Spring系列-3.1 registerBeanPostProcessors
Spring版本:Spring 5.2.9.BUILD-SNAPSHOT
修改过部分源码,但不影响主体流程
概述
BeanPostProcessor接口是Spring初始化bean时对外暴露的扩展点,Spring IoC容器允许BeanPostProcessor在容器初始化bean的前后,添加自己的逻辑处理。在registerBeanPostProcessors方法只是注册到BeanFactory中,具体调用是在bean初始化的时候。
调用时机:在所有bean实例化时,执行初始化方法前会调用所有BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法,在执行初始化方法后会调用所有BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization方法。
BeanPostProcessor
/**
* bean的后置处理器接口,在依赖注入的初始化方法前后进行调用
*
* Factory hook that allows for custom modification of new bean instances —
* for example, checking for marker interfaces or wrapping beans with proxies.
*
* <p>Typically, post-processors that populate beans via marker interfaces
* or the like will implement {@link #postProcessBeforeInitialization},
* while post-processors that wrap beans with proxies will normally
* implement {@link #postProcessAfterInitialization}.
*
* <h3>Registration</h3>
* <p>An {@code ApplicationContext} can autodetect {@code BeanPostProcessor} beans
* in its bean definitions and apply those post-processors to any beans subsequently
* created. A plain {@code BeanFactory} allows for programmatic registration of
* post-processors, applying them to all beans created through the bean factory.
*
* <h3>Ordering</h3>
* <p>{@code BeanPostProcessor} beans that are autodetected in an
* {@code ApplicationContext} will be ordered according to
* {@link org.springframework.core.PriorityOrdered} and
* {@link org.springframework.core.Ordered} semantics. In contrast,
* {@code BeanPostProcessor} beans that are registered programmatically with a
* {@code BeanFactory} will be applied in the order of registration; any ordering
* semantics expressed through implementing the
* {@code PriorityOrdered} or {@code Ordered} interface will be ignored for
* programmatically registered post-processors. Furthermore, the
* {@link org.springframework.core.annotation.Order @Order} annotation is not
* taken into account for {@code BeanPostProcessor} beans.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Sam Brannen
* @since 10.10.2003
* @see InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
* @see DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor
* @see ConfigurableBeanFactory#addBeanPostProcessor
* @see BeanFactoryPostProcessor
*/
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* 初始化方法调用前要进行的处理逻辑
*
* Apply this {@code BeanPostProcessor} to the given new bean instance <i>before</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* <p>The default implementation returns the given {@code bean} as-is.
* @param bean the new bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one;
* if {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
*/
@Nullable
default Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
/**
* 在初始化方法指定后要进行的处理逻辑
*
* Apply this {@code BeanPostProcessor} to the given new bean instance <i>after</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* <p>In case of a FactoryBean, this callback will be invoked for both the FactoryBean
* instance and the objects created by the FactoryBean (as of Spring 2.0). The
* post-processor can decide whether to apply to either the FactoryBean or created
* objects or both through corresponding {@code bean instanceof FactoryBean} checks.
* <p>This callback will also be invoked after a short-circuiting triggered by a
* {@link InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation} method,
* in contrast to all other {@code BeanPostProcessor} callbacks.
* <p>The default implementation returns the given {@code bean} as-is.
* @param bean the new bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one;
* if {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean
*/
@Nullable
default Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
}
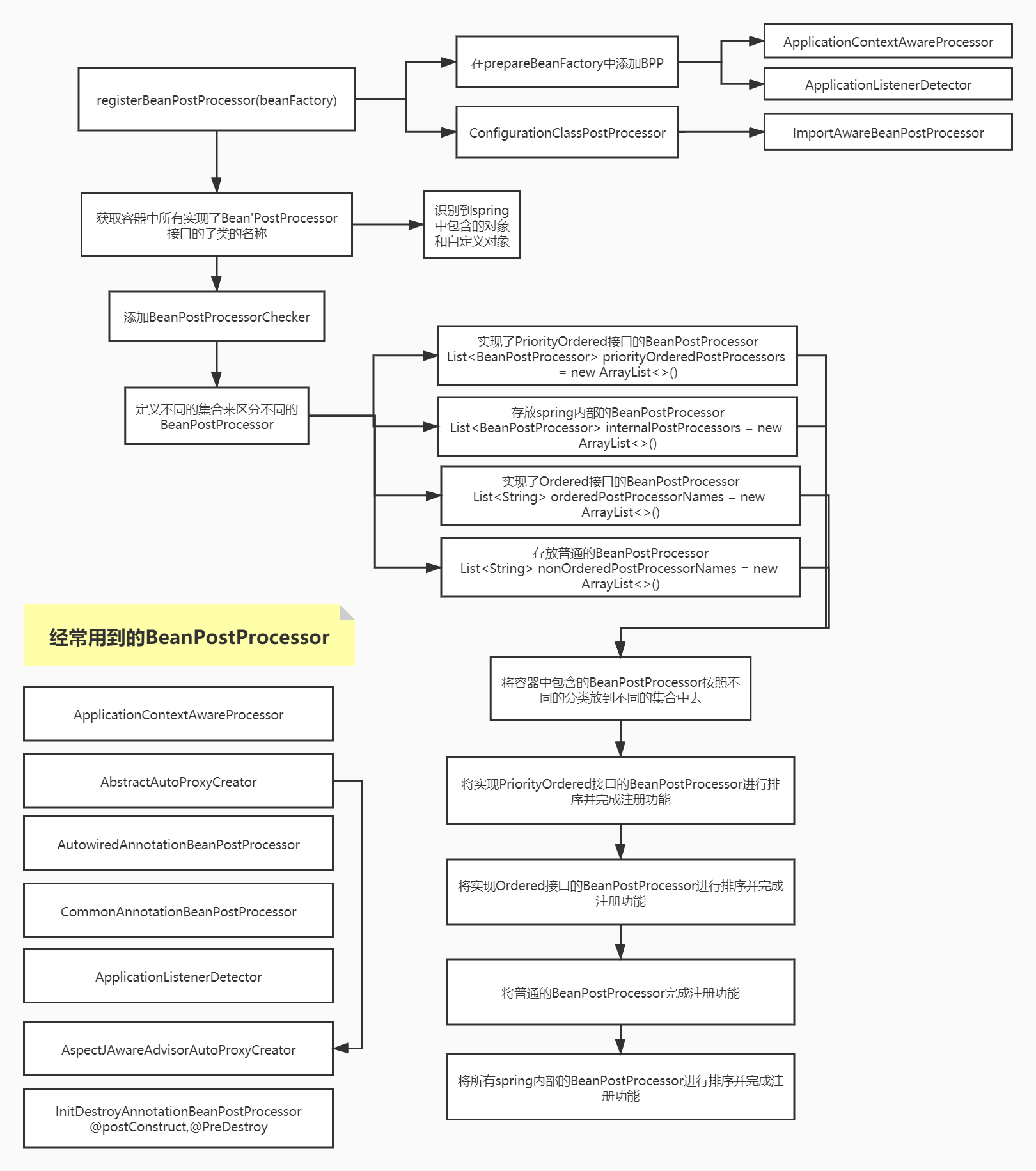
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory)
/**
* 实例化并且注册所有的beanPostProcessor
* 处理PriorityOrdered、Ordered接口,Bean的执行顺序的优先级
* Instantiate and register all BeanPostProcessor beans,
* respecting explicit order if given.
* <p>Must be called before any instantiation of application beans.
*/
protected void registerBeanPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, this);
}
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory,applicationContext)
/**
* 注册beanPostProcessor
* @param beanFactory
* @param applicationContext
*/
public static void registerBeanPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) {
// 找到所有实现了BeanPostProcessor接口的类
String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when
// a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when
// a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors.
// 记录下BeanPostProcessor的目标计数
// 此处为什么要+1呢,原因非常简单,在此方法的最后会添加一个BeanPostProcessorChecker的类
int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length;
// 添加BeanPostProcessorChecker(主要用于记录信息)到beanFactory中
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount));
// Separate between BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
// 定义存放实现了PriorityOrdered接口的BeanPostProcessor集合
List<BeanPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// 定义存放spring内部的BeanPostProcessor
List<BeanPostProcessor> internalPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// 定义存放实现了Ordered接口的BeanPostProcessor的name集合
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
// 定义存放普通的BeanPostProcessor的name集合
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
// 遍历beanFactory中存在的BeanPostProcessor的集合postProcessorNames,
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
// 如果ppName对应的BeanPostProcessor实例实现了PriorityOrdered接口,则获取到ppName对应的BeanPostProcessor的实例添加到priorityOrderedPostProcessors中
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
// 如果ppName对应的BeanPostProcessor实例也实现了MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor接口,那么则将ppName对应的bean实例添加到internalPostProcessors中
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
// 如果ppName对应的BeanPostProcessor实例没有实现PriorityOrdered接口,但是实现了Ordered接口,那么将ppName对应的bean实例添加到orderedPostProcessorNames中
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
} else {
// 否则将ppName添加到nonOrderedPostProcessorNames中
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// First, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
// 首先,对实现了PriorityOrdered接口的BeanPostProcessor实例进行排序操作
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 注册实现了PriorityOrdered接口的BeanPostProcessor实例添加到beanFactory中
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
// Next, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
// 注册所有实现Ordered的beanPostProcessor
List<BeanPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
// 根据ppName找到对应的BeanPostProcessor实例对象
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
// 将实现了Ordered接口的BeanPostProcessor添加到orderedPostProcessors集合中
orderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
// 如果ppName对应的BeanPostProcessor实例也实现了MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor接口,那么则将ppName对应的bean实例添加到internalPostProcessors中
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
// 对实现了Ordered接口的BeanPostProcessor进行排序操作
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 注册实现了Ordered接口的BeanPostProcessor实例添加到beanFactory中
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);
// Now, register all regular BeanPostProcessors.
// 创建存放没有实现PriorityOrdered和Ordered接口的BeanPostProcessor的集合
List<BeanPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size());
// 遍历集合
for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
// 根据ppName找到对应的BeanPostProcessor实例对象
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
// 将没有实现PriorityOrdered和Ordered接口的BeanPostProcessor添加到nonOrderedPostProcessors集合中
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
// 如果ppName对应的BeanPostProcessor实例也实现了MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor接口,那么则将ppName对应的bean实例添加到internalPostProcessors中
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
// 注册没有实现PriorityOrdered和Ordered的BeanPostProcessor实例添加到beanFactory中
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors);
// Finally, re-register all internal BeanPostProcessors.
// 将所有实现了MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor类型的BeanPostProcessor进行排序操作
sortPostProcessors(internalPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 注册所有实现了MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor类型的BeanPostProcessor到beanFactory中
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors);
// Re-register post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners,
// moving it to the end of the processor chain (for picking up proxies etc).
// 注册ApplicationListenerDetector到beanFactory中
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(applicationContext));
}
-
获取实现了
BeanPostProcessor的beanName,最开始Bean的信息注册到了beandifinitionMap中。 -
将获取到的
BeanPostProcessor分类,分为PriorityOrdered、internal、Ordered、nonOrdered的类型。 -
分别将
PriorityOrdered、internal、Ordered、nonOrdered的BeanPostProcessor排序后添加进ApplicationContext的beanPostProcessors中。
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory,postProcessors)
/**
* 注册给定的BeanPostProcessor类型Bean对象
*
* Register the given BeanPostProcessor beans.
*/
private static void registerBeanPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanPostProcessor> postProcessors) {
// 遍历postProcessors
for (BeanPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
//将 postProcessor 添加到beanFactory,它将应用于该工厂创建的Bean。在工厂配置期间调用
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(postProcessor);
}
}
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(postProcessor)
@Override
public void addBeanPostProcessor(BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor) {
Assert.notNull(beanPostProcessor, "BeanPostProcessor must not be null");
// 后添加的BeanPostProcessor会覆盖之前的,先删除,然后在添加
// Remove from old position, if any
// 从老的位置移除此beanPostProcessor
this.beanPostProcessors.remove(beanPostProcessor);
// Track whether it is instantiation/destruction aware
// 此处是为了设置某些状态变量,这些状态变量会影响后续的执行流程,只需要判断是否是指定的类型,然后设置标志位即可
if (beanPostProcessor instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
// 该变量表示beanfactory是否已注册过InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
this.hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors = true;
}
if (beanPostProcessor instanceof DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
// 该变量表示beanfactory是否已注册过DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor
this.hasDestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors = true;
}
// Add to end of list
// 将beanPostProcessor添加到beanPostProcessors缓存中
this.beanPostProcessors.add(beanPostProcessor);
}
总结