
__secretCount = 0
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
self.__inName = "ads"
def visit_private_attribute(self):
Person.__secretCount += 1
print("__secretCount:",Person.__secretCount)
print("__inName:",self.__inName)
p=Person("perl")
p.visit_private_attribute()
print("在类外直接通过实例访问私有属性")
print(p.__inName)
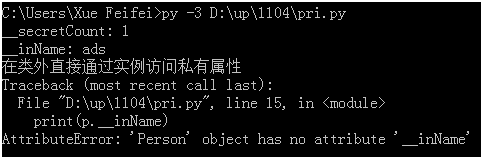
虽然Python不允许实例化的类从外部访问私有数据,但我们可以使用 object._className__attrName 访问私有属性
可以使用如下方法访问私有属性
class Person(object):
__secretCount = 0
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
self.__inName = "ads"
def visit_private_attribute(self):
Person.__secretCount += 1
print("__secretCount:",Person.__secretCount)
print("__inName:",self.__inName)
p=Person("perl")
p.visit_private_attribute()
print("使用另外一种方法访问私有属性")
print(p._Person__secretCount) #一个下划线+类名+两个下划线+私有变量
print(p._Person__inName)
私有方法
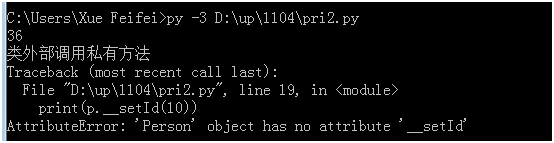
类中方法名前面有两个下划线,表示是Python中的私有方法,类似于java中的private,不能在类外部调用(如__setId()),在类内部调用语法: self.__private_methods。
class Person(object): id = 12 #类静态成员在这儿定义,注意缩进 def __init__(self,name): self.name = name self.__inName = "ads" def __setId(self,id): #隐藏方法 Person.id = id * 2 def getId(self): self.__setId(18) #类内部调用隐藏方法 return Person.id p = Person("prel") print(p.getId()) print("类外部调用私有方法") print(p.__setId(10))
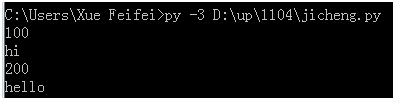
继承
class P(object):
a = 100
def print_str(self,content):
print(content)
class Q(P):
b = 200
def print_content(self,content):
print(content)
q= Q()
print(q.a)
q.print_str("hi")
print(q.b)
q.print_content("hello")
class Bird(object):
def __init__(self,name,sound):
self.name = name
self.sound = sound
def get_name(self):
print(self.name)
def get_sound(self):
print(self.sound)
class Seagull(Bird):
def __init__(self,name,sound,location):
Bird.__init__(self,name,sound) #需要将父类写一下
self.location = location
def get_location(self):
print(self.location)
s = Seagull("huahua","gugu","qingdao")
s.get_name()
s.get_sound()
s.get_location()
子类调用父类的方法有两种:
- Parent.parentMethod(self)
- Self.parentMethod()
调用父类的_init__方法:(一般用第二种方法)
1、super(subclassName, self).__init__( [parameter1[,parameter2....]])
2、superclassName.__init__(self, [parameter1[,parameter2....]])



