多线程
package cn.bdqn.test; /** * * 进程: 应用程序的执行实例!有自己独立的内存空间和系统资源! * 是由一个或者多个线程构成! cpu上真正执行的是线程! * 比喻: * 我们电脑上运行QQ! QQ程序启动后在电脑就是一个 进程! * QQ可以有多个对话框!每一个对话框,我们就可以理解成一个线程! * 线程: CPU调度和分派的基本单位! * * 多线程: * 如果在一个进程中,同时运行多个线程,来完成不同的工作,我们称之为 多线程! * 难道是cpu上同时执行多个线程吗? 不是! * 多个线程是交替占用CPU资源!并不是真正的同时执行! * 例子: * 01. 现在地铁有5个进站口! 有5个人 可以 同时(看着想同时)进站! * 02. 现在地铁有1个进站口! 有5个人 必须 排队 进站! * 问题? * 哪个效率高? 01效率高! * * 地铁 : CPU * 进站口:线程 * 多线程的好处: * 01.充分利用CPU的资源 * 02.给用户带来更好的体验 * */ public class MyThread { //主线程的入口! public static void main(String[] args) { //获取当前执行的线程 Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); System.out.println("当前线程的名称是:"+t.getName()); //更改线程的名称 t.setName("主线程"); System.out.println("当前线程的名称是:"+t.getName()); } }
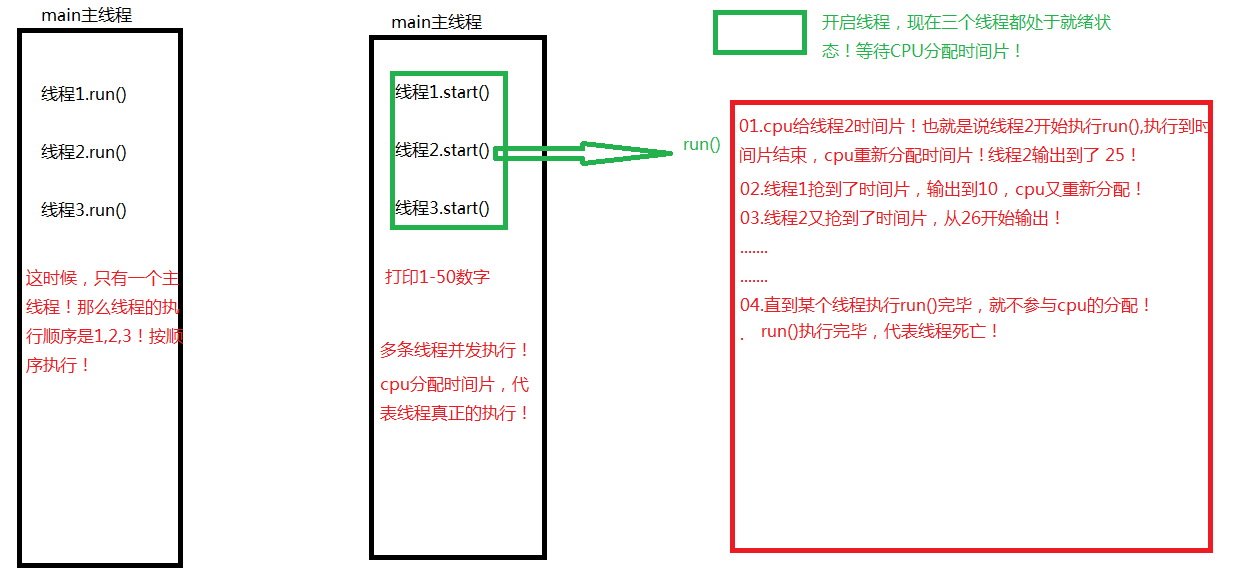
/** * * @author 小豆腐 * *实现多线程的方法: * 01.继承Thread类!重写run(); * 02.实现Runnable接口!重写 run(); * * * 并发: * 在操作系统系统中,在一个时间段中 有多个程序都处于已启动到运行完毕之间,并且这几个程序都处于一个处理器中运行, * 则在一个时间点,只能有一个程序在处理器上运行! * 当有多个线程在操作时,如果系统只有一个CPU,则它根本不可能真正同时进行一个以上的线程, * 它只能把CPU运行时间划分成若干个时间段,再将时间 段分配给各个线程执行, * 在一个时间段的线程代码运行时,其它线程处于挂起状。这种方式我们称之为并发(Concurrent)。 * * * run()和start()的区别 * * start():真正的启动线程!并不是线程真正的执行!在调用start(),底层默认会执行run()! * * run():普通的方法,也称为线程体!cpu分配时间片给当前线程的时候, 线程才真正的执行! * * 比喻: * 玩游戏==》 魂斗罗 * 现在只有一台电脑!很多人想玩? * * 01.报名 * 02.排队 * 03.上机 (肯定是一个人在玩游戏) 执行run(); * 04.特殊情况 (两个人发生争执) * 05.游戏结束 * * 线程的生命周期 * 01.新生状态 * MyThread thread=new MyThread(); * 02.就绪状态 * thread.start(); * 03.运行状态 * cpu分配时间片给thread的时候,开始运行run() * 04.阻塞状态 * sleep();wait();join() * 05.死亡状态 * 001.正常 run()执行完毕 正常的! * 002.异常 run()执行过程中,出现异常的情况,非正常退出! * * */ public class MyThread extends Thread { //重写run() @Override public void run() { for (int i = 1; i <=50; i++) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"==="+i); } } //多个线程并发执行 public static void main(String[] args) { //创建线程对象1 MyThread thread1=new MyThread(); //创建线程对象2 MyThread thread2=new MyThread(); //启动线程1 thread1.start(); //启动线程2 thread2.start(); } /** public static void main(String[] args) { //只有一个主线程 main //创建线程对象1 MyThread thread1=new MyThread(); //创建线程对象2 MyThread thread2=new MyThread(); //调用thread类中的run()不是启动线程 thread1.run(); //调用thread2类中的run()不是启动线程 thread2.run(); }*/ }
/** * * @author 小豆腐 * 实现了Runnable接口 重写run() */ public class MyThread implements Runnable { //重写run() @Override public void run() { for (int i = 1; i <=50; i++) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"==="+i); } } public static void main(String[] args) { //创建线程对象 MyThread thread=new MyThread(); //通过Thread带参构造创建线程的实例 Thread runnable1 = new Thread(thread); Thread runnable2 = new Thread(thread); //开启线程 runnable1.start(); runnable2.start(); } }

/** * * @author 小豆腐 * 线程的状态 */ public class MyThread implements Runnable { //重写run() @Override public void run() { try { System.out.println("线程运行状态........"); System.out.println("线程阻塞状态........"); //让当前线程休息一下 ******* run()不允许声明异常 只能捕获***** Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("线程异常死亡........"); } System.out.println("线程正常死亡.........."); } public static void main(String[] args) { //通过Thread带参构造创建线程的实例 Thread t = new Thread(new MyThread()); System.out.println("线程新生状态........"); t.start(); System.out.println("线程就绪状态........"); } }
/** * * @author 小豆腐 * 线程的优先级 * 线程的优先级1--10 默认值 5 * 优先级越高代表获得cpu资源的概率大,概率大并不代表一定能拿到资源! */ public class MyThread implements Runnable { //重写run() @Override public void run() { for (int i = 1; i <=50; i++) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"==="+i); } } public static void main(String[] args) { //通过Thread带参构造创建线程的实例 Thread t1 = new Thread(new MyThread(),"线程A"); Thread t2 = new Thread(new MyThread(),"线程B"); System.out.println("t1默认的优先级:"+t1.getPriority()); System.out.println("t2默认的优先级:"+t2.getPriority()); //设置线程的优先级 MAX_PRIORITY=10 MIN_PRIORITY=1 t1.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY); t2.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY); System.out.println("设置之后的优先级==============="); System.out.println("t1默认的优先级:"+t1.getPriority()); System.out.println("t2默认的优先级:"+t2.getPriority()); //开启线程 t1.start(); t2.start(); } }
join的使用
/** * * @author 小豆腐 * 线程调度: * 按照特定的机制为多个线程分配CPU资源的使用权! * * 01.setPriority()设置线程的优先级 * 02.sleep()在指定的毫秒数内让当前正在执行的线程休眠 * 03.join() 等待该线程执行完毕 * 04.yield()礼让,暂停当前正在执行的线程,执行其他的线程 * 05.interrup()中断线程 * 06.isAlive()判断线程是否处于活动状态 */ public class MyThread implements Runnable { //重写run() @Override public void run() { for (int i = 1; i <=10; i++) { try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"===="+i); } } }
测试代码
public class JoinTest { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("=====join====="); Thread thread=new Thread(new MyThread(),"Join线程"); thread.start(); //启动线程 for (int i = 1; i <=20; i++) { if (i==5) { try { //阻塞主线程!Join线程强制执行 thread.join(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"===="+i); } } }
yield线程的礼让
/** * * @author 小豆腐 * 线程的礼让,也是一个概率问题 */ public class MyThread implements Runnable { //重写run() @Override public void run() { for (int i = 1; i <=50; i++) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"===="+i); if (i%3==0) { System.out.println("线程礼让....."); Thread.yield(); } } } }
测试类
public class YieldTest { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("=====yield====="); Thread t1=new Thread(new MyThread(),"线程A"); Thread t2=new Thread(new MyThread(),"线程B"); //启动线程 t1.start(); t2.start(); } }
/** * * @author 小豆腐 * 01.线程不安全的网络购票 * */ public class MyThread implements Runnable { private int count=10; //剩余的票数 private int num=0; //记录买到的第几张票 //重写run() @Override public void run() { while(true){ //没有票,跳出循环 if (count<=0) { break; } //01.修改数据 num++; count--; try { Thread.sleep(1000); //让cpu重新分配时间片 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } //02.显示信息 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread(). getName()+"抢到了第"+num+"张票====剩余的票数:"+count); } } }
/** * * @author 小豆腐 * 同步方法实现 ===》线程安全的网络购票 * */ public class MyThread implements Runnable { private int count=10; //剩余的票数 private int num=0; //记录买到的第几张票 private boolean flag=false; //给当前的方法加锁 public synchronized void sale(){ if (count<=0) { //票数少于0 flag=true; return; } //01.修改数据 num++; count--; try { Thread.sleep(1000); //让cpu重新分配时间片 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } //02.显示信息 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread(). getName()+"抢到了第"+num+"张票====剩余的票数:"+count); } //重写run() @Override public void run() { while(!flag){ sale(); } } }
/** * * @author 小豆腐 * 同步代码块实现 ====》线程安全的网络购票 * * * 多个并发线程访问同一个资源的同步代码块时: * 01.同一时刻只能有一个线程进入synchronized(this)代码块 * 02.当一个线程访问synchronized(this)同步代码块时;其他的synchronized(this) * 同步代码块也被锁定 * 03.当一个线程访问synchronized(this)同步代码块时;其他的线程可以访问该资源的 * 非synchronized(this)代码块 * */ public class MyThread implements Runnable { private int count=10; //剩余的票数 private int num=0; //记录买到的第几张票 //重写run() @Override public void run() { while(true){ /** * 同步代码块 * this:需要同步的对象,一般写成this */ synchronized (this) { //没有余票,退出循环 if (count<=0) { break; } num++; count--; try { Thread.sleep(1000); //让cpu重新分配时间片 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } //02.显示信息 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread(). getName()+"抢到了第"+num+"张票====剩余的票数:"+count); } } } }
public class SynchronizedTest { /** * 模拟三个人同时抢票 * * 多个线程在操作同一个共享的资源是,将引发数据不安全的问题! * 怎么解决这种不安全的问题??? * 使用synchronized修饰的方法或者代码块! * synchronized:就是为当前的线程声明一个锁! */ public static void main(String[] args) { MyThread thread=new MyThread(); Thread t1=new Thread(thread, "老黄牛"); Thread t2=new Thread(thread, "小白"); Thread t3=new Thread(thread, "小黑"); System.out.println("**************开始抢票******************"); t1.start(); t2.start(); t3.start(); } }
/** * *模拟10个特需号病人看病 */ public class MyThread implements Runnable { @Override public void run(){ for (int i = 1; i <=10; i++) { System.out.println("******特需号:"+i+"号在看病"); try { //看病时间是普通号的2倍 Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Thread t=new Thread(new MyThread()); //特需号的优先级比普通号高 t.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY); t.start(); //主线程模拟普通号看病 for (int i = 1; i <=20; i++) { System.out.println("普通号:"+i+"号在看病"); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } //普通号看到第10人时,特需号病人必须全部看完 if (i==10) { try { t.join(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
/** * 模拟多人400接力跑 * * 使用同步方法 * 多个线程访问同一个共享的资源! * */ public class MyThread implements Runnable { private int meters=400; //定义一共跑的米数 //同步方法 public synchronized void running(){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"拿到了接力棒!***********"); for (int i = 0; i < 100; i+=10) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"跑了"+(i+10)+"米"); try { Thread.sleep(100); //sleep没有释放锁 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } //更新路程 meters-=100; } @Override public void run(){ while(true){ if (meters<100) { break; } running(); //开始跑步 } } }
/** * 模拟多人400接力跑 * * 使用同步代码块 * 多个线程访问同一个共享的资源! * */ public class MyThread implements Runnable { private int meters=400; //定义一共跑的米数 @Override public void run(){ while(true){ synchronized (this) { //同步代码块 if (meters<100) { break; } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"拿到了接力棒!***********"); for (int i = 0; i < 100; i+=10) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"跑了"+(i+10)+"米"); try { Thread.sleep(100); //sleep没有释放锁 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } //更新路程 meters-=100; } } } }
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建线程对象 MyThread thread=new MyThread(); Thread t1=new Thread(thread, "1号选手"); Thread t2=new Thread(thread, "2号选手"); Thread t3=new Thread(thread, "3号选手"); Thread t4=new Thread(thread, "4号选手"); //开始跑步 t1.start(); t2.start(); t3.start(); t4.start(); } }
public class MyThread implements Runnable { private int index=0; //集合中的下标 private ArrayList<String> list=new ArrayList<String>(); @Override public void run(){ while(true){ if (index>100) { break; } list.add(index+""); System.out.println("下标:"+index+"的值是:=="+list.get(index)); index++; } } }
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建线程对象 MyThread thread=new MyThread(); //10个线程往集合中增加数据 for (int i = 0; i <10; i++) { new Thread(thread).start(); } } }
作者:Rick__想太多先森
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/xtdxs/
注意:本文仅代表个人理解和看法哟!和本人所在公司和团体无任何关系!



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号