KMP 算法详解
KMP 算法详解
KMP 算法是一个十分高效的字符串查找算法,目的是在一个字符串 s 中,查询 s 是否包含子字符串 p,若包含,则返回 p 在 s 中起点的下标。
KMP 算法全称为 Knuth-Morris-Pratt 算法,由 Knuth 和 Pratt 在1974年构思,同年 Morris 也独立地设计出该算法,最终由三人于1977年联合发表。
举一个简单的例子,在字符串 s = ababcabababca 中查找子字符串 p = abababca,如果暴力查找,我们会遍历 s 中的每一个字符,若 s[i] = p[0],则向后查询 p.length() 位是否都相等。这种朴素的暴力的算法复杂度为 \(O(m \times n)\),其中 \(m\) 和 \(n\) 分别是 p 和 s 的长度。
KMP 算法可以方便地简化这一查询的时间复杂度,达到 \(O(m + n)\)。
1. PMT 序列
PMT 序列是 KMP 算法的核心,即 Partial Match Table(部分匹配表)。举个例子:
| char | a | b | a | b | a | b | c | a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
index |
0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
PMT |
0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 1 |
PMT 的值是字符串的前缀集合与后缀集合的交集中最长元素的长度。
PMT[0] = 0: 字符串a既没有前缀,也没有后缀;PMT[1] = 0: 字符串ab前缀集合为{a},后缀集合为{b},没有交集;PMT[2] = 1: 字符串aba前缀集合为{a, ab},后缀集合为{ba, a},交集为{a},交集元素的最长长度为1;PMT[3] = 2: 字符串abab前缀集合为{a, ab, aba},后缀集合为{bab, ab, b},交集为{ab},交集元素的最长长度为2;- …… 以此类推。
2. 算法主体
现在我们已经知道了 PMT 序列的含义,那么假设在 PMT 序列已经给定的情况下,如何加速字符串匹配算法?
tar存储s的下标,从 0 开始,若tar > s.length() - 1, 代表匹配失败;pos存储p的下标,从 0 开始,若s[tar] != p[pos],则pos走到下一个可能匹配的位置。
Step 1:
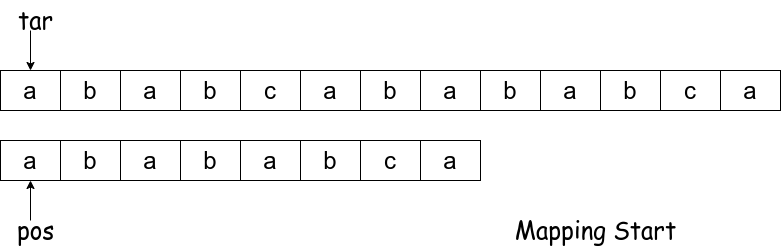
Step 2:
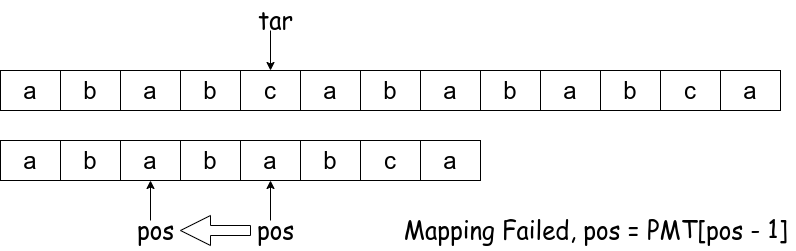
Step 3:
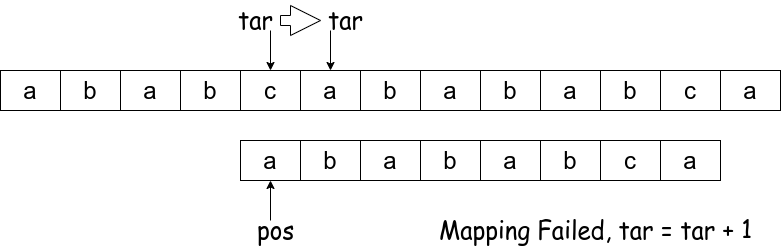
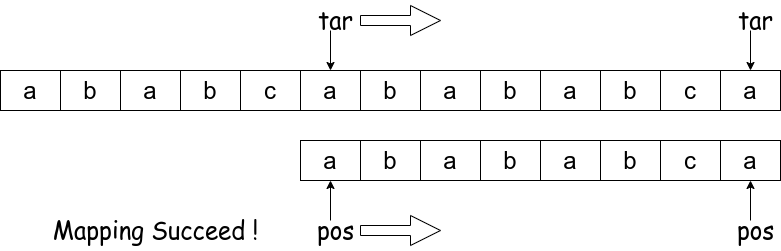
Step 4:
/**
* @brief KMP algorithm: A string-searching algorithm.
*
* @param s Source string.
* @param p Search pattern.
* @return int The first index of s's substring, which equals to p. If not found, return -1.
*/
int KMP(string s, string p) {
int tar = 0; /** Index of source string s */
int pos = 0; /** Index of pattern string p */
vector<int> PMT = genPMT(p); /** Pattern p's PMT sequence */
while(tar < s.length()) {
if(s[tar] == p[pos]) { /** If s[tar] == p[pos], go step forward */
tar++;
pos++;
}
else if(pos) /** Failed map, go to the last map index of p */
pos = PMT[pos - 1];
else /** pos[0] failed map, go to the next s's index */
tar++;
if(pos == p.length()) /** Mapping success */
return tar - pos;
}
}
3. 生成 PMT 序列
快速生成 PMT 序列,是 KMP 算法的精髓所在,其核心思想是 自己与自己做匹配。
Step 1:
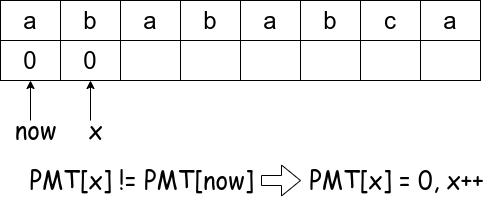
Step 2:
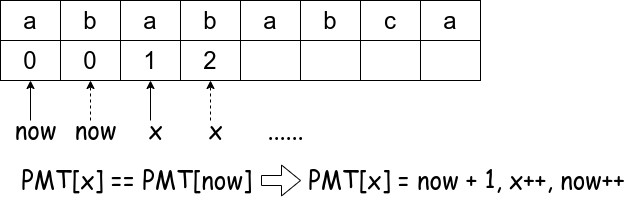
Step 3:
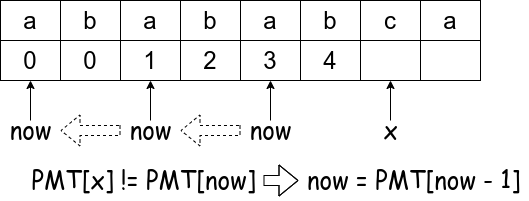
Step 4:
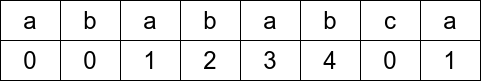
/**
* @brief KMP algorithm: Generate PMT sequence.
*
* @param p Search pattern.
* @return vector<int> PMT sequence.
*/
vector<int> genPMT(string p) {
vector<int> PMT{ 0 }; /** PMT[0] = 0 always stand up. */
int x = 1; /** Index of pattern string */
int now = 0;
while(x < p.length()) {
if(p[now] == p[x]) { /** If p[now] == p[x], go step forward */
now++;
x++;
PMT.push_back(now);
}
else if(now) /** Failed map, go to the last map index of p */
now = PMT[now - 1];
else { /** p[0] failed map, no intersection */
PMT.push_back(0);
x++;
}
}
return PMT;
}

