Spring和Hibernate集成--声明式事务
采用声明式事务
一、声明式事务配置
a、配置SessionFactory
b、配置事务管理器
c、事务的传播特性
d、那些类那些方法使用事务
<!-- 配置sessionFactory --> <bean id="sessionFactory" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.LocalSessionFactoryBean"> <property name="configLocation"> <value>classpath:hibernate.cfg.xml</value> </property> </bean> <!-- 配置事务管理器 --> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager"> <property name="sessionFactory"> <ref bean="sessionFactory"/> </property> </bean> <!-- 配置事务的传播特性 --> <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager"> <tx:attributes> <tx:method name="add*" propagation="REQUIRED"/> <tx:method name="del*" propagation="REQUIRED"/> <tx:method name="modify*" propagation="REQUIRED"/> <tx:method name="*" read-only="true"/> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice> <!-- 那些类的哪些方法参与事务 --> <aop:config> <aop:pointcut id="allManagerMethod" expression="execution(* com.ncepu.usermgr.manager.*.*(..))"/> <aop:advisor pointcut-ref="allManagerMethod" advice-ref="txAdvice"/> </aop:config>
二、编写业务逻辑方法
1、 继承HibernateDaoSupport类,使用HibernateTemplate来持久化,HibernateTemplate是 Hibernate Session的轻量级封装
2、默认情况下运行期异常才会回滚(包括继承了RuntimeException子类),普通异常是不会滚的
3、编写业务逻辑方法时,最好将异常一直向上抛出,在表示层(struts)处理
4、关于事务边界的设置,通常设置到业务层,不要添加到Dao上
三、事务的几种传播特性
1. PROPAGATION_REQUIRED: 如果存在一个事务,则支持当前事务。如果没有事务则开启
2. PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS: 如果存在一个事务,支持当前事务。如果没有事务,则非事务的执行
3. PROPAGATION_MANDATORY: 如果已经存在一个事务,支持当前事务。如果没有一个活动的事务,则抛出异常。
4. PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW: 总是开启一个新的事务。如果一个事务已经存在,则将这个存在的事务挂起。
5. PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED: 总是非事务地执行,并挂起任何存在的事务。
6. PROPAGATION_NEVER: 总是非事务地执行,如果存在一个活动事务,则抛出异常
7. PROPAGATION_NESTED:如果一个活动的事务存在,则运行在一个嵌套的事务中. 如果没有活动事务,
则按TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED 属性执行
四、Spring事务的隔离级别
1. ISOLATION_DEFAULT: 这是一个PlatfromTransactionManager默认的隔离级别,使用数据库默认的事务隔离级别.
另外四个与JDBC的隔离级别相对应
2. ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED: 这是事务最低的隔离级别,它充许令外一个事务可以看到这个事务未提交的数据。
这种隔离级别会产生脏读,不可重复读和幻像读。
3. ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED: 保证一个事务修改的数据提交后才能被另外一个事务读取。另外一个事务不能读取该事务未提交的数据
4. ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ: 这种事务隔离级别可以防止脏读,不可重复读。但是可能出现幻像读。
它除了保证一个事务不能读取另一个事务未提交的数据外,还保证了避免下面的情况产生(不可重复读)。
5. ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE 这是花费最高代价但是最可靠的事务隔离级别。事务被处理为顺序执行。
除了防止脏读,不可重复读外,还避免了幻像读。
五、例子(日志管理,添加用户时添加相应的日志)
User.java
package com.ncepu.usermgr.model;
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
User.hbm.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-mapping package="com.ncepu.usermgr.model"> <class name="User" table="t_user"> <id name="id"> <generator class="native"/> </id> <property name="name"/> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
Log.java
package com.ncepu.usermgr.model;
import java.util.Date;
public class Log {
private int id;
//操作日志、安全日志、事件日志
private String type;
private String detail;
private Date time;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public String getDetail() {
return detail;
}
public void setDetail(String detail) {
this.detail = detail;
}
public Date getTime() {
return time;
}
public void setTime(Date time) {
this.time = time;
}
}
Log.hbm.xml
<hibernate-mapping package="com.ncepu.usermgr.model"> <class name="Log" table="t_log"> <id name="id"> <generator class="native"/> </id> <property name="type"/> <property name="detail"/> <property name="time"/> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
UserManager接口
package com.ncepu.usermgr.manager;
import com.ncepu.usermgr.model.User;
public interface UserManager {
public void addUser(User user);
}
UserManagerImpl实现类
package com.ncepu.usermgr.manager;
import java.util.Date;
import org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.support.HibernateDaoSupport;
import com.ncepu.usermgr.model.Log;
import com.ncepu.usermgr.model.User;
public class UserManagerImpl extends HibernateDaoSupport implements UserManager {
private LogManager logManager;
public void addUser(User user) {
this.getHibernateTemplate().save(user);
Log log = new Log();
log.setType("安全日志");
log.setDetail("xxx进入系统");
log.setTime(new Date());
logManager.addLog(log);
}
public void setLogManager(LogManager logManager) {
this.logManager = logManager;
}
}
LogManager接口
package com.ncepu.usermgr.manager;
import com.ncepu.usermgr.model.Log;
public interface LogManager {
public void addLog(Log log);
}
LogManagerImpl实现类
package com.ncepu.usermgr.manager;
import org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.support.HibernateDaoSupport;
import com.ncepu.usermgr.model.Log;
public class LogManagerImpl extends HibernateDaoSupport implements LogManager {
public void addLog(Log log) {
this.getHibernateTemplate().save(log);
}
}
Client.java
package com.ncepu.usermgr.client;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import com.ncepu.usermgr.manager.UserManager;
import com.ncepu.usermgr.model.User;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
User user = new User();
user.setName("张三");
BeanFactory factory = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext-*.xml");
UserManager userManager = (UserManager)factory.getBean("userManager");
userManager.addUser(user);
}
}
hibernate.cfg.xml
<hibernate-configuration> <session-factory> <property name="hibernate.connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost/hibernate</property> <property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property> <property name="hibernate.connection.username">root</property> <property name="hibernate.connection.password">admin</property> <property name="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property> <property name="hibernate.show_sql">true</property> <property name="hibernate.current_session_context_class">thread</property> <!-- <property name="hibernate.current_session_context_class">jta</property> --> <mapping resource="com/ncepu/usermgr/model/User.hbm.xml"/> <mapping resource="com/ncepu/usermgr/model/Log.hbm.xml"/> </session-factory> </hibernate-configuration>
Spring配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.0.xsd">
<!-- 配置sessionFactory -->
<bean id="sessionFactory" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.LocalSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="configLocation">
<value>classpath:hibernate.cfg.xml</value>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置事务管理器 -->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager">
<property name="sessionFactory">
<ref bean="sessionFactory"/>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置事务的传播特性 -->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="add*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="del*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="modify*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="*" read-only="true"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!-- 那些类的哪些方法参与事务 -->
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="allManagerMethod" expression="execution(* com.ncepu.usermgr.manager.*.*(..))"/>
<aop:advisor pointcut-ref="allManagerMethod" advice-ref="txAdvice"/>
</aop:config>
<bean id="userManager" class="com.ncepu.usermgr.manager.UserManagerImpl">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory"/>
<property name="logManager" ref="logManager"/>
</bean>
<bean id="logManager" class="com.ncepu.usermgr.manager.LogManagerImpl">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory"/>
</bean>
</beans>
工具类SessionFactory
package com.ncepu.usermgr.util;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
public class HibernateUtils {
private static SessionFactory factory;
static {
try {
Configuration cfg = new Configuration().configure();
factory = cfg.buildSessionFactory();
}catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static SessionFactory getSessionFactory() {
return factory;
}
public static Session getSession() {
return factory.openSession();
}
public static void closeSession(Session session) {
if (session != null) {
if (session.isOpen()) {
session.close();
}
}
}
}
导入数据库工具类
package com.ncepu.usermgr.util;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.hibernate.tool.hbm2ddl.SchemaExport;
public class ExportDB {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//读取hibernate.cfg.xml文件
Configuration cfg = new Configuration().configure();
SchemaExport export = new SchemaExport(cfg);
export.create(true, true);
}
}
hibernate编程式事务 http://blog.csdn.net/ncepustrong/article/details/7959573
数据库的隔离级别 http://blog.csdn.net/ncepustrong/article/details/7948231
Spring事务配置的五种方式 http://blog.csdn.net/it_man/article/details/5074371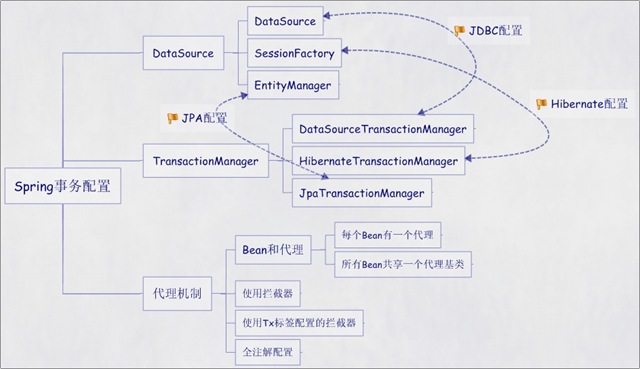




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律