第二次软工实践
二、PSP表格
|
PSP2.1 |
Personal Software Process Stages |
预估耗时(分钟) |
实际耗时(分钟) |
|
Planning |
计划 |
20 |
30 |
|
• Estimate |
• 估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
815 |
830 |
|
Development |
开发 |
685 |
690 |
|
• Analysis |
• 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
50 |
60 |
|
• Design Spec |
• 生成设计文档 |
20 |
15 |
|
• Design Review |
• 设计复审 |
10 |
15 |
|
• Coding Standard |
• 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
30 |
30 |
|
• Design |
• 具体设计 |
100 |
120 |
|
• Coding |
• 具体编码 |
360 |
350 |
|
• Code Review |
• 代码复审 |
100 |
90 |
|
• Test |
• 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
15 |
20 |
|
Reporting |
报告 |
110 |
120 |
|
• Test Repor |
• 测试报告 |
60 |
75 |
|
• Size Measurement |
• 计算工作量 |
20 |
20 |
|
• Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
• 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 |
30 |
25 |
|
|
合计 |
815 |
830 |
三、需求分析与具体设计:
题目要求,对一个文本进行字符统计,单词统计与词频统计。考虑到是对双关键字的排序,使用了pair的类型数据以及sort的函数。
设置头文件与全局变量:
#include<cstdio> #include<fstream> #include<iostream> #include <vector> #include<string> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; typedef pair<string, int> t; pair<string, int> num[10000]; int word=0;
几个关键的函数如下:
字符统计:
int jszf(char t[1000]) { int n=0; while (t[n] != '\0') { n++; } return n; }
每次读取一行的字符进行计数。
单词统计以及排序:
int wordnu(char t[1000],int n2) { int f1=0; int i=0; int f2 = 0; int n = 0; char a[100] = {'\0'}; while (t[i] != '\0') { if (t[i] >= 'A'&&t[i] <= 'Z') { a[f1] = t[i] + 32; f1++; } if (t[i] >= 'a'&&t[i] <= 'z') { a[f1] = t[i]; f1++; } if(f1>=4&& (t[i] >= '0' &&t[i] <= '9')) { a[f1] = t[i]; f1++; } if (((t[i]<'A' || (t[i] > 'z'&&t[i] < 'a') || t[i]>'z') && f1 < 4) || (f1 >= 4 && (t[i]<'0' || (t[i] > '9'&&t[i] < 'A') || (t[i] > 'Z'&&t[i] < 'a') || t[i]>'z'))||(f1>=4&&t[i+1]=='\0')) { if (f1 >= 4) { for (int z = 0; z <n2; z++) { if (num[z].first== a) { num[z].second++; f2 = 1; break; } } if (f2 == 0) { num[n2].first = a; num[n2].second = 1; n2++; } else { f2 = 0; } memset(a, '\0', sizeof(a)); word++; } f1 = 0; } i++; } return n2; }
bool cmp(const t &a, const t &b) { if (a.second != b.second) { return a.second > b.second; } else { return a.first < b.first; } } void paixu(int n) { sort(num, num+n, cmp); }
判断是否是一个单词,通过f1变量计数字母字符与字母数字字符的有效个数,遇到其它字符,则记录单词并重新计数。
通过逐行的读取,将字符数与单词数累计输出。
四、接口设计:
通过分离相应的功能,作为函数独立出来,因为读取的方式以及运行效率的考虑,每个函数的实际效果是统计一行的字符与单词数目。
五、测试结果:
测试用例:
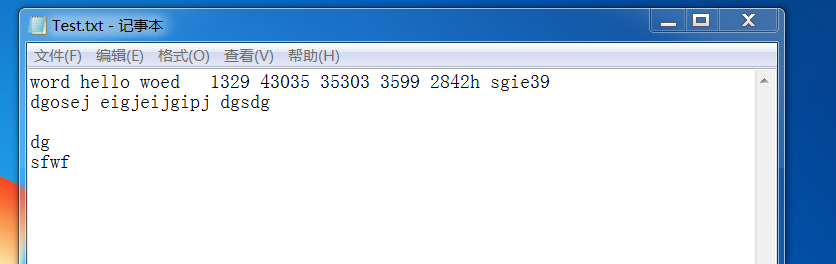
运行结果:
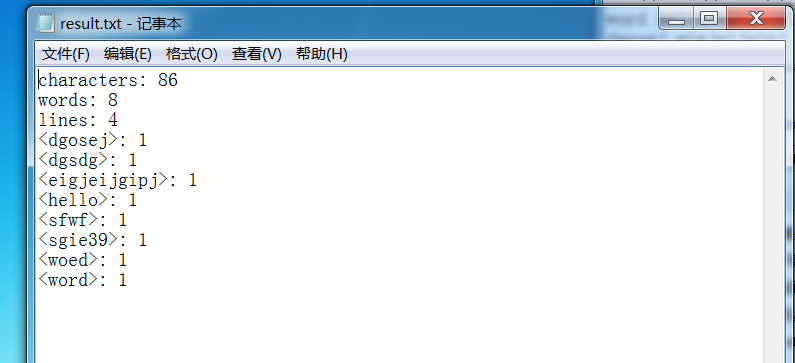
六、异常处理:
发现没有文档时,输出错误提示。
测试样例:
测试结果:
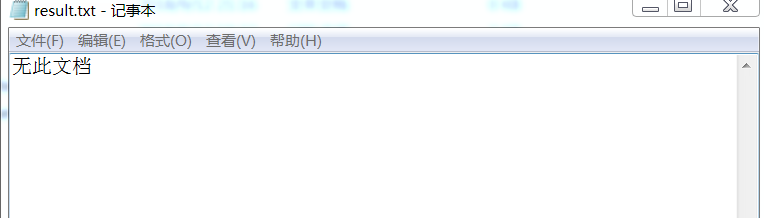
收获:
这次的实践,我认识到了在具体实现代码之前,一定要有分析与设计,考虑好要用的数据结构,实现的算法。在具体设计的时候,接口封装遇到了一些问题,不能很好的将整个功能完全的剥离成函数。
编程的过程缺少注释,还不能规范化的写代码。通过这次的学习,与同学之间的交流沟通,认识到自己还有许多的不足。希望在下次的实践中能够改正这些错误。


