CompletableFuture源码阅读
1.以如下代码为例运行
CompletableFuture<String> task1 = new CompletableFuture<>();
CompletableFuture<String> task2 = task1.thenApply(s -> s + " 2");
CompletableFuture<String> task3 = task2.thenApply(s -> s + " 3");
task3.thenAccept((s) -> System.err.println(s));
CompletableFuture<String> task4 = task1.thenApply(s -> s + " x");
task4.thenAccept(s -> System.err.println(s));
task1.complete("1");
//1 x
//1 2 3
1.1方法thenApply
public class CompletableFuture<T> implements Future<T>, CompletionStage<T> {
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApply(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn) {
//直接看这个方法
return uniApplyStage(null, fn);
}
private <V> CompletableFuture<V> uniApplyStage(Executor e, Function<? super T,? extends V> f) {
if (f == null) throw new NullPointerException();
//创建了一个新的CompletableFuture
CompletableFuture<V> d = new CompletableFuture<V>();
//如果没有传入执行器,则直接尝试运行(Function f)详见1.1.1,尝试运行如果成功则不会运行if中内容
if (e != null || !d.uniApply(this, f, null)) {
//详见1.1.2
UniApply<T,V> c = new UniApply<T,V>(e, d, this, f);
//压栈
push(c);
//尝试执行c
c.tryFire(SYNC);
}
return d;
}
/** Pushes the given completion (if it exists) unless done. */
final void push(UniCompletion<?,?> c) {
if (c != null) {
while (result == null && !tryPushStack(c))
lazySetNext(c, null); // clear on failure
}
}
/** Returns true if successfully pushed c onto stack. */
/**
* 将c.next指向当前stack,将当前stack指向c
* before: stack->h,c
* after: c.next->h,stack->c
*/
final boolean tryPushStack(Completion c) {
Completion h = stack;
// c.next -> h
lazySetNext(c, h);
// this.stack -> c
return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, STACK, h, c);
}
static void lazySetNext(Completion c, Completion next) {
//c.next = next
UNSAFE.putOrderedObject(c, NEXT, next);
}
}
1.2方法uniApply
public class CompletableFuture<T> implements Future<T>, CompletionStage<T> {
//该方法的目标是尝试执行f
final <S> boolean uniApply(CompletableFuture<S> a, Function<? super S,? extends T> f, UniApply<S,T> c) {
//结果
Object r;
//报错
Throwable x;
//上一步为空 || 上一步还没获取结果 || f为空 --> 直接返回false
if (a == null || (r = a.result) == null || f == null)
return false;
tryComplete: if (result == null) {
if (r instanceof AltResult) {
//上一步报错了
if ((x = ((AltResult)r).ex) != null) {
//将r封装成AltResult,并不再尝试执行,直接作为结果
completeThrowable(x, r);
break tryComplete;
}
r = null;
}
try {
if (c != null && !c.claim())
return false;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
S s = (S) r;
//运行f,将result替换为运行结果
completeValue(f.apply(s));
} catch (Throwable ex) {
completeThrowable(ex);
}
}
//返回true意味着已经运行结束了
return true;
}
final boolean completeThrowable(Throwable x) {
return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, RESULT, null,encodeThrowable(x));
}
final boolean completeValue(T t) {
return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, RESULT, null,(t == null) ? NIL : t);
}
}
1.3静态内部类UniApply、UniCompletion、Completion
public class CompletableFuture<T> implements Future<T>, CompletionStage<T> {
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
static final class UniApply<T,V> extends UniCompletion<T,V> {
Function<? super T,? extends V> fn;
UniApply(Executor executor, CompletableFuture<V> dep,CompletableFuture<T> src,
Function<? super T,? extends V> fn) {
super(executor, dep, src);
this.fn = fn;
}
final CompletableFuture<V> tryFire(int mode) {
CompletableFuture<V> d;
CompletableFuture<T> a;
//尝试执行 dep
if ((d = dep) == null || !d.uniApply(a = src, fn, mode > 0 ? null : this))
return null;
//置空用于标记此Completion已经执行完毕
dep = null;
src = null;
fn = null;
//dep的后续执行,
return d.postFire(a, mode);
}
}
abstract static class UniCompletion<T,V> extends Completion {
Executor executor; // executor to use (null if none)
CompletableFuture<V> dep; // the dependent to complete 依赖->下一个需要执行的
CompletableFuture<T> src; // source for action 源->当前需要执行的
UniCompletion(Executor executor, CompletableFuture<V> dep,
CompletableFuture<T> src) {
this.executor = executor;
this.dep = dep;
this.src = src;
}
//TODO 待研究
/**
* Returns true if action can be run. Call only when known to
* be triggerable. Uses FJ tag bit to ensure that only one
* thread claims ownership. If async, starts as task -- a
* later call to tryFire will run action.
*/
final boolean claim() {
Executor e = executor;
if (compareAndSetForkJoinTaskTag((short)0, (short)1)) {
if (e == null)
return true;
executor = null; // disable
e.execute(this);
}
return false;
}
final boolean isLive() {
//判断是否有依赖的CompletableFuture
return dep != null;
}
}
abstract static class Completion extends ForkJoinTask<Void>
implements Runnable, AsynchronousCompletionTask {
volatile Completion next; // Treiber stack link 驱动程序堆栈链接
/**
* Performs completion action if triggered, returning a
* dependent that may need propagation, if one exists.
*
* @param mode SYNC, ASYNC, or NESTED
*/
abstract CompletableFuture<?> tryFire(int mode);
/** Returns true if possibly still triggerable. Used by cleanStack. */
abstract boolean isLive();
public final void run() { tryFire(ASYNC); }
public final boolean exec() { tryFire(ASYNC); return true; }
public final Void getRawResult() { return null; }
public final void setRawResult(Void v) {}
}
}
1.4方法postComplete和postFire
public class CompletableFuture<T> implements Future<T>, CompletionStage<T> {
// Modes for Completion.tryFire. Signedness matters.
static final int SYNC = 0;
static final int ASYNC = 1;
static final int NESTED = -1;
// 递归直到当前任务以及dep的栈都为空为止
final void postComplete() {
/*
* On each step, variable f holds current dependents to pop
* and run. It is extended along only one path at a time,
* pushing others to avoid unbounded recursion.
*/
CompletableFuture<?> f = this;
Completion h;
//操作-> 将f.stack赋值给h || 当 f!=this 时将f再次赋值为this,将h赋值为this.stack
//判断-> h != null || (f != this && h != null)
while ((h = f.stack) != null || (f != this && (h = (f = this).stack) != null)) {
CompletableFuture<?> d;
Completion t;
//如果f中的stack字段值为h,则将f.stack替换为h.next(先循环执行stack,再执行stack.next)
if (f.casStack(h, t = h.next)) {
if (t != null) {
//TODO 待研究
if (f != this) {
pushStack(h);
continue;
}
//f.stack已经被赋予了h.next的值,所以h.next被拆卸
h.next = null; // detach
}
//此时f.stack已从h变为了h.next,h被出栈
//执行h
f = (d = h.tryFire(NESTED)) == null ? this : d;
}
}
}
}
/**
* Post-processing by dependent after successful UniCompletion
* tryFire. Tries to clean stack of source a, and then either runs
* postComplete or returns this to caller, depending on mode.
*/
final CompletableFuture<T> postFire(CompletableFuture<?> a, int mode) {
if (a != null && a.stack != null) {
if (mode < 0 || a.result == null)
a.cleanStack();
else
a.postComplete();
}
if (result != null && stack != null) {
if (mode < 0)
return this;
else
postComplete();
}
return null;
}
}
总结
CompletableFuture<String> task1 = new CompletableFuture<>();
CompletableFuture<String> task2 = task1.thenApply(s -> s + "2");
CompletableFuture<Void> task3 = task2.thenAccept(s -> System.err.println(s));
task1.complete("1");
执行到task1.complete("1")时task1的结构:
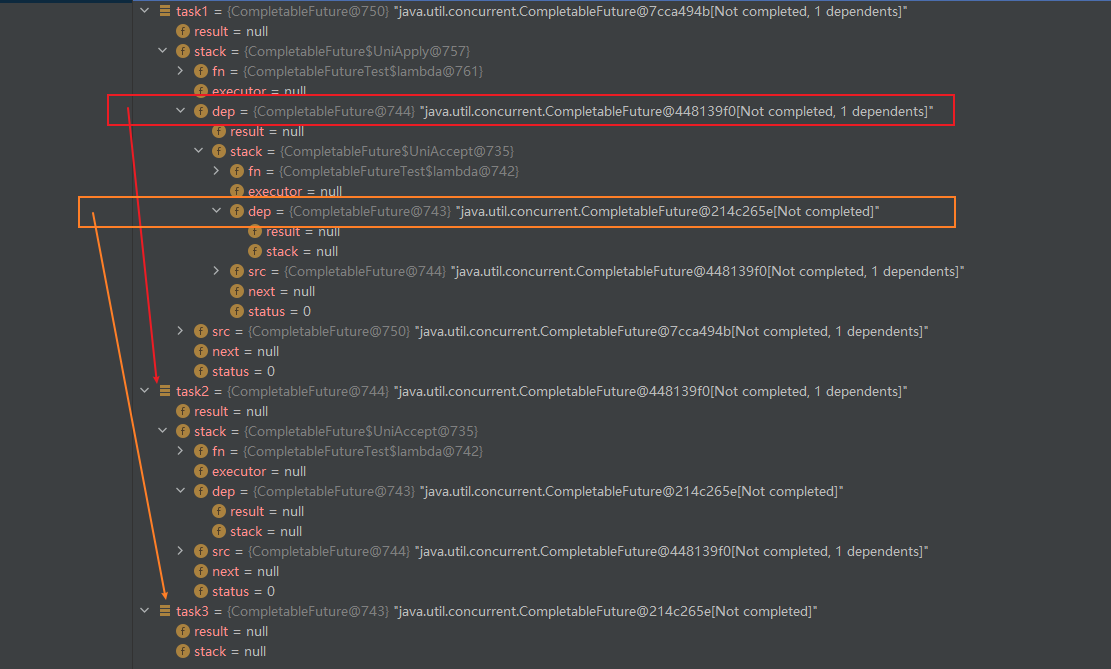
创建过程:
- 创建
task1
task1.stack = null
task1.result = null- 在task1的基础上创建后续任务task2
- 创建一个新的
CompletableFuture-->task2尝试直接执行task2,但由于task1仍未开始执行所以无法执行task2- 构造一个
Completion(这里将他称为c2)
- 执行器
executor(Executor)- 关联任务
dep(CompletableFuture-->task2)- 原始任务
src(CompletableFuture-->task1)- 关联任务待执行函数
fn(fn)- 将
c2压入task1的栈(stack)task.stack = c2 --next--> c1task2的栈仍然为null
- 将
c2.next替换为c1- 将
task1.stack替换为c2- 总结就是:
task1.stack =c2
task1.result = null
c2.executor = 入参executor
c2.dep = task2
c2.src = task1
c2.fn = 入参fn
c2.next = task1.stack = nulltask2.stack = null
task2.result = null- 在task2的基础上创建后续任务task3,同上(将task2看做task1,将task3看做task2)。
task2.stack = c3
task2.result = null
c3.executor = 入参executor
c3.dep = task3
c3.src = task2
c3.fn = 入参fn
c3.next = task2.stack = nulltask3.stack = null
task3.result = null执行过程:
- task1执行 -->
task1.result=1-->postComplete执行task1.stack.dep(task2)-->回到postComplete- task2执行 -->
task2.result=12-->- task3执行 --> 输出
12



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号