源代码:
package javaio;
import java.io.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
public class FIleWrite_ReaderTest extends JFrame {
private JScrollPane scrollPane;
private static final long serialVersionUID=1L;
private JPanel jContentPane = null;
private JTextArea jTextArea = null;
private JPanel controlPanel = null;
private JButton openButton = null;
private JButton closeButton = null;
private JTextArea getJTextArea() {
if (jTextArea == null) {
jTextArea = new JTextArea();
}
return jTextArea;
}
private JPanel getControlPanel() {
if (controlPanel == null) {
FlowLayout flowLayout = new FlowLayout();
flowLayout.setVgap(1);
controlPanel = new JPanel();
controlPanel.setLayout(flowLayout);
controlPanel.add(getOpenButton(), null);
controlPanel.add(getCloseButton(), null);
}
return controlPanel;
}
private JButton getOpenButton() {
if(openButton == null) {
openButton = new JButton();
openButton.setText("写入文件");
openButton.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
File file = new File("F:/test/file.txt");
try {
FileWriter out = new FileWriter(file);
String s = jTextArea.getText();
out.write(s);
out.close();
}catch(Exception e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
return openButton;
}
private JButton getCloseButton() {
if(closeButton == null) {
closeButton = new JButton();
closeButton.setText("读取文件");
closeButton.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
File file = new File("F:/test/file.txt");
try {
FileReader in = new FileReader(file);
char byt[] = new char[1024];
int len = in.read(byt);
jTextArea.setText(new String(byt,0,len));
in.close();
}catch(Exception e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
return closeButton;
}
public FIleWrite_ReaderTest() {
super();
initialize();
}
private void initialize() {
this.setSize(700,500);
this.setContentPane(getJContentPane());
this.setTitle("JFrame");
}
private JPanel getJContentPane() {
if(jContentPane == null) {
jContentPane = new JPanel();
jContentPane.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
jContentPane.add(getJTextArea(),BorderLayout.CENTER);
jContentPane.add(getControlPanel(),BorderLayout.SOUTH);
}
return jContentPane;
}
public static void main(String args[] ) {
FIleWrite_ReaderTest thisClass = new FIleWrite_ReaderTest();
thisClass.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
thisClass.setVisible(true);
}
protected JScrollPane getScrollPane() {
if (scrollPane == null) {
scrollPane = new JScrollPane();
scrollPane.setViewportView(getJTextArea());
}
return scrollPane;
}
}
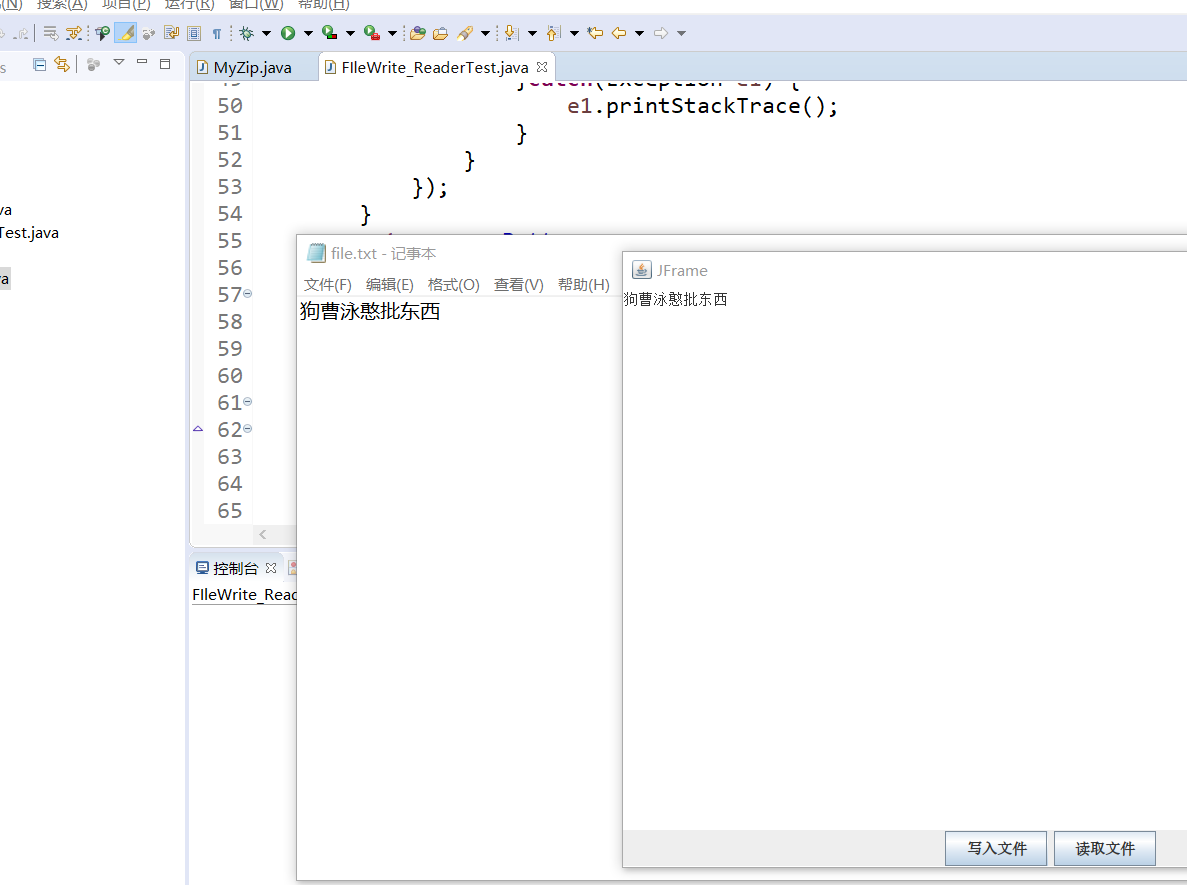
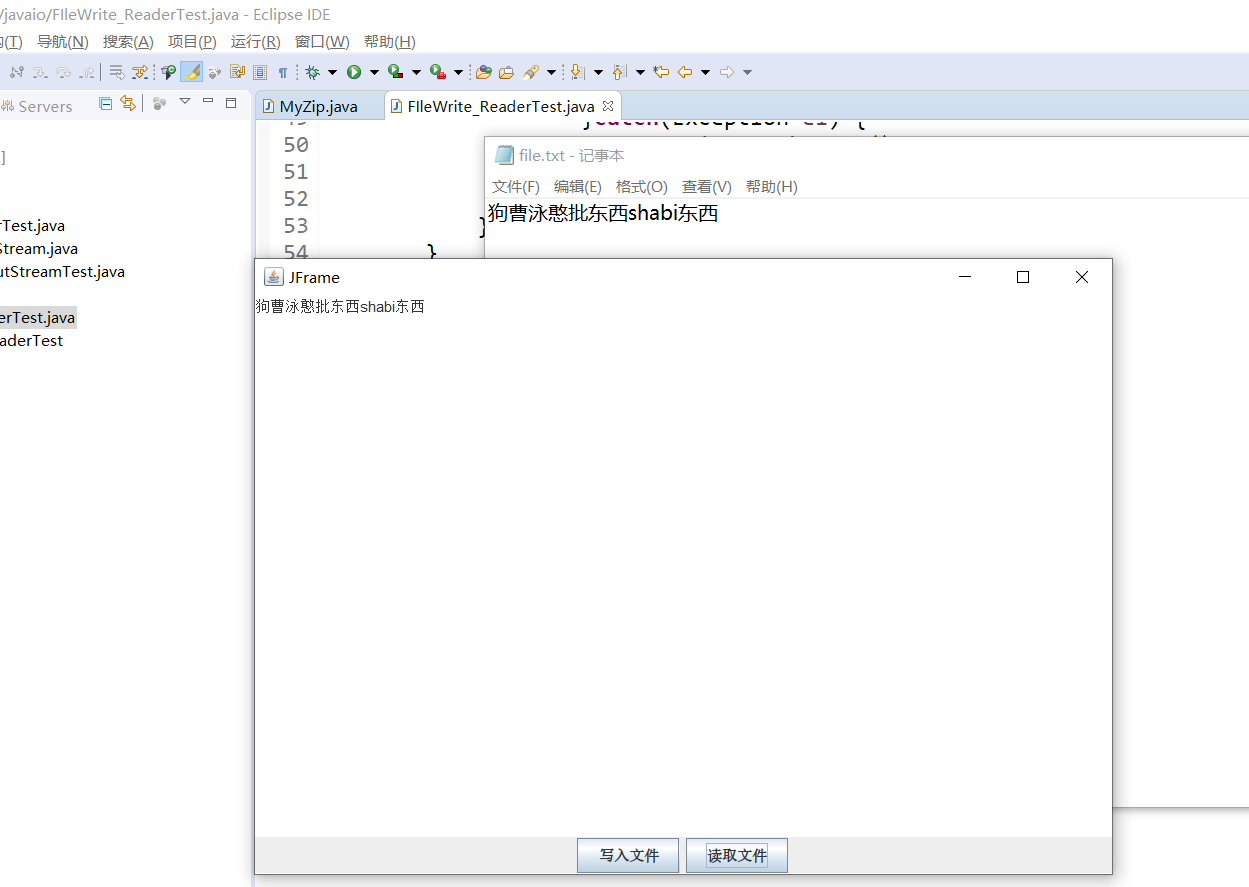
运行截图:
- Swing简介
Swing 是 Java 为图形界面应用开发提供的一组工具包,是 Java 基础类的一部分。
Swing 包含了构建图形界面(GUI)的各种组件,如: 窗口、标签、按钮、文本框等。
Swing 提供了许多比 AWT 更好的屏幕显示元素,使用纯 Java 实现,能够更好的兼容跨平台运行。
为了和 AWT 组件区分,Swing 组件在javax.swing.*包下,类名均以 J 开头,例如: JFrame、JLabel、JButton等。
- Swing组件
一个 Java 的图形界面,由各种不同类型的“元素”组成,例如: 窗口、菜单栏、对话框、标签、按钮、文本框等等,这些“元素”统一被称为 组件(Component)。
组件按照不同的功能,可分为 顶层容器、中间容器、基本组件。一个简单窗口的组成,如下层级结构所示:
顶层容器
菜单栏
中间容器
基本组件
基本组件
组件类型的继承关系:
顶层容器 属于窗口类组件,继承自java.awt.Window;
中间容器 和 基本组件 继承自javax.swing.JComponent。
(1)顶层容器
顶层容器属于窗口类组件,可以独立显示,一个图形界面至少需要一个窗口,例如:
| 内容 | 组件 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | JFrame | 一个普通的窗口(绝大多数 Swing 图形界面程序使用 JFrame 作为顶层容器) |
| 2 | JDialog | 对话框 |
(2)中间容器
中间容器充当基本组件的载体,不可独立显示。中间容器可以添加若干基本组件(也可以嵌套添加中间容器),对容器内的组件进行管理,类似于给各种复杂的组件进行分组管理。最顶层的一个中间容器必须依托在顶层容器(窗口)内。
常用的中间容器(面板):
| 内容 | 组件 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | JPanel | 一般轻量级面板容器组件 |
| 2 | JScrollPane | 带滚动条的,可以水平和垂直滚动的面板组件 |
| 3 | JSplitPane | 分隔面板 |
| 4 | JTabbedPane | 选项卡面板 |
| 5 | JLayeredPane | 层级面板 |
特殊的中间容器:
| 内容 | 组件 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | JMenuBar | 菜单栏 |
| 2 | JToolBar | 工具栏 |
| 3 | JPopupMenu | 弹出菜单 |
| 4 | JInternalFrame | 内部窗口 |
(3)基本组件
基本组件是直接实现人机交互的组件。
常用的简单的基本组件:
| 内容 | 组件 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | JLabel | 标签 |
| 2 | JButton | 按钮 |
| 3 | JRadioButton | 单选按钮 |
| 4 | JCheckBox | 复选框 |
| 5 | JToggleButton | 开关按钮 |
| 6 | JTextField | 文本框 |
| 7 | JPasswordField | 密码框 |
| 8 | JTextArea | 文本区域 |
| 9 | JComboBox | 下拉列表框 |
| 10 | JList | 列表 |
| 11 | JProgressBar | 进度条 |
| 12 | JSlider | 滑块 |
选取器组件:
| 内容 | 组件 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | JFileChooser | 文件选取器 |
| 2 | JColorChooser | 颜色选取器 |
其他较为复杂的基本组件:
| 内容 | 组件 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | JTable | 表格 |
| 2 | JTree | 树 |
- 布局管理器
把 Swing 的各种组件(JComponent)添加到面板容器中(JPanel),需要给面板容器指定布局管理器(LayoutManager),明确容器(Container)内的各个组件之间的排列布局方式。
常用的布局管理器:
| 内容 | 布局管理器 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | FlowLayout | 流式布局,按组件加入的顺序,按水平方向排列,排满一行换下一行继续排列。 |
| 2 | GridLayout | 网格布局,把Container按指定行列数分隔出若干网格,每一个网格按顺序放置一个控件。 |
| 3 | GridBagLayout | 网格袋布局,按网格划分Container,每个组件可占用一个或多个网格,可将组件垂直、水平或沿它们的基线对齐。 |
| 4 | BoxLayout | 箱式布局,将Container中的多个组件按 水平 或 垂直 的方式排列。 |
| 5 | GroupLayout | 分组布局,将组件按层次分组(串行 或 并行),分别确定 组件组 在 水平 和 垂直 方向上的位置。 |
| 6 | CardLayout | 卡片布局,将Container中的每个组件看作一张卡片,一次只能显示一张卡片,默认显示第一张卡片。 |
| 7 | BorderLayout | 边界布局,把Container按方位分为 5 个区域(东、西、南、北、中),每个区域放置一个组件。 |
| 8 | SpringLayout | 弹性布局,通过定义组件四条边的坐标位置来实现布局。 |
| 9 | null | 绝对布局,通过设置组件在Container中的坐标位置来放置组件。 |
作者:xudo~
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/xudo/
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号