算法: skiplist 跳跃表代码实现和原理
SkipList在leveldb以及lucence中都广为使用,是比较高效的数据结构。由于它的代码以及原理实现的简单性,更为人们所接受。
所有操作均从上向下逐层查找,越上层一次next操作跨度越大。其实现是典型的空间换时间。
Skip lists are data structures that use probabilistic balancing rather than strictly enforced balancing.
As a result, the algorithms for insertion and deletion in skip lists are much simpler and significantly
faster than equivalent algorithms for balanced trees.
后面的图片来自:http://www.cnblogs.com/xuqiang/archive/2011/05/22/2053516.html
后面的代码当然是我自己写的呀。
(1)SkipList图示
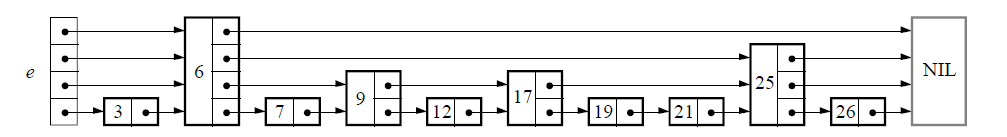
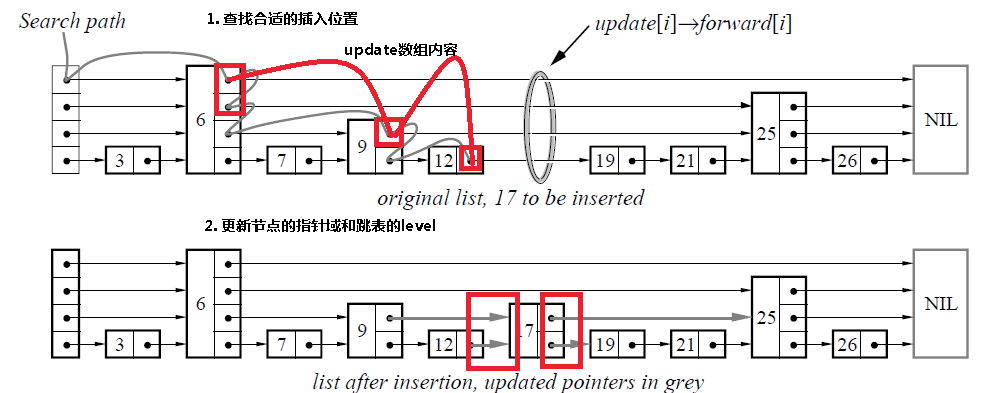
(2)SkipList插入
(3)SkipList删除

(3)SkipList查找
查找操作也是上面的套路
实现中主要有几点需要注意:
(1) 如何支持各种数据类型的数据。 通用的做法就是 char数组保存value + char数组对应value的长度。
(2) 看图中,每个节点有多个指向不同层级的指针。代码中可以使用指针数组 + 节点的level来保存。
(3) 查找、插入、删除操作,都要找到(或者经过)需要操作点的前驱节点。这个操作可以封装起来,极大减少代码量。
(4) skiplist整体是一个链表, 设置一个头节点方便后续的各种操作。
数据结构如下:
1 truct SkipNode{ 2 int key; //key 3 char *value; //value,可以支持任意类型 4 int length; //value_length, 记录数据长度 5 int level; //保存当前节点的level 6 SkipNode** next; //记录各层后续的地址 7 };
skiplist.h
class SkipList{ public: SkipList(int level = 10); ~SkipList(); //根据key获取数据 int get(const int key, char* value, int &length); //链表插入新节点 int insert( const int key, const char* value, const int length); //删除key对应节点 int del(const int key); private: //初始化链表头, 路过链表 int init(); //空间释放 int deinit(); //新建一个节点 SkipNode* createNode( const int key, const char* value, const int &length, const int level); //所用随机函数获取一个level值, 用于后续新建节点使用 int getNewNodeLevel(); //init update node int init_updatenode(); //get node pre(get update) int get_update(const int key); //记录skiplist支持的最大level, 以及当前高度 int max_level; int curr_level; SkipNode* List; //skiplist 第一个节点 SkipNode** Update; //记录每层搜索节点的前驱节点 };
cpp代码比较长,这里就不贴了。



