原型模式 学习手记
概述
用原型实例指定创建对象的种类,并用通过拷贝这些原型来创建新的实例。
模型图:
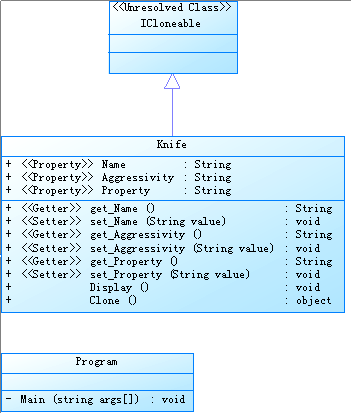
在.Net中可以通过ICloneable来实现
public class Knife:ICloneable
{
public String Name { get; set; }
public String Aggressivity { get; set; }
public String Property { get; set; }
public void Display()
{
Console.WriteLine(Name + Aggressivity + Property);
}
public object Clone()
{
return this.MemberwiseClone();
}
}
{
public String Name { get; set; }
public String Aggressivity { get; set; }
public String Property { get; set; }
public void Display()
{
Console.WriteLine(Name + Aggressivity + Property);
}
public object Clone()
{
return this.MemberwiseClone();
}
}
客户端调用:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Knife k = new Knife();
k.Name = "恶魔刀锋";
k.Aggressivity = "攻击力:1000";
k.Property = "无视一切防御";
k.Display();
Knife k2= k.Clone() as Knife;
k2.Display();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Knife k = new Knife();
k.Name = "恶魔刀锋";
k.Aggressivity = "攻击力:1000";
k.Property = "无视一切防御";
k.Display();
Knife k2= k.Clone() as Knife;
k2.Display();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
通过 this.MemberwiseClone() 实现浅CLONE。上述方式实现了浅复制。
浅复制: 实现浅复制需要使用Object类的MemberwiseClone方法用于创建一个浅表副本
深复制: 须实现 ICloneable接口中的Clone方法,且需要需要克隆的对象加上[Serializable]特性
说复杂点是椎、栈的问题,简单点理解浅复制是原来对象,而深复对原来对象的进行COPY
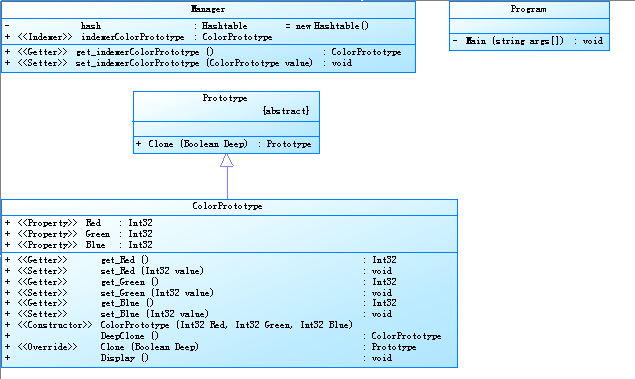
具体编码:
Prototype类:
[Serializable]
abstract class Prototype
{
public abstract Prototype Clone(Boolean Deep);
}
abstract class Prototype
{
public abstract Prototype Clone(Boolean Deep);
}
ColorPrototype类:
[Serializable]
class ColorPrototype:Prototype
{
public Int32 Red { get; set; }
public Int32 Green { get; set; }
public Int32 Blue { get; set; }
public ColorPrototype(Int32 Red, Int32 Green, Int32 Blue)
{
this.Red = Red;
this.Green = Green;
this.Blue = Blue;
}
public ColorPrototype DeepClone()
{
ColorPrototype p;
MemoryStream stream = new MemoryStream();
BinaryFormatter f = new BinaryFormatter();
f.Serialize(stream, this);
stream.Position = 0;
p = (ColorPrototype)f.Deserialize(stream);
return p;
}
public override Prototype Clone(Boolean Deep)
{
if (Deep)
return DeepClone();
else
return (ColorPrototype)this.MemberwiseClone();
}
public void Display()
{
Console.WriteLine("RGB 颜色值为: {0} {1} {2}",Red,Green,Blue);
}
}
class ColorPrototype:Prototype
{
public Int32 Red { get; set; }
public Int32 Green { get; set; }
public Int32 Blue { get; set; }
public ColorPrototype(Int32 Red, Int32 Green, Int32 Blue)
{
this.Red = Red;
this.Green = Green;
this.Blue = Blue;
}
public ColorPrototype DeepClone()
{
ColorPrototype p;
MemoryStream stream = new MemoryStream();
BinaryFormatter f = new BinaryFormatter();
f.Serialize(stream, this);
stream.Position = 0;
p = (ColorPrototype)f.Deserialize(stream);
return p;
}
public override Prototype Clone(Boolean Deep)
{
if (Deep)
return DeepClone();
else
return (ColorPrototype)this.MemberwiseClone();
}
public void Display()
{
Console.WriteLine("RGB 颜色值为: {0} {1} {2}",Red,Green,Blue);
}
}
Manager类:
class Manager
{
Hashtable hash = new Hashtable();
public ColorPrototype this[String name]
{
get
{
return (ColorPrototype)hash[name];
}
set
{
hash.Add(name, value);
}
}
}
{
Hashtable hash = new Hashtable();
public ColorPrototype this[String name]
{
get
{
return (ColorPrototype)hash[name];
}
set
{
hash.Add(name, value);
}
}
}
客户端调用:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Manager manager = new Manager();
manager["red"] = new ColorPrototype(255, 0, 0);
manager["green"] = new ColorPrototype(0, 255, 0);
manager["blue"] = new ColorPrototype(0, 0, 255);
ColorPrototype c0= (ColorPrototype)manager["red"].Clone(false);
c0.Display();
ColorPrototype c1 = (ColorPrototype)manager["red"].Clone(false);
c0.Green = 300;
c1.Display();
ColorPrototype c2 = (ColorPrototype)manager["blue"].Clone(true);
c2.Display();
ColorPrototype c3 = (ColorPrototype)manager["blue"].Clone(true);
c3.Green = 300;
c3.Display();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Manager manager = new Manager();
manager["red"] = new ColorPrototype(255, 0, 0);
manager["green"] = new ColorPrototype(0, 255, 0);
manager["blue"] = new ColorPrototype(0, 0, 255);
ColorPrototype c0= (ColorPrototype)manager["red"].Clone(false);
c0.Display();
ColorPrototype c1 = (ColorPrototype)manager["red"].Clone(false);
c0.Green = 300;
c1.Display();
ColorPrototype c2 = (ColorPrototype)manager["blue"].Clone(true);
c2.Display();
ColorPrototype c3 = (ColorPrototype)manager["blue"].Clone(true);
c3.Green = 300;
c3.Display();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
Prototype模式允许客户只通过注册原型实例就可以将一个具体产品类并入到系统中,客户可以在运行时刻建立和删除原型。
Prototype模式的最主要缺点就是每一个类必须配备一个克隆方法。而且这个克隆方法需要对类的功能进行通盘考虑,这对全新的类来说不是很难,但对已有的类进行改造时,不一定是件容易的事。


