Struts2自定义过滤器的小例子-入门篇
创建web项目 实现的效果! 用户点击页面不同的链接,后台调用不同的代码!
创建两个类实现共同的接口!
public interface Action {
String execute();
}
public class LoginAction implements Action{
public String execute(){
System.out.println("LoginAction......");
return "success";
}
}
public class ListAction implements Action {
public String execute(){
System.out.println("ListAction......");
return "success";
}
}
想让用户能访问到我们的后台代码,要么使用servlet 要么使用filter!
使用filter
创建一个filter用来拦截用户的请求
public class DoFilter implements Filter {
//全局的变量
Map<String,String> map=new HashMap<String, String>();
//初始化操作
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig arg0) throws ServletException {
System.out.println("DoFilter 初始化了.............................");
// key是用户请求的路径 value 是对应的全类名
map.put("/login","cn.bdqn.action.LoginAction");
map.put("/list","cn.bdqn.action.ListAction");
}
//真正的处理
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
//向下转型
HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest=(HttpServletRequest) request;
HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse=(HttpServletResponse) response;
//看一下 各个路径的区别
System.out.println("getContextPath()==>"+httpServletRequest.getContextPath());//项目名
System.out.println("getServletPath()==>"+httpServletRequest.getServletPath());//访问的路径
System.out.println("getRequestURI()==>"+httpServletRequest.getRequestURI());//项目下面的路径
System.out.println("getRequestURL()==>"+httpServletRequest.getRequestURL());//带协议的完整路径
//应该使用getServletPath
String path=httpServletRequest.getServletPath();
try {
if (path.equals("/index.jsp")) {
chain.doFilter(request, response); //放行
}else{
Action action=(Action) Class.forName(map.get(path)).newInstance();
action.execute();
//跳转到成功界面
httpServletRequest.getRequestDispatcher("/success.jsp").forward(request, response);
}
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
}
前台页面
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP 'index.jsp' starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
<a href="login">登录 </a>
<a href="list">详情 </a>
</body>
</html>
sucess.jsp页面就是一个成功界面!!!省略掉!
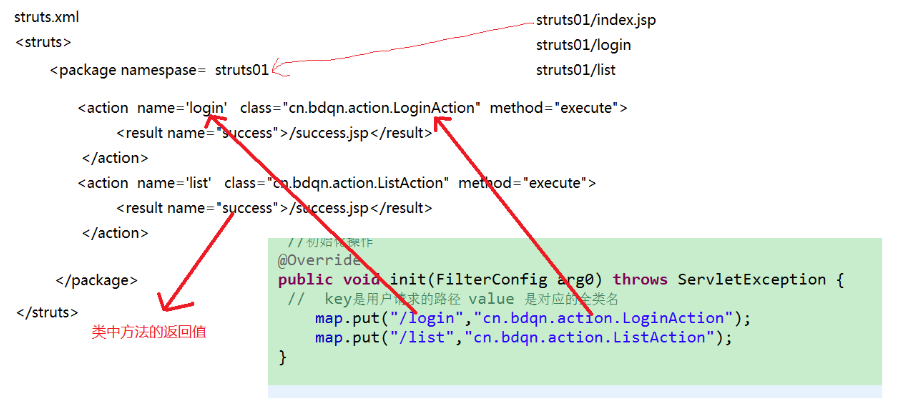
我们使用xml文件来代替 map中 所保存的 键值对 信息!
key:用户的请求
value:对应的后台实现类 全类名!
作者:Rick__想太多先森
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/xtdxs/
注意:本文仅代表个人理解和看法哟!和本人所在公司和团体无任何关系!




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号