Android Annotation ——XArch
注解并不是第一次看到,类似于见过最多的 @Override
【遇】
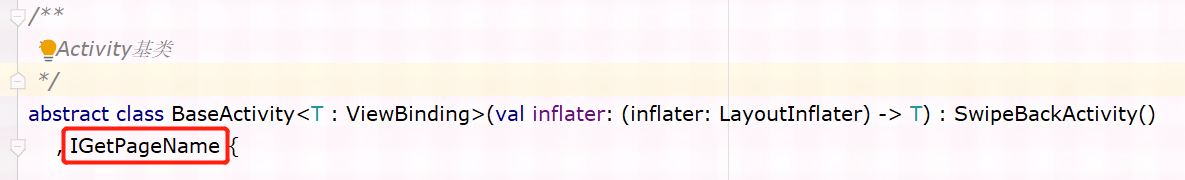
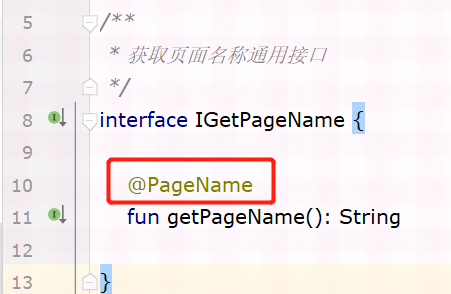
BaseActivity中实现了 IGetPageName 接口,接口中 定义了 getPageName方法,添加 @PageName 注解,MainActivity中重写BaseActivity中的 getPageName 方法并设置返回值,这里达到了返回值只能设置为 PageName枚举中值的效果,而枚举使用静态常量+@StringDef 的方法定义。
@PageName 自定义注解,@StringDef (androidx.annotation包内)
BaseActivity.java
IGetPageName.java
PageName.java

MainActivity.java
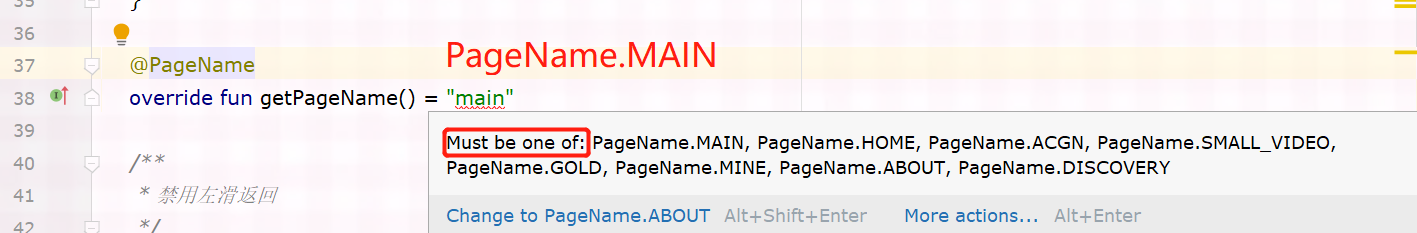
【问】
注解是什么,注解有什么作用?
在什么情况下会想到要使用注解?
【知】
参考博文:Java Annotation认知(包括框架图、详细介绍、示例说明) - 如果天空不死 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
1、 Java Annotation是JDK5.0引入的一种注释机制
2、我对于Annotation的理解

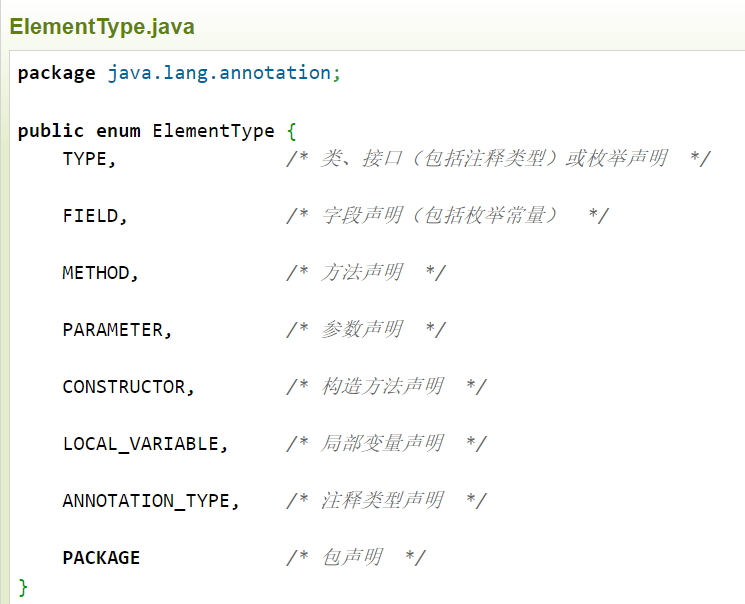
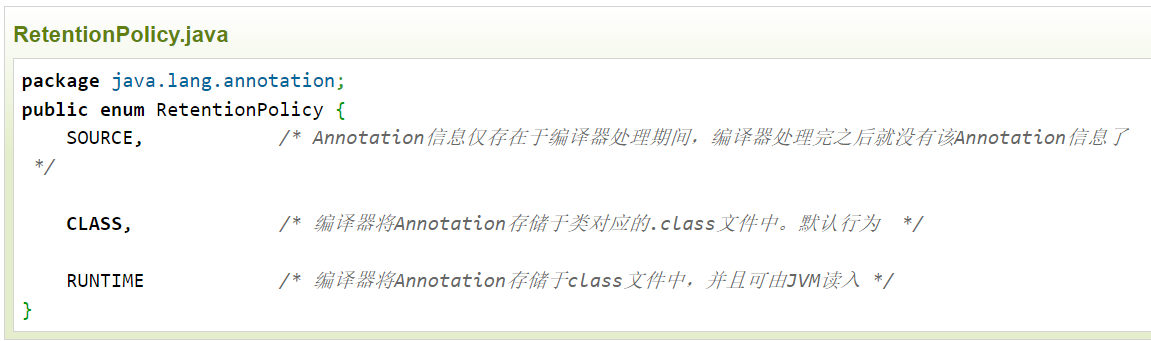
ElementType、RetentionPolicy是枚举,Annotation是一个接口。然后我们由他们创建新的Annotation注解。新的注解,就是通过实现 Annotation的接口,然后再通过@Target、@Retention注解分别来指定ElementType、RetentionPolicy的值,结构图中1..n表示@Target可以指定多个枚举值(用来只能注解可以修饰的位置),而@Retention注解就只能指定一个枚举值(表示注解作用域,保留到的位置)。
①@Target本身也是注解,那么上面说注解创建时就要通过@Target来修饰Target的注解。所以存在以下代码
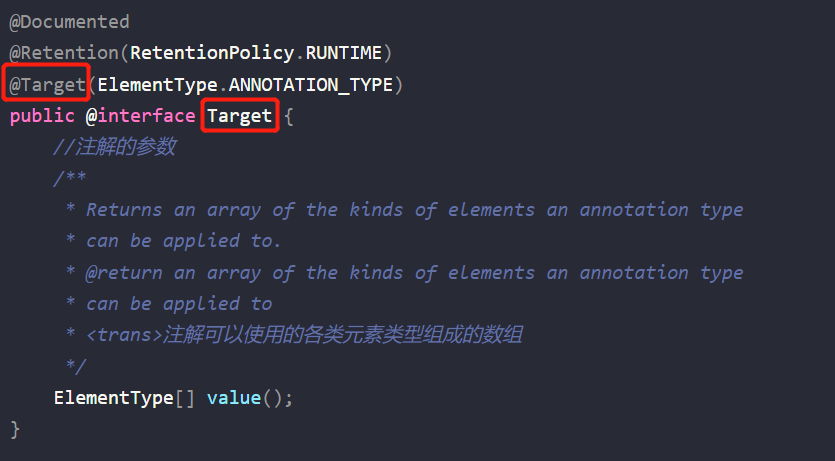
⭐为什么@Target能够修饰 Target Annotation?不是还在创建阶段吗
有关于这个问题,我还没有答案。有人回答我说,就像递归,自己调用自己。对哇,递归,我以前为什么没有问,函数为什么能够自己调用自己?(从网上我得出的理解时,方法定义并不分配内存,而是相当于存储一个方法的指针,调用的时候再去执行具体的方法,所以当它调用自己的时候,它早就已经告诉编译器,它存在了。为什么函数能递归调用自己? - 知乎 (zhihu.com))
除了@Target修饰Target,还存在@Target修饰 Retention 创建,@Retention修饰Target创建,这或许有点像在A函数里面调用B函数,B函数里面调用A函数。
很难解释,那么是否可以跳过Target 创建,把@Target单纯看做成对该注解的注解。即我们只需要知道 @Target 只能修饰 ANNOTATION_TYPE(像这种只能修饰注解的注解称为元注解),JDK提供了一系列其他的注解,我们可通过注解上方的注解,了解这个注解的作用域和作用。
②ElementType枚举值以及说明
③RetentionPolicy的枚举值及说明
④元注解:修饰注解的注解,以下四个
@Documented -- @Documented 所标注内容,可以出现在javadoc中。若不设置默认为否
@Inherited -- @Inherited只能被用来标注“Annotation类型”,它所标注的Annotation具有继承性。就是使用该Annotation的类的子类也自动继承该父类的注解。若不设置默认为否
@Retention -- @Retention只能被用来标注“Annotation类型”,而且它被用来指定Annotation的RetentionPolicy属性。若不设置默认为RetentionPolicy.CLASS
@Target -- @Target只能被用来标注“Annotation类型”,而且它被用来指定Annotation的ElementType属性。若不设置默认为可作用域任何地方
@Repeatable -- @Repeatable(重复) 用于声明标记的注解为可重复类型注解,可以在同一个地方多次使用
⑤其他注解
@SuppressWarnings -- @SuppressWarnings 所标注内容产生的警告,编译器会对这些警告保持静默。
@Deprecated -- @Deprecated 所标注内容,不再被建议使用。
3、kotlin中的Annotation 有什么不同
①元注解不同 @Documented改成 @MustBeDocumented
去掉了@Inherited(查看:Inherited annotations and other reflections enchancements - Support - Kotlin Discussions (kotlinlang.org))
②ElementType名对应AnnotationTarget,RetentionPolicy名对应AnnotationRetention
③@Retention的默认值不同,Java中默认值为 RetentionPolicy.CLASS,Kotlin中是AnnotationRetention.RUNTIME
package kotlin.annotation
import kotlin.annotation.AnnotationTarget.*
/**
* Contains the list of code elements which are the possible annotation targets
*/
public enum class AnnotationTarget {
/** Class, interface or object, annotation class is also included */
CLASS,
/** Annotation class only */
ANNOTATION_CLASS,
/** Generic type parameter */
TYPE_PARAMETER,
/** Property */
PROPERTY,
/** Field, including property's backing field */
FIELD,
/** Local variable */
LOCAL_VARIABLE,
/** Value parameter of a function or a constructor */
VALUE_PARAMETER,
/** Constructor only (primary or secondary) */
CONSTRUCTOR,
/** Function (constructors are not included) */
FUNCTION,
/** Property getter only */
PROPERTY_GETTER,
/** Property setter only */
PROPERTY_SETTER,
/** Type usage */
TYPE,
/** Any expression */
EXPRESSION,
/** File */
FILE,
/** Type alias */
@SinceKotlin("1.1")
TYPEALIAS
}
/**
* Contains the list of possible annotation's retentions.
*
* Determines how an annotation is stored in binary output.
*/
public enum class AnnotationRetention {
/** Annotation isn't stored in binary output */
SOURCE,
/** Annotation is stored in binary output, but invisible for reflection */
BINARY,
/** Annotation is stored in binary output and visible for reflection (default retention) */
RUNTIME
}
/**
* This meta-annotation indicates the kinds of code elements which are possible targets of an annotation.
*
* If the target meta-annotation is not present on an annotation declaration, the annotation is applicable to the following elements:
* [CLASS], [PROPERTY], [FIELD], [LOCAL_VARIABLE], [VALUE_PARAMETER], [CONSTRUCTOR], [FUNCTION], [PROPERTY_GETTER], [PROPERTY_SETTER].
*
* @property allowedTargets list of allowed annotation targets
*/
@Target(AnnotationTarget.ANNOTATION_CLASS)
@MustBeDocumented
public annotation class Target(vararg val allowedTargets: AnnotationTarget)
/**
* This meta-annotation determines whether an annotation is stored in binary output and visible for reflection. By default, both are true.
*
* @property value necessary annotation retention (RUNTIME, BINARY or SOURCE)
*/
@Target(AnnotationTarget.ANNOTATION_CLASS)
public annotation class Retention(val value: AnnotationRetention = AnnotationRetention.RUNTIME)
/**
* This meta-annotation determines that an annotation is applicable twice or more on a single code element
*/
@Target(AnnotationTarget.ANNOTATION_CLASS)
public annotation class Repeatable
/**
* This meta-annotation determines that an annotation is a part of public API and therefore should be included in the generated
* documentation for the element to which the annotation is applied.
*/
@Target(AnnotationTarget.ANNOTATION_CLASS)
public annotation class MustBeDocumented④定义Annotation的方法不同
java中使用 @interface ,kotlin 中使用 annotation class。
⑤枚举中的部分字段就不同。比如Java中RetentionPolity.CLASS对应 Kotlin中AnnotationRetention.BINARY,ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE 对应 AnnotationTarget.ANNOTATION_CLASS 但功能类似,改成了更为可读名称
@Retention(AnnotationRetention.SOURCE)
annotation class PageName{
//语法形式上模拟了静态类的调用方法
companion object{
const val MAIN = "main"
const val HOME = "home"
const val ACGN = "acgn"
const val SMALL_VIDEO = "small_video"
const val GOLD = "gold"
const val MINE = "mine"
const val ABOUT = "about"
const val DISCOVERY = "discovery"
}
}
4、Androidx中的一些注解(androidx.annotation | Android Developers (google.cn))
- @CallSuper 子类重写方法是必须加 super.方法名
- @StringDef 由于enum性能问题,使用静态常量代替enum,开发者在使用时不能很好的找到取值范围,并且在不知道源码的情况下可能导致传值错误,于是用@StringDef可以指定常量,编译器可以给出提示。(Android中不使用枚举类(enum)替代为@IntDef @StringDef - 简书 (jianshu.com))

- 为什么enum影响性能?
因为没有enum的值都会创建了一个Object对象,占用内存。
5、为什么@PageName能够限定方法的返回值是PageName内枚举值
这里@PageName和@StringDef结合,实际上达到的是枚举的作用效果,可以方法参数前面,或者方法上方,指定参数的传值区间和返回值区间。这里是用作枚举。
6、有关PermissionX使用注解对是否请求权限的检查
【注解的作用】
1、编译检查
@PageName实际上也是起到这样的效果、@Override
2、生成对应的帮助文档



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)