参考、来源:http://www.cnblogs.com/Terrylee/archive/2006/04/13/374173.html
https://github.com/castleproject/ActiveRecord/blob/master/docs/validation-support.md
主要内容
1.概述
2.使用Validation
3.如何扩展
4.深入分析验证
一.概述
在录入数据时,对数据有效性的验证是必不可少的,很多时候我们在UI层上就会做一层验证,但有时也需要在底层做一些必要的处理,这就要用到ActiveRecord中的数据有效性的验证。ActiveRecord为我们提供了如下几个验证:
1.ValidateEmail
2.ValidateIsUnique
3.ValidateRegExp
4.ValidateNonEmpty
5.ValidateConfirmation
需要引入:using Castle.Components.Validator;
二.如何使用
为了使用上面这些验证,我们必须用ActiveRecordValidationBase来代替ActiveRecordBase,即实体类必须继承于ActiveRecordValidationBase。
1 2 | [ActiveRecord("Customs")]public class Custom : ActiveRecordValidationBase{ } |
ActiveRecordValidationBase类为我们提供了如下一个方法和属性:
IsValid():返回验证是否通过
ValidationErrorMessages:获取验证错误信息数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 | [ActiveRecord("Customs")] public class Custom : ActiveRecordValidationBase { //IsValid():返回验证是否通过 //ValidationErrorMessages:获取验证错误信息数组 private int _id; private string _name; private string _email; private string _address; private string _post; private string _phone; [PrimaryKey(PrimaryKeyType.Identity)] public int ID { get { return this._id; } set { this._id = value; } } [Property, ValidateNonEmpty] public string Name { get { return this._name; } set { this._name = value; } } [Property, ValidateEmail] public string Email { get { return this._email; } set { this._email = value; } } [Property] public string Address { get { return this._address; } set { this._address = value; } } [Property, ValidateRegExp(@"\d{6}")] public string Post { get { return this._post; } set { this._post = value; } } [Property, ValidateRegExp(@"(\(\d{3,4}\)|\d{3,4}-)?\d{8}")] public string Phone { get { return this._phone; } set { this._phone = value; } } public static void DeleteAll() { ActiveRecordBase.DeleteAll(typeof(Custom)); } public static Custom[] FindAll() { return ((Custom[])(ActiveRecordBase.FindAll(typeof(Custom)))); } } |
三.如何扩展
上面这些验证已经能够满足我们绝大多数的需求,但是我们也可以去添加自己的验证。来看看ActiveRecord中的Validation的类结构图(只画出了部分)
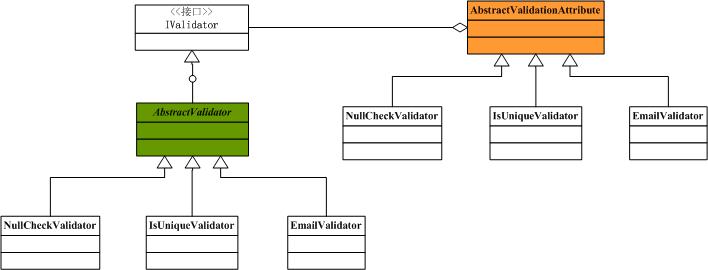
需要继承AbstractValidator和继承于AbstractValidationAttribute的类
四.深入分析验证
通过上面的分析我们都知道所有的实体类都继承于ActiveRecordValidationBase基类,那么ActiveRecord是如何通过特性来进行验证的呢?下面我们结合源码进一步分析一下。
我们在属性上加上了验证, Attribute并不做任何实质性的工作,它只是调用验证器进行验证,示例代码:
Model中使用:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | using Castle.ActiveRecord;using Castle.ActiveRecord.Queries;using NHibernate;using System;using System.Collections;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Linq;using System.Text;using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace Models{ [ActiveRecord("UserInfo")] public class UserInfo : ActiveRecordValidationBase<UserInfo>//必须继承ActiveRecordValidationBase { [Validators.ValidateIsUnique ,Property("Name")]//加入验证特性描述 public virtual string Name { get; set; }<br> }} |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 | using System;using System.Collections;using Castle.ActiveRecord.Framework.Internal;using NHibernate;using NHibernate.Classic;using NHibernate.Criterion;using Castle.Components.Validator;//需要添加引用using Castle.ActiveRecord;namespace Models.Validators{ [Serializable] public class IsUniqueValidator : AbstractValidator { /// <summary> /// Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="IsUniqueValidator"/> class. /// </summary> public IsUniqueValidator() { } /// <summary> /// Perform the check that the property value is unqiue in the table /// </summary> /// <param name="instance"></param> /// <param name="fieldValue"></param> /// <returns><c>true</c> if the field is OK</returns> public override bool IsValid(object instance, object fieldValue) { Type instanceType = instance.GetType();//需要验证的属性 所在类 string name = fieldValue.ToString();//属性值 //验证逻辑 if (name == "jay") { return true; } return false; //ActiveRecordModel model = ActiveRecordBase.GetModel(instance.GetType()); //while (model != null) //{ // if (model.PrimaryKey != null) // { // pkModel = model.PrimaryKey; // } // model = model.Parent; //} //if (pkModel == null) //{ // throw new ValidationFailure("We couldn't find the primary key for " + instanceType.FullName + " so we can't ensure the uniqueness of any field. Validatior failed"); //} //IsUniqueValidator.fieldValue = fieldValue; //SessionScope scope = null; //FlushMode? originalMode = null; //if (SessionScope.Current == null /*|| // SessionScope.Current.ScopeType != SessionScopeType.Transactional*/) //{ // scope = new SessionScope(); //} //else //{ // originalMode = ActiveRecordBase.holder.CreateSession(instanceType).FlushMode; // ActiveRecordBase.holder.CreateSession(instanceType).FlushMode = FlushMode.Never; //} //try //{ //return (bool)ActiveRecordMediator.Execute(instanceType, CheckUniqueness, instance); //} //finally //{ // if (scope != null) // { // scope.Dispose(); // } // if (originalMode != null) // { // ActiveRecordBase.holder.CreateSession(instanceType).FlushMode = originalMode ?? FlushMode.Commit; // } //} } //private object CheckUniqueness(ISession session, object instance) //{ // ICriteria criteria = session.CreateCriteria(instance.GetType()); // if (Property.Name.Equals(pkModel.Property.Name, StringComparison.InvariantCultureIgnoreCase)) // { // // IsUniqueValidator is on the PrimaryKey Property, simplify query // criteria.Add(Expression.Eq(Property.Name, fieldValue)); // } // else // { // object id = pkModel.Property.GetValue(instance, new object[0]); // ICriterion pKeyCriteria = (id == null) // ? Expression.IsNull(pkModel.Property.Name) // : Expression.Eq(pkModel.Property.Name, id); // criteria.Add(Expression.And(Expression.Eq(Property.Name, fieldValue), Expression.Not(pKeyCriteria))); // } // return criteria.List().Count == 0; //} /// <summary> /// Builds the error message when the property value is not unique 构造错误消息 /// </summary> /// <returns></returns> protected override string BuildErrorMessage() { if (!String.IsNullOrEmpty(ErrorMessage)) return ErrorMessage; return String.Format("{0} is currently in use. Please pick up a new {0}.", Property.Name); } /// <summary> /// Gets a value indicating whether this validator supports browser validation. 是否支持客户端验证 /// </summary> /// <value> /// <see langword="true"/> if browser validation is supported; otherwise, <see langword="false"/>. /// </value> public override bool SupportsBrowserValidation { get { return false; } } /// <summary> /// Applies the browser validation by setting up one or /// more input rules on <see cref="IBrowserValidationGenerator"/>. /// </summary> /// <param name="config">The config.</param> /// <param name="inputType">Type of the input.</param> /// <param name="generator">The generator.</param> /// <param name="attributes">The attributes.</param> /// <param name="target">The target.</param> public override void ApplyBrowserValidation(BrowserValidationConfiguration config, InputElementType inputType, IBrowserValidationGenerator generator, IDictionary attributes, string target) { } }} |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 | using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Linq;using System.Web;using Castle.ActiveRecord.Framework.Validators;using Castle.Components.Validator;namespace Models.Validators{ /// <summary> /// Validate that the property's value is unique in the database when saved /// </summary> [Serializable] public class ValidateIsUniqueAttribute : AbstractValidationAttribute { private readonly IValidator validator; /// <summary> /// Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="ValidateIsUniqueAttribute"/> class. /// </summary> public ValidateIsUniqueAttribute() { validator = new IsUniqueValidator(); } /// <summary> /// Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="ValidateIsUniqueAttribute"/> class. /// </summary> /// <param name="errorMessage">The error message.</param> public ValidateIsUniqueAttribute(String errorMessage) : base(errorMessage) { validator = new IsUniqueValidator(); } /// <summary> /// Constructs and configures an <see cref="IValidator"/> /// instance based on the properties set on the attribute instance. /// </summary> /// <returns></returns> public override IValidator Build() { ConfigureValidatorMessage(validator); return validator; } }} |
前台使用:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | protected void Button6_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { Models.UserInfo tui = new Models.UserInfo(); tui.Name = TextBox2.Text; if (tui.IsValid()) { ltlMsg.Text = "验证通过"; } else { ltlMsg.Text = "验证失败"; } } |
五、启动程序时,可以初始化数据、根据模型生成数据表、运行指定的Sql文件创建数据库:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 | protected void Application_Start(object sender, EventArgs e) { // 在应用程序启动时运行的代码 //AuthConfig.RegisterOpenAuth(); //RouteConfig.RegisterRoutes(RouteTable.Routes); InitActiveRecord(); } //Castle Record Register Model private void InitActiveRecord() { try { //加载配置文件 string NHibernateFilePath = Server.MapPath("~/NHibernate.config"); XmlConfigurationSource source = new XmlConfigurationSource(NHibernateFilePath); //注册数据模型 ActiveRecordStarter.Initialize(source, typeof(Models.LogInfo), typeof(Models.UserInfo), typeof(Models.ThemeInfo), typeof(Models.CommentInfo), typeof(Models.CategoryInfo)); //根据模型生成数据库 //ActiveRecordStarter.CreateSchema(); //运行指定的数据库脚本生成数据库等 //ActiveRecordStarter.CreateSchemaFromFile("MySqlScript.sql"); } catch (Exception) { throw; } } |
六.使用空属类型
在进行数据库操作时,有时候需要进行空值的处理,在ActiveRecord中给我们提供了一组空属类型,可以方便的进行处理,比如可以这样写属性:
1 2 | [Property("CreateDate")]public virtual Nullable<DateTime> CreateDate { get; set; } |
七.使用枚举类型
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | 定义: public enum StatusType { Editing = 0, Published = 1, Archived = 2 } [Property("status_id")] public virtual StatusType Status { get; set; }使用: Models.UserInfo userinfo = new Models.UserInfo(); userinfo.Status = Models.UserInfo.StatusType.Archived; |
八.Hooks
有时候我们会在保存,加载,删除等操作时做一些必需的处理,这时可以通过重载以下三个方法来实现:
BeforeSave(IDictionary state)
BeforeLoad(IDictionary state)
BeforeDelete(IDictionary state)
比如说我们想在保存的时候设置创建时间为当前时间,可以这样去写:
1 2 3 4 5 | protected override bool BeforeSave(IDictionary state){ state["Created"] = DateTime.Now; return true;} |




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· .NET周刊【3月第1期 2025-03-02】