Spring系列-3.3 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
Spring版本:Spring 5.2.9.BUILD-SNAPSHOT
修改过部分源码,但不影响主体流程
概述#
该BeanPostProcessor为每个bean进行属性自动装配。这里支持的自动装配注解有:
-
@Autowired -
@Value -
@Inject (JSR-330)– 仅在@Inject类存在于classpath的情况才支持它
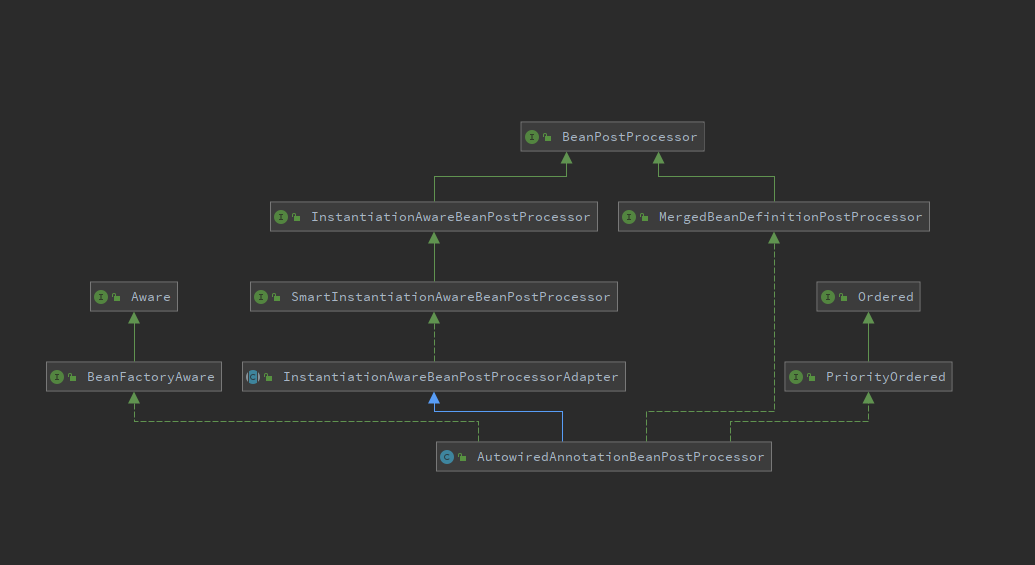
类图#
可以看到AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor继承InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter类、实现MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor、PriorityOrdered、BeanFactoryAware接口。
注册时机#
AnnotationConfigUtils#registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(BeanDefinitionRegistry, Object);
// 注册内部管理的用于处理@Autowired,@Value,@Inject以及@Lookup注解的后置处理器bean
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
源码解析#
determineCandidateConstructors#
determineCandidateConstructors方法是InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter接口中的方法。其作用是从bean的所有构造函数中过滤出可以作为构造注入的构造函数列表。
调用时机#
createBeanInstance -> determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors(beanClass, beanName) -> ibp.determineCandidateConstructors(beanClass, beanName)
/**
* 确定用于给定bean的候选构造函数,使用bean的后置处理器机制
*
* Determine candidate constructors to use for the given bean, checking all registered
* {@link SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors}.
* @param beanClass the raw class of the bean
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the candidate constructors, or {@code null} if none specified
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.config.SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#determineCandidateConstructors
*/
@Nullable
protected Constructor<?>[] determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors(@Nullable Class<?> beanClass, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
if (beanClass != null && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
// 从SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor判断
SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
Constructor<?>[] ctors = ibp.determineCandidateConstructors(beanClass, beanName);
if (ctors != null) {
return ctors;
}
}
}
}
return null;
}
源码#
/**
* 获取构造器集合
* 如果有多个Autowired,required为true,不管有没有默认构造方法,会报异常
* 如果只有一个Autowired,required为false,没有默认构造方法,会报警告
* 如果没有Autowired注解,定义了两个及以上有参数的构造方法,没有无参构造方法,就会报错 ???
* 其他情况都可以,但是以有Autowired的构造方法优先,然后才是默认构造方法
*
*
* @param beanClass
* @param beanName
* @return
* @throws BeanCreationException
*/
@Override
@Nullable
public Constructor<?>[] determineCandidateConstructors(Class<?> beanClass, final String beanName)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Let's check for lookup methods here...
// 处理包含@Loopup注解的方法,如果集合中没有beanName,则走一遍bean中的所有方法,过滤是否含有lookup方法
if (!this.lookupMethodsChecked.contains(beanName)) {
if (AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(beanClass, Lookup.class)) {
try {
Class<?> targetClass = beanClass;
do {
// 遍历当前类以及所有父类,找出lookup注解的方法进行处理
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {
// 获取method上的Lookup注解
Lookup lookup = method.getAnnotation(Lookup.class);
// 存在此注解的话,就将方法和注解中的内容构建LookupOverride对象,设置进BeanDefinition中
if (lookup != null) {
Assert.state(this.beanFactory != null, "No BeanFactory available");
LookupOverride override = new LookupOverride(method, lookup.value());
try {
RootBeanDefinition mbd = (RootBeanDefinition)
this.beanFactory.getMergedBeanDefinition(beanName);
mbd.getMethodOverrides().addOverride(override);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Cannot apply @Lookup to beans without corresponding bean definition");
}
}
});
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
}
//遍历父类,直到Object
while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Lookup method resolution failed", ex);
}
}
// 无论对象中是否含有@Lookup方法,过滤完成后都会放到集合中,证明此bean已经检查完@Lookup注解
this.lookupMethodsChecked.add(beanName);
}
// Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.
// 从缓存中拿构造函数,不存在的话就进入代码块中再拿一遍,还不存在的话就进行下方的逻辑,
Constructor<?>[] candidateConstructors = this.candidateConstructorsCache.get(beanClass);
// 没找到再同步
if (candidateConstructors == null) {
// Fully synchronized resolution now...
synchronized (this.candidateConstructorsCache) {
//再检测一遍,双重检测
candidateConstructors = this.candidateConstructorsCache.get(beanClass);
if (candidateConstructors == null) {
Constructor<?>[] rawCandidates;
try {
//获取bean中所有的构造函数
rawCandidates = beanClass.getDeclaredConstructors();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Resolution of declared constructors on bean Class [" + beanClass.getName() +
"] from ClassLoader [" + beanClass.getClassLoader() + "] failed", ex);
}
// 暂时候选构造函数集合,
List<Constructor<?>> candidates = new ArrayList<>(rawCandidates.length);
// 带有依赖项的构造函数
Constructor<?> requiredConstructor = null;
// 默认使用的构造函数
Constructor<?> defaultConstructor = null;
// 获取主构造函数
Constructor<?> primaryConstructor = BeanUtils.findPrimaryConstructor(beanClass);
// 标识,表示不是合成构造函数的数量
// 合成构造函数->有方法参数并对实例进行赋值的构造函数
int nonSyntheticConstructors = 0;
// 遍历所有的构造函数
for (Constructor<?> candidate : rawCandidates) {
// 构造函数不是合成构造函数,标识累加
if (!candidate.isSynthetic()) {
nonSyntheticConstructors++;
}
else if (primaryConstructor != null) {
continue;
}
// 查找构造函数上@Autowired注解的属性,
MergedAnnotation<?> ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(candidate);
// 注解不存在,则再通过方法获取用户类,如果是用户类则返回用户类,还判断了cglib的情况,cglib情况则返回目标类
// 然后获取参数一致的构造函数再获取注解
if (ann == null) {
Class<?> userClass = ClassUtils.getUserClass(beanClass);
// 如果是有代理的,找到被代理
if (userClass != beanClass) {
try {
// 获取构造方法
Constructor<?> superCtor =
userClass.getDeclaredConstructor(candidate.getParameterTypes());
//继续寻找Autowired和value的注解
ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(superCtor);
}
catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
// Simply proceed, no equivalent superclass constructor found...
}
}
}
// 构造函数上存在注解
if (ann != null) {
//有两个Autowired注解,冲突了
if (requiredConstructor != null) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Invalid autowire-marked constructor: " + candidate +
". Found constructor with 'required' Autowired annotation already: " +
requiredConstructor);
}
// 获取@Autowired注解中required属性的值
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
// 为true则将这个构造函数设置为带有依赖项的构造函数并进行判断,不可存在多个带有依赖项的构造函数
if (required) {
//如果已经有required=false了,又来了一个required=true的方法就报异常了,这样两个可能就不知道用哪个了
if (!candidates.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Invalid autowire-marked constructors: " + candidates +
". Found constructor with 'required' Autowired annotation: " +
candidate);
}
requiredConstructor = candidate;
}
// 加入集合
candidates.add(candidate);
}
// 如果构造函数的参数为零,则是默认构造函数
else if (candidate.getParameterCount() == 0) {
defaultConstructor = candidate;
}
}
// 存在@Autowired注解的函数,并且required值为false,则此注解不起作用,但是存在默认构造函数
// 则将默认构造函数添加到集合中,并将集合变为数组使用
if (!candidates.isEmpty()) {
// Add default constructor to list of optional constructors, as fallback.
if (requiredConstructor == null) {
if (defaultConstructor != null) {
//添加默认构造函数
candidates.add(defaultConstructor);
}
else if (candidates.size() == 1 && logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Inconsistent constructor declaration on bean with name '" + beanName +
"': single autowire-marked constructor flagged as optional - " +
"this constructor is effectively required since there is no " +
"default constructor to fall back to: " + candidates.get(0));
}
}
candidateConstructors = candidates.toArray(new Constructor<?>[0]);
}
// 如果只存在一个构造函数,且这个构造函数有参数列表,则使用这个构造函数
else if (rawCandidates.length == 1 && rawCandidates[0].getParameterCount() > 0) {
//只有一个函数且有参数
candidateConstructors = new Constructor<?>[] {rawCandidates[0]};
}
// 如果非合成构造存在两个且有主构造和默认构造,且主构造和默认构造不相等,则这两个一块使用
else if (nonSyntheticConstructors == 2 && primaryConstructor != null &&
defaultConstructor != null && !primaryConstructor.equals(defaultConstructor)) {
//有两个非合成方法,有优先方法和默认方法,且不相同
candidateConstructors = new Constructor<?>[] {primaryConstructor, defaultConstructor};
}
// 如果只有一个非合成构造且有主构造,使用主构造
else if (nonSyntheticConstructors == 1 && primaryConstructor != null) {
//只有一个优先的
candidateConstructors = new Constructor<?>[] {primaryConstructor};
}
// 否则没有能够直接使用的构造
else {
//大于2个没注解的构造方法就不知道要用什么了,所以就返回null
candidateConstructors = new Constructor<?>[0];
}
this.candidateConstructorsCache.put(beanClass, candidateConstructors);
}
}
}
// 使用构造列表中没有值,则返回null
return (candidateConstructors.length > 0 ? candidateConstructors : null);
}
核心流程#
-
解析
@Lookup注解的方法,保存到RootBeanDefinition中。 -
从缓存中拿构造函数,不存在的话就进入代码块中再拿一遍,存在就返回。
-
通过反射获取
bean中所有的构造函数并进行筛选,筛选每个构造函数是否被@Autowired、@Inject、@Value注解修饰。 -
判断当前
bean是否是Cglib动态代理类,如果是,则获取原始类的构造函数,再判断构造函数是否被@Autowired、@Inject、@Value注解修饰。 -
按照指定的规则来筛选并返回构造方法列表。
postProcessMergedBeanDefinition#
-
处理合并的
bean定义信息。 -
解析
@Autowired等注解然后转换。 -
把注解信息转换为
InjectionMetadata然后缓存到上面的injectionMetadataCache里面。
调用时机#
doCreateBean -> applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName) -> bdp.postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanType, beanName)
/**
* 应用MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors类型的beanPostProcessor到指定的beanDefinition中,
* 执行postProcessMergedBeanDefinition方法
*
* Apply MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors to the specified bean definition,
* invoking their {@code postProcessMergedBeanDefinition} methods.
* @param mbd the merged bean definition for the bean
* @param beanType the actual type of the managed bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @see MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor#postProcessMergedBeanDefinition
*/
protected void applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(RootBeanDefinition mbd, Class<?> beanType, String beanName) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor bdp = (MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) bp;
bdp.postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
}
}
源码#
/**
* 处理合并的bean定义信息
* 1、解析@Autowired等注解然后转换
* 2、把注解信息转换为InjectionMetadata然后缓存到上面的injectionMetadataCache里面
* @param beanDefinition the merged bean definition for the bean
* @param beanType the actual type of the managed bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
*/
@Override
public void postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition, Class<?> beanType, String beanName) {
// 解析注解并缓存
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, beanType, null);
metadata.checkConfigMembers(beanDefinition);
}
/**
* 方法名为查找到该bean的依赖注入元信息,内部只要查找到了就会加入到缓存内,下次没必要再重复查找了~
* 它是一个模版方法,真正做事的方法是:buildAutowiringMetadata,它复杂把标注有@Autowired注解的属性转换为Metadata元数据信息,从而消除注解的定义
* 此处查找包括了字段依赖注入和方法依赖注入~~~
* @param beanName
* @param clazz
* @param pvs
* @return
*/
private InjectionMetadata findAutowiringMetadata(String beanName, Class<?> clazz, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) {
// Fall back to class name as cache key, for backwards compatibility with custom callers.
String cacheKey = (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) ? beanName : clazz.getName());
// Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.
// 从缓存中获取该类的信息
InjectionMetadata metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
// 判断是否需要刷新缓存
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
synchronized (this.injectionMetadataCache) {
metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
if (metadata != null) {
metadata.clear(pvs);
}
// 构建自动装配的属性和方法元数据
metadata = buildAutowiringMetadata(clazz);
this.injectionMetadataCache.put(cacheKey, metadata);
}
}
}
return metadata;
}
postProcessProperties#
完成bean中@Autowired,@Inject,@Value注解的解析并注入的功能
调用时机#
doCreateBean -> populateBean -> postProcessProperties
源码#
/**
* 完成bean中@Autowired,@Inject,@Value注解的解析并注入的功能
* @param pvs
* @param bean
* @param beanName
* @return
*/
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) {
// 从缓存中取出这个bean对应的依赖注入的元信息~
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);
try {
// 进行属性注入
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of autowired dependencies failed", ex);
}
return pvs;
}
findAutowiringMetadata#
/**
* 方法名为查找到该bean的依赖注入元信息,内部只要查找到了就会加入到缓存内,下次没必要再重复查找了~
* 它是一个模版方法,真正做事的方法是:buildAutowiringMetadata,它复杂把标注有@Autowired注解的属性转换为Metadata元数据信息,从而消除注解的定义
* 此处查找包括了字段依赖注入和方法依赖注入~~~
* @param beanName
* @param clazz
* @param pvs
* @return
*/
private InjectionMetadata findAutowiringMetadata(String beanName, Class<?> clazz, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) {
// Fall back to class name as cache key, for backwards compatibility with custom callers.
String cacheKey = (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) ? beanName : clazz.getName());
// Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.
// 从缓存中获取该类的信息
InjectionMetadata metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
// 判断是否需要刷新缓存
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
synchronized (this.injectionMetadataCache) {
metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
if (metadata != null) {
metadata.clear(pvs);
}
// 构建自动装配的属性和方法元数据
metadata = buildAutowiringMetadata(clazz);
this.injectionMetadataCache.put(cacheKey, metadata);
}
}
}
return metadata;
}
buildAutowiringMetadata#
/**
* 去寻找有Autowired和Value注解的属性和方法,也包括自定义的父类的,封装成AutowiredMethodElement放入集合中
* @param clazz
* @return
*/
private InjectionMetadata buildAutowiringMetadata(final Class<?> clazz) {
// 如果clazz是JDK中的类,直接忽略,因为不可能标注有这些标注
if (!AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(clazz, this.autowiredAnnotationTypes)) {
return InjectionMetadata.EMPTY;
}
List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> elements = new ArrayList<>();
Class<?> targetClass = clazz;
do {
final List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> currElements = new ArrayList<>();
// 遍历类中的每个属性,判断属性是否包含指定的属性(通过 findAutowiredAnnotation 方法)
// 如果存在则保存,这里注意,属性保存的类型是 AutowiredFieldElement
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalFields(targetClass, field -> {
MergedAnnotation<?> ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(field);
if (ann != null) {
//Autowired注解不支持静态方法
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static fields: " + field);
}
return;
}
//查看是否是required的
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
currElements.add(new AutowiredFieldElement(field, required));
}
});
// 遍历类中的每个方法,判断属性是否包含指定的属性(通过 findAutowiredAnnotation 方法)
// 如果存在则保存,这里注意,方法保存的类型是 AutowiredMethodElement
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {
Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);
if (!BridgeMethodResolver.isVisibilityBridgeMethodPair(method, bridgedMethod)) {
return;
}
MergedAnnotation<?> ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(bridgedMethod);
if (ann != null && method.equals(ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, clazz))) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static methods: " + method);
}
return;
}
// 如果方法没有入参,输出日志,不做任何处理
if (method.getParameterCount() == 0) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation should only be used on methods with parameters: " +
method);
}
}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);
// AutowiredMethodElement里封装了一个PropertyDescriptor(比字段多了一个参数)
currElements.add(new AutowiredMethodElement(method, required, pd));
}
});
// 父类的都放在第一位,所以父类是最先完成依赖注入的
elements.addAll(0, currElements);
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
}
while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
// InjectionMetadata就是对clazz和elements的一个包装而已
return InjectionMetadata.forElements(elements, clazz);
}
metadata.inject#
/**
* 遍历前面注册的InjectedElement,然后进行注入
* @param target
* @param beanName
* @param pvs
* @throws Throwable
*/
public void inject(Object target, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Collection<InjectedElement> checkedElements = this.checkedElements;
Collection<InjectedElement> elementsToIterate =
(checkedElements != null ? checkedElements : this.injectedElements);
if (!elementsToIterate.isEmpty()) {
for (InjectedElement element : elementsToIterate) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Processing injected element of bean '" + beanName + "': " + element);
}
element.inject(target, beanName, pvs);
}
}
}
element.inject#
/**
* 进行属性或者方法注入,但是方法注入前会判断是否已经有设置值了,有设置就不会注入,直接返回
*
* Either this or {@link #getResourceToInject} needs to be overridden.
*/
protected void inject(Object target, @Nullable String requestingBeanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs)
throws Throwable {
// 属性注入
if (this.isField) {
Field field = (Field) this.member;
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);
// 如果是使用字段形式的注入,getResourceToInject由子类@ResourceElement实现
field.set(target, getResourceToInject(target, requestingBeanName));
}
else {
// 此步骤检测如果bean已经显示的设置一个对象依赖引用则跳过使用setter方法再次赋值
if (checkPropertySkipping(pvs)) {
return;
}
try {
// 方法注入
Method method = (Method) this.member;
// 支持私有方法
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(method);
method.invoke(target, getResourceToInject(target, requestingBeanName));
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw ex.getTargetException();
}
}
}
总结#
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的属性注入是通过类型注入的,如果是属性,则直接从Spring容器中根据类型获取bean,通过反射赋值。如果是方法,则获取方法的参数列表,从容器中获取对应的参数,获取到后通过反射调用方法。




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 【杭电多校比赛记录】2025“钉耙编程”中国大学生算法设计春季联赛(1)