python学习笔记day08 文件功能详解
file.read():读取文件的全部内容
file=open("dang",mode='r+',encoding='utf-8') print(type(file.read())) #str对象 file.close()
read()函数中可以写参数,指定读取几个字符(字符:你能看到的文字最小组成单位)
file=open("dang",mode='r+',encoding='utf-8') print(file.read(6)) #str对象 只读取前六个字符 file.close()

file.seek():移动光标的位置,读取的是字节(utf-8 一个英文字符一个字节表示;一个中文字符用三个字节表示)
file=open("dang",mode='r+',encoding='utf-8') file.seek(6) #由于seek是按照字节读的,所以读取中文时seek中的参数必须是3的倍数,由于英文一个字符用一个字节表示,所以seek参数无所谓 print(file.read(5)) file.close()
运行结果:

需要注意:
read()函数以字符读取的,里面参数是几就代表需要读取几个字节;
seek()函数是以字节读的,如果文件中存储的都是中文,那么seek参数必须是3的倍数,因为utf-8一个中文字符用三个字节表示;如果文件存储的都是英文,那么seek参数无所谓了,因为一个英文字符只用一个字节表示;
file.tell() 告诉文件此时的光标在哪里,断点续传中有用;
file=open("dang",mode='r+',encoding='utf-8') file.seek(4) #因为文件存储的英文字符,seek()参数可以不是3倍数,一个英文字符用一个字节表示 print(file.tell()) #返回光标的位置 此时应该是4 因为上面光标移动到4了 # print(file.read(5)) file.close()

比如读取倒数第几个字符:
file=open("dang",mode='r+',encoding='utf-8') print(file.read()) #读完之后,光标定位在最后一个位置 index=file.tell() file.seek(index-6) #由于是英文字符,所以seek(index-6) 就是从倒数第六个字符开始读;如果是中文字符的话就是从倒数第二个字符开始读 print(file.read()) #从倒数第六个字符开始读,因为光标定位在倒数第六个字符;

readline():仅仅读取文件的一行--->str
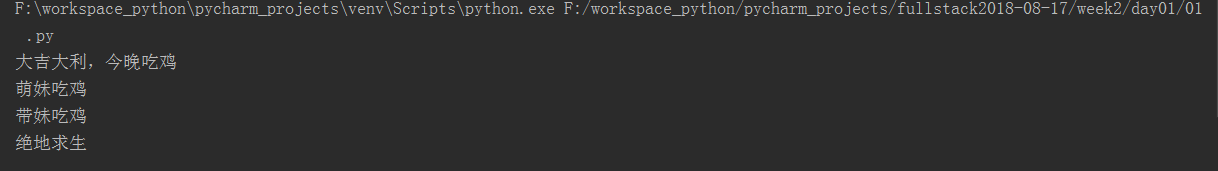
file=open("dang",mode='r',encoding='utf-8') line=file.readline() print(line) file.close()

我们也可以使用readline()函数一行一行读文件,迭代读取多行:
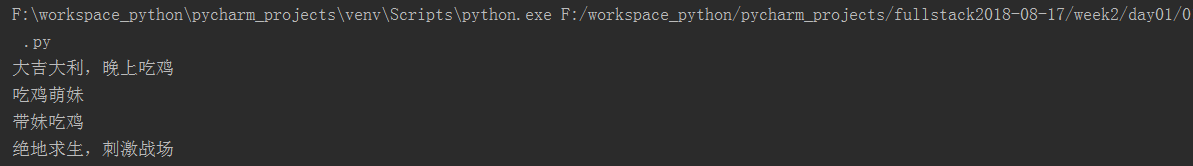
file=open("dang",mode='r',encoding='utf-8') for i in range(3): line=file.readline().split() #d读取每一行,然后split函数把尾部的换行符等去掉,把readline得到的str-->list print(line) file.close()
realdines():读取文件全部内容,存成一个list,文件每一行存成list的一个元素;
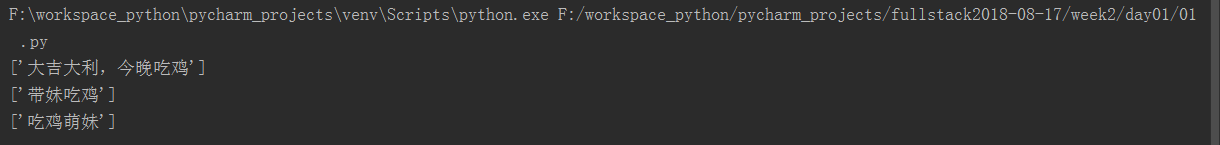
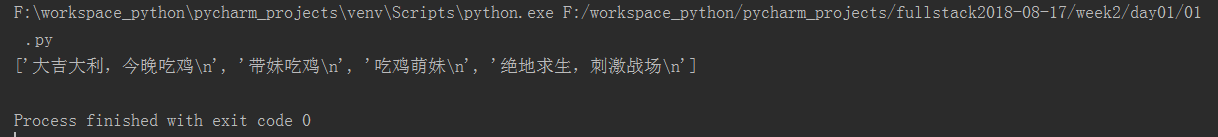
file=open("dang",mode='r+',encoding='utf-8') contents=file.readlines() #读取全部内容,每一行作为list的一个元素存储 print(contents) file.close()
文件操作的另外两个小知识点:
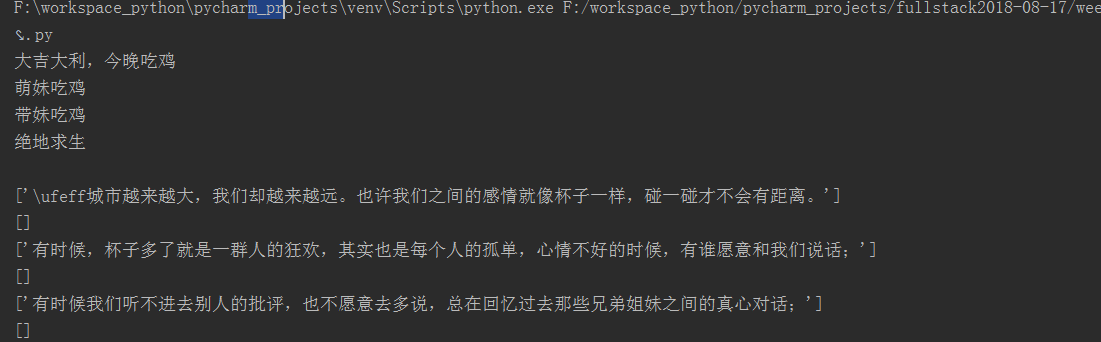
for line in file: 读取文件的全部内容一行一行;
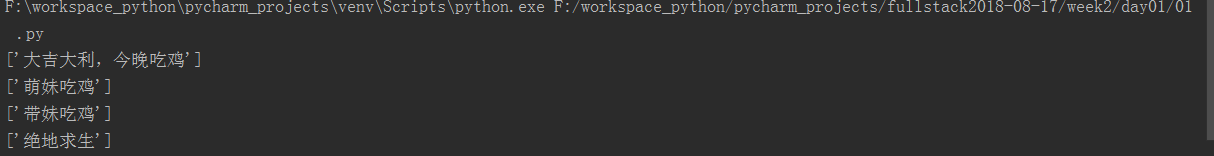
file=open('dang',mode='r',encoding='utf-8') for line in file: print(line.split()) file.close()
with open as 方式打开文件,不用对文件close
之前open()打开文件,最后都得file.close() 很麻烦,现在可以这样:
with open('dang',mode='r+',encoding='utf-8') as file: print(file.read()) #可以对文件file句柄进行其他操作
并且使用with open as 可以同时打开多个文件:
with open("dang",mode='r',encoding='utf-8') as file1,open('xixi.txt',mode='r+',encoding='utf-8') as file2: print(file1.read()) #读取文件dang 相对路径 for line in file2: #读取文件xixi.txt print(line.split())
talk is cheap,show me the code




