期末大作业
# boston房价预测
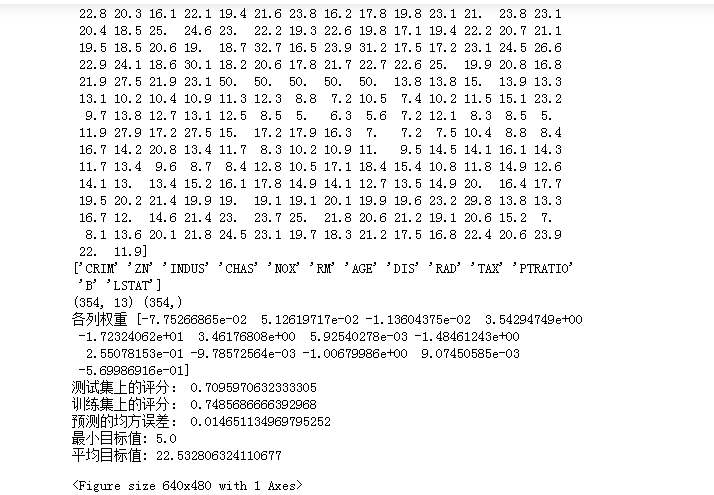
import numpy as np from sklearn.datasets import load_boston from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 读取数据集 boston = load_boston() print(boston.keys()) print(boston.target)# 房价数据 print(boston.feature_names) # 数据集特征 # 划分训练集与测试集 #随机擦痒25%的数据构建测试样本,剩余作为训练样本 X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(boston.data,boston.target,test_size=0.3) #random_state:是随机数的种子 print(X_train.shape,y_train.shape) # 建立模型 LineR = LinearRegression() LineR.fit(X_train,y_train) # 检查模型好坏 x_predict = LineR.predict(X_test) print("各列权重",LineR.coef_) print("测试集上的评分:",LineR.score(X_test, y_test)) print("训练集上的评分:",LineR.score(X_train, y_train)) print("预测的均方误差:", np.mean(x_predict - y_test)**2) print("最小目标值:",np.min(boston.target)) print("平均目标值:",np.mean(boston.target)) # 画图 X = boston.data[:,12].reshape(-1,1) y = boston.target plt.scatter(X,y) LineR2 = LinearRegression() LineR2.fit(X,y) y_predict = LineR2.predict(X) plt.plot(X,y_predict,'r') plt.show()
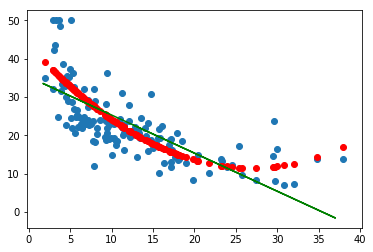
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 读取数据集 boston = load_boston() # 划分训练集与测试集 #随机擦痒25%的数据构建测试样本,剩余作为训练样本 x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(boston.data,boston.target,test_size=0.3) #random_state:是随机数的种子 x = x_train[:,12].reshape(-1,1) poly= PolynomialFeatures(degree=2) x_poly = poly.fit_transform(x) # 建立多项式回归模型 lrp = LinearRegression() lrp.fit(x_poly,y_train) lr = LinearRegression() lr.fit(x,y_train) w = lr.coef_ b = lr.intercept_ # 预测 x_poly2 = poly.transform(x_test[:, 12].reshape(-1,1)) y_ploy_predict = lrp.predict(x_poly2) # 画图 plt.scatter(x_test[:,12], y_test) plt.plot(x, w * x + b, 'g') plt.scatter(x_test[:,12], y_ploy_predict, c='r') plt.show()
#中文文本分类
#新闻文本分类
import os
import jieba
#读取文件内容
content=[]#存放新闻的内容
label=[]#存放新闻的类别
def read_txt(path):
folder_list=os.listdir(path)#遍历data下的文件名
for file in folder_list:
new_path=os.path.join(path,file) #读取文件夹的名称,生成新的路径
files=os.listdir(new_path)#存放文件的内容
#遍历每个txt文件
for f in files:
with open(os.path.join(new_path,f),'r',encoding='UTF-8')as f: #打开txt文件
temp_file=f.read()
content.append(processing(temp_file))
label.append(file)
#对数据进行预处理
with open(r'D:\stopsCN.txt', encoding='utf-8') as f:
stopwords = f.read().split('\n')
def processing(texts):
# 去掉非法的字符
texts = "".join([char for char in texts if char.isalpha()])
# 用jieba分词
texts = [text for text in jieba.cut(texts,cut_all=True) if len(text) >=2]
# 去掉停用词
texts = " ".join([text for text in texts if text not in stopwords])
return texts
if __name__== '__main__':
path=r'F:\258'
read_txt(path)
print('新闻内容:',content[0:1])
print('类别内容:',label[0:30])

#划分训练集和测试,用TF-IDF算法进行单词权值的计算
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
tfidf= TfidfVectorizer()
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(content,label,test_size=0.2)
X_train=tfidf.fit_transform(x_train)
X_test=tfidf.transform(x_test)
#构建贝叶斯模型
from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB #用于离散特征分类,文本分类单词统计,以出现的次数作为特征值
mulp=MultinomialNB ()
mulp_NB=mulp.fit(X_train,y_train)
#对模型进行预测
y_predict=mulp.predict(X_test)
# # 从sklearn.metrics里导入classification_report做分类的性能报告
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
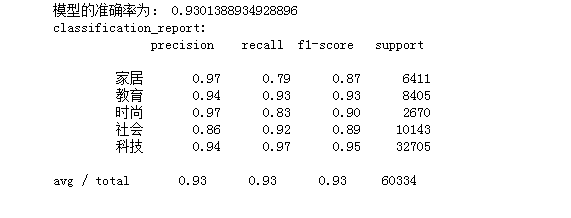
print('模型的准确率为:', mulp.score(X_test, y_test))
print('classification_report:\n',classification_report(y_test, y_predict))