代码随想录算法Day20 | 654.最大二叉树 , 617.合并二叉树 , 700.二叉搜索树中的搜索 , 98.验证二叉搜索树
654.最大二叉树
题目链接:654. 最大二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
题目
给定一个不重复的整数数组 nums 。 最大二叉树 可以用下面的算法从 nums 递归地构建:
创建一个根节点,其值为 nums 中的最大值。
递归地在最大值 左边 的 子数组前缀上 构建左子树。
递归地在最大值 右边 的 子数组后缀上 构建右子树。
返回 nums 构建的 最大二叉树 。
示例 1:
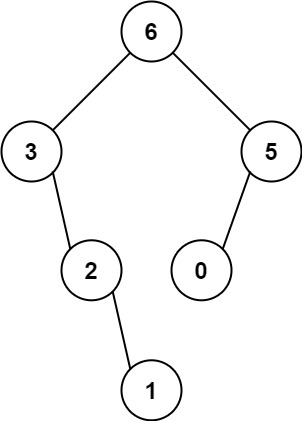
输入:nums = [3,2,1,6,0,5] 输出:[6,3,5,null,2,0,null,null,1] 解释:递归调用如下所示: - [3,2,1,6,0,5] 中的最大值是 6 ,左边部分是 [3,2,1] ,右边部分是 [0,5] 。 - [3,2,1] 中的最大值是 3 ,左边部分是 [] ,右边部分是 [2,1] 。 - 空数组,无子节点。 - [2,1] 中的最大值是 2 ,左边部分是 [] ,右边部分是 [1] 。 - 空数组,无子节点。 - 只有一个元素,所以子节点是一个值为 1 的节点。 - [0,5] 中的最大值是 5 ,左边部分是 [0] ,右边部分是 [] 。 - 只有一个元素,所以子节点是一个值为 0 的节点。 - 空数组,无子节点。
示例 2:
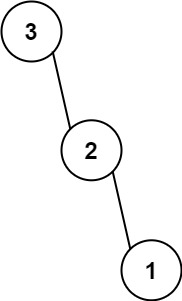
输入:nums = [3,2,1] 输出:[3,null,2,null,1]
思路
这道题和 构造二叉树 思路差不多,比 构造二叉树 还简单点。
注意类似用数组构造二叉树的题目,每次分隔尽量不要定义新的数组,而是通过下标索引直接在原数组上操作,这样可以节约时间和空间上的开销。
什么时候递归函数前面加if,什么时候不加if?
其实就是不同代码风格的实现,一般情况来说:如果让空节点(空指针)进入递归,就不加if,如果不让空节点进入递归,就加if限制一下, 终止条件也会相应的调整。
代码
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * public class TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode left; 6 * TreeNode right; 7 * TreeNode() {} 8 * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } 9 * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { 10 * this.val = val; 11 * this.left = left; 12 * this.right = right; 13 * } 14 * } 15 */ 16 class Solution { 17 public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree(int[] nums) { 18 return constructMaximumBinaryTree1(nums, 0, nums.length); 19 } 20 21 public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree1(int[] nums, int leftIndex, int rightIndex) { 22 // if (rightIndex - leftIndex < 1) {// 没有元素了 23 // return null; 24 // } 25 // if (rightIndex - leftIndex == 1) {// 只有一个元素 26 // return new TreeNode(nums[leftIndex]); 27 // } 28 if(leftIndex >= rightIndex){ 29 return null; 30 } 31 int maxIndex = leftIndex;// 最大值所在位置 32 int maxVal = nums[maxIndex];// 最大值 33 for (int i = leftIndex + 1; i < rightIndex; i++) { 34 if (nums[i] > maxVal){ 35 maxVal = nums[i]; 36 maxIndex = i; 37 } 38 } 39 TreeNode root = new TreeNode(maxVal); 40 // 根据maxIndex划分左右子树 41 root.left = constructMaximumBinaryTree1(nums, leftIndex, maxIndex); 42 root.right = constructMaximumBinaryTree1(nums, maxIndex + 1, rightIndex); 43 return root; 44 } 45 }
617.合并二叉树
题目链接:617. 合并二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
题目
给你两棵二叉树: root1 和 root2 。
想象一下,当你将其中一棵覆盖到另一棵之上时,两棵树上的一些节点将会重叠(而另一些不会)。你需要将这两棵树合并成一棵新二叉树。合并的规则是:如果两个节点重叠,那么将这两个节点的值相加作为合并后节点的新值;否则,不为 null 的节点将直接作为新二叉树的节点。
返回合并后的二叉树。
注意: 合并过程必须从两个树的根节点开始。
示例 1:
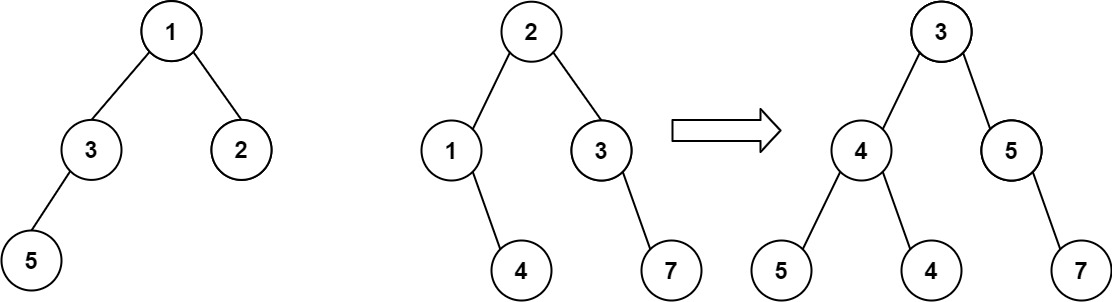
输入:root1 = [1,3,2,5], root2 = [2,1,3,null,4,null,7] 输出:[3,4,5,5,4,null,7]
示例 2:
输入:root1 = [1], root2 = [1,2]
输出:[2,2]
思路
遍历两个数和遍历一个树逻辑是一样的,只不过传入两个树的节点,同时操作。
递归法:
本题使用哪种遍历都是可以的!
因为是传入了两个树,那么就有两个树遍历的节点t1 和 t2,如果t1 == NULL 了,两个树合并就应该是 t2 了(如果t2也为NULL也无所谓,合并之后就是NULL)。
反过来如果t2 == NULL,那么两个数合并就是t1(如果t1也为NULL也无所谓,合并之后就是NULL)。
迭代法:
可以参考 对称二叉树 的思路,在求 二叉树对称 的时候就是把两个树的节点同时加入队列进行比较。
代码
1 class Solution { 2 // 递归 3 public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) { 4 if (root1 == null) return root2; 5 if (root2 == null) return root1; 6 7 root1.val += root2.val; 8 root1.left = mergeTrees(root1.left,root2.left); 9 root1.right = mergeTrees(root1.right,root2.right); 10 return root1; 11 } 12 }
class Solution { // 使用栈迭代 public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) { if (root1 == null) { return root2; } if (root2 == null) { return root1; } Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); stack.push(root2); stack.push(root1); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { TreeNode node1 = stack.pop(); TreeNode node2 = stack.pop(); node1.val += node2.val; if (node2.right != null && node1.right != null) { stack.push(node2.right); stack.push(node1.right); } else { if (node1.right == null) { node1.right = node2.right; } } if (node2.left != null && node1.left != null) { stack.push(node2.left); stack.push(node1.left); } else { if (node1.left == null) { node1.left = node2.left; } } } return root1; } }
class Solution { // 使用队列迭代 public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) { if (root1 == null) return root2; if (root2 ==null) return root1; Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(root1); queue.offer(root2); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { TreeNode node1 = queue.poll(); TreeNode node2 = queue.poll(); // 此时两个节点一定不为空,val相加 node1.val = node1.val + node2.val; // 如果两棵树左节点都不为空,加入队列 if (node1.left != null && node2.left != null) { queue.offer(node1.left); queue.offer(node2.left); } // 如果两棵树右节点都不为空,加入队列 if (node1.right != null && node2.right != null) { queue.offer(node1.right); queue.offer(node2.right); } // 若node1的左节点为空,直接赋值 if (node1.left == null && node2.left != null) { node1.left = node2.left; } // 若node1的右节点为空,直接赋值 if (node1.right == null && node2.right != null) { node1.right = node2.right; } } return root1; } }
700.二叉搜索树中的搜索
题目链接:700. 二叉搜索树中的搜索 - 力扣(LeetCode)
题目
给定二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点 root 和一个整数值 val。
你需要在 BST 中找到节点值等于 val 的节点。 返回以该节点为根的子树。 如果节点不存在,则返回 null 。
示例 1:
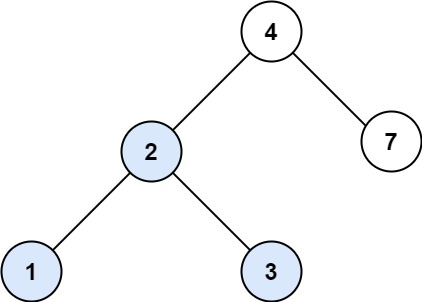
输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3], val = 2
输出:[2,1,3]
示例 2:
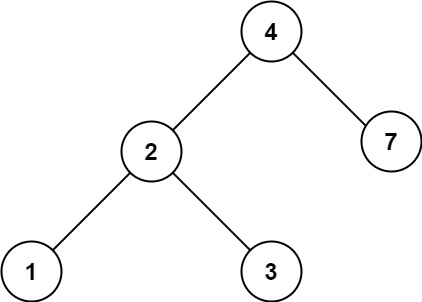
输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3], val = 5
输出:[]
思路
因为二叉搜索树的有序性,遍历的时候要比普通二叉树简单很多。
一提到二叉树遍历的迭代法,可能立刻想起使用栈来模拟深度遍历,使用队列来模拟广度遍历。
对于二叉搜索树可就不一样了,因为二叉搜索树的特殊性,也就是节点的有序性,可以不使用辅助栈或者队列就可以写出迭代法。
对于一般二叉树,递归过程中还有回溯的过程,例如走一个左方向的分支走到头了,那么要调头,在走右分支。
而对于二叉搜索树,不需要回溯的过程,因为节点的有序性就帮我们确定了搜索的方向。
例如要搜索元素为3的节点,我们不需要搜索其他节点,也不需要做回溯,查找的路径已经规划好了。
代码
1 class Solution { 2 // 递归,普通二叉树 3 public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) { 4 if (root == null || root.val == val) { 5 return root; 6 } 7 TreeNode left = searchBST(root.left, val); 8 if (left != null) { 9 return left; 10 } 11 return searchBST(root.right, val); 12 } 13 } 14 15 class Solution { 16 // 递归,利用二叉搜索树特点,优化 17 public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) { 18 if (root == null || root.val == val) { 19 return root; 20 } 21 if (val < root.val) { 22 return searchBST(root.left, val); 23 } else { 24 return searchBST(root.right, val); 25 } 26 } 27 }
1 class Solution { 2 // 迭代,普通二叉树 3 public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) { 4 if (root == null || root.val == val) { 5 return root; 6 } 7 Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); 8 stack.push(root); 9 while (!stack.isEmpty()) { 10 TreeNode pop = stack.pop(); 11 if (pop.val == val) { 12 return pop; 13 } 14 if (pop.right != null) { 15 stack.push(pop.right); 16 } 17 if (pop.left != null) { 18 stack.push(pop.left); 19 } 20 } 21 return null; 22 } 23 } 24 25 class Solution { 26 // 迭代,利用二叉搜索树特点,优化,可以不需要栈 27 public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) { 28 while (root != null) 29 if (val < root.val) root = root.left; 30 else if (val > root.val) root = root.right; 31 else return root; 32 return null; 33 } 34 }
98.验证二叉搜索树
题目链接:98. 验证二叉搜索树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
题目
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,判断其是否是一个有效的二叉搜索树。
有效 二叉搜索树定义如下:
节点的左子树只包含 小于 当前节点的数。
节点的右子树只包含 大于 当前节点的数。
所有左子树和右子树自身必须也是二叉搜索树。
示例 1:
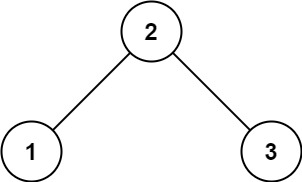
输入:root = [2,1,3] 输出:true
示例 2:
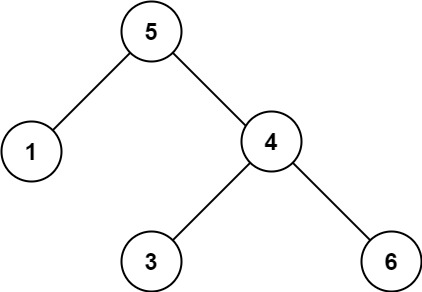
输入:root = [5,1,4,null,null,3,6] 输出:false 解释:根节点的值是 5 ,但是右子节点的值是 4 。
思路
首先要清楚搜索二叉数的一个特性:在中序遍历下,输出的二叉搜索树节点的数值是有序序列,注意二叉搜索树中不能有重复元素。
有了这个特性,验证二叉搜索树,就相当于变成了判断一个序列是不是递增的了。
我们可以通过把二叉树转变为数组来判断,是最直观的,但其实不用转变成数组,可以在递归遍历的过程中直接判断是否有序。
递归遍历时要注意
- 不能单纯的比较左节点小于中间节点,右节点大于中间节点就完事了。我们要比较的是 左子树所有节点小于中间节点,右子树所有节点大于中间节点。
- 样例中最小节点 可能是int的最小值,如果这样使用最小的int来比较也是不行的。可以使用long的最小值进行比较。
代码
1 class Solution { 2 // 递归 3 TreeNode max; 4 public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) { 5 if (root == null) { 6 return true; 7 } 8 // 左 9 boolean left = isValidBST(root.left); 10 if (!left) { 11 return false; 12 } 13 // 中 14 if (max != null && root.val <= max.val) { 15 return false; 16 } 17 max = root; 18 // 右 19 boolean right = isValidBST(root.right); 20 return right; 21 } 22 } 23 24 25 // 简洁实现·递归解法 26 class Solution { 27 public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) { 28 return validBST(Long.MIN_VALUE, Long.MAX_VALUE, root); 29 } 30 boolean validBST(long lower, long upper, TreeNode root) { 31 if (root == null) return true; 32 if (root.val <= lower || root.val >= upper) return false; 33 return validBST(lower, root.val, root.left) && validBST(root.val, upper, root.right); 34 } 35 }
1 // 简洁实现·中序遍历 2 class Solution { 3 private long prev = Long.MIN_VALUE; 4 public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) { 5 if (root == null) { 6 return true; 7 } 8 if (!isValidBST(root.left)) { 9 return false; 10 } 11 if (root.val <= prev) { // 不满足二叉搜索树条件 12 return false; 13 } 14 prev = root.val; 15 return isValidBST(root.right); 16 } 17 }
class Solution { // 迭代 public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return true; } Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); TreeNode pre = null; while (root != null || !stack.isEmpty()) { while (root != null) { stack.push(root); root = root.left;// 左 } // 中,处理 TreeNode pop = stack.pop(); if (pre != null && pop.val <= pre.val) { return false; } pre = pop; root = pop.right;// 右 } return true; } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号