课后习题
现在要开发一个系统,管理对多种汽车的收费工作。
给出下面的一个基类框架
class Vehicle
{
protected:
string NO;
public:
Vehicle(string n){
NO = n;
}
virtual int fee()=0;//计算应收费用
};
以Vehicle为基类,构建出Car、Truck和Bus三个类。
Car的收费公式为: 载客数*8+重量*2
Truck的收费公式为:重量*5
Bus的收费公式为: 载客数*3
生成上述类并编写主函数
主函数根据输入的信息,相应建立Car,Truck或Bus类对象,对于Car给出载客数和重量,Truck给出重量,Bus给出载客数。假设载客数和重量均为整数
输入格式:第一行输入测试用例数。接着每个测试用例占一行,每行给出汽车的基本信息,第一个数据为当前汽车的类型:1为car,2为Truck,3为Bus。第二个数据为它的编号,接下来Car是载客数和重量,Truck要求输入重量,Bus要求输入载客数。
要求输出各车的编号和收费。
设计思路:
1.设计一个基类Vechile。
2.由基类衍生出子类Car,Truck,Bus.Car构造函数包括载客数和重量,Truck的构造函数包括重量,Bus的构造函数包括载客数。
3.在Car中返回载客数*8+重量*2,在Truck中返回重量*5,在Bus中返回载客数*3

代码实现:
#include<iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; class Vehicle { protected: string NO;//编号 public: Vehicle(string n) { NO = n; } virtual int fee() = 0;//计算应收费用 }; class Car :public Vehicle { private: int guest, weight; public: Car(string a, int b, int c) :Vehicle(a) { guest = b; weight = c; } virtual int fee() { return guest * 8 + weight * 2; } }; class Truck :public Vehicle { private: int weight; public: Truck(string a, int c) :Vehicle(a) { weight = c; } virtual int fee() { return weight * 5; } }; class Bus :public Vehicle { private: int guest; public: Bus(string a, int b) :Vehicle(a) { guest = b; } virtual int fee() { return guest * 3; } }; int main() { Car c("", 0, 0); Truck t("", 0); Bus b("", 0); int i, repeat, ty, weight, guest; string no; cin >> repeat; for (i = 0; i < repeat; i++) { cin >> ty >> no; switch (ty) { case 1: cin >> guest >> weight; c = Car(no, guest, weight); cout << no << ' ' << c.fee() << endl; break; case 2: cin >> weight; t = Truck(no, weight); cout << no << ' ' << t.fee() << endl; break; case 3: cin >> guest; b = Bus(no, guest); cout << no << ' ' << b.fee() << endl; break; } } return 0; }
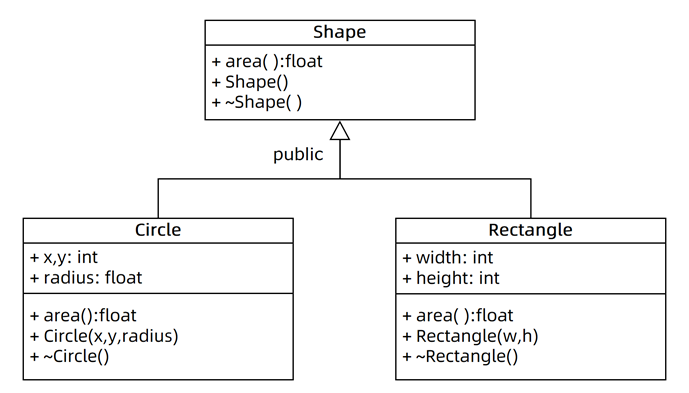
请结合如图所示的继承关系设计Shape、Circle以及Rectangle类,使得下述代码可以正确计算并输出矩形和圆的面积。
提升:Shape的析构以及area()函数都应为虚函数。
设计思路:1.设计一个基类Shape包括空构造函数和析构函数和area函数。
2.由基类衍生出子类Circle,Rectangle.Circle构造函数包括构造函数(xyradius)析构函数和返回area的函数π*radius*radius,Rectangle的构造函数包括wh,析构函数和area(w*h)
![]()
代码实现:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; class Shape { private: public: Shape() { } ~Shape() {} virtual float area() = 0; }; class Circle :public Shape { private: int x, y; float radius; public: Circle(int c, int d, float b) { radius = b; x = c; y = d; } virtual float area() { return 3.1415 * radius * radius; } }; class Rectangle :public Shape { private: int x, y; public: Rectangle(int c, int d) { x = c; y = d; } virtual float area() { return x * y; } }; int main() { Shape* shapes[2]; int w, h; cin >> w >> h; //输入矩形的长宽 shapes[0] = new Rectangle(w, h); float r; //输入圆的半径 cin >> r; shapes[1] = new Circle(0, 0, 2); //圆心在(0,0),半径为r的圆 printf("Area of rectangle:%.2f\n", shapes[0]->area()); printf("Area of circle:%.2f\n", shapes[1]->area()); for (auto i = 0; i < 2; i++) delete shapes[i]; return 0; }
如本章开篇所述,当小学里的上课铃响之后,学生(Student)、教师(Teacher)和校长(Principal)会对同一个消息表现出不同的行为。请设计Person、Student、Teacher以及Principal类,合理安排他们之间的继承关系并将所有类的bellRing()及析构函数设计为虚函数,使得下述代码可以正常执行并产生期望的执行结果。
设计思路:
1.基类Person包括虚析构函数和虚bellRing函数。
2设计子类Student,teacherPrincipal类包括虚析构函数和虚bellRing函数。其中输出内容不同。

#include <iostream> using namespace std; class Person { public: virtual void bellRing() { } virtual ~Person() { } }; class Student :public Person { public: virtual void bellRing() { cout << "I am a student learning in classroom." << endl; } virtual ~Student() { cout << "A student object destroyed." << endl; } }; class Teacher :public Person { public: virtual void bellRing() { cout << "I am a teacher teaching in classroom." << endl; } virtual ~Teacher() { cout << "A teacher object destroyed." << endl; } }; class Principal :public Person { public: virtual void bellRing() { cout << "I am the principal inspecting in campus." << endl; } virtual ~Principal() { cout << "A principal object destroyed."; } }; int main() { cout << "School bell rings..." << endl; Person* persons[3] = { new Student(),new Teacher(),new Principal() }; persons[0]->bellRing(); persons[1]->bellRing(); persons[2]->bellRing(); for (auto i = 0; i < 3; i++) delete persons[i]; return 0; }






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 全程不用写代码,我用AI程序员写了一个飞机大战
· MongoDB 8.0这个新功能碉堡了,比商业数据库还牛
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」
· 白话解读 Dapr 1.15:你的「微服务管家」又秀新绝活了