POI导出EXCEL经典实现
1.Apache POI简介
Apache POI是Apache软件基金会的开放源码函式库,POI提供API给Java程式对Microsoft Office格式档案读和写的功能。 .NET的开发人员则可以利用NPOI (POI for .NET) 来存取 POI 的功能。
2.POI结构
HSSF - 提供读写Microsoft Excel XLS格式档案的功能。
XSSF - 提供读写Microsoft Excel OOXML XLSX格式档案的功能。
HWPF - 提供读写Microsoft Word DOC格式档案的功能。
HSLF - 提供读写Microsoft PowerPoint格式档案的功能。
HDGF - 提供读Microsoft Visio格式档案的功能。
HPBF - 提供读Microsoft Publisher格式档案的功能。
HSMF - 提供读Microsoft Outlook格式档案的功能。
3.Busy Developers' Guide to HSSF and XSSF Features
官方网站:http://poi.apache.org/spreadsheet/quick-guide.html
参考博客:http://langhua9527.iteye.com/blog/388005
4.参考实例
引用:http://blog.csdn.net/lenolong/article/details/3957735
在web开发中,有一个经典的功能,就是数据的导入导出。特别是数据的导出,在生产管理或者财务系统中用的非常普遍,因为这些系统经常要做一些报表打印的 工作。而数据导出的格式一般是EXCEL或者PDF,我这里就用两篇文章分别给大家介绍下。(注意,我们这里说的数据导出可不是数据库中的数据导出!么误 会啦^_^)
呵呵,首先我们来导出EXCEL格式的文件吧。现在主流的操作Excel文件的开源工具有很多,用得比较多的就是Apache的POI及 JExcelAPI。这里我们用Apache POI!我们先去Apache的大本营下载POI的jar包:http://poi.apache.org/ ,我这里使用的是3.0.2版本。
将3个jar包导入到classpath下,什么?忘了怎么导包?不会吧!好,我们来写一个导出Excel的实用类(所谓实用,是指基本不用怎么修改就可 以在实际项目中直接使用的!)。我一直强调做类也好,做方法也好,一定要通用性和灵活性强。下面这个类就算基本贯彻了我的这种思想。那么,熟悉许老师风格 的人应该知道,这时候该要甩出一长串代码了。没错,大伙请看:
Student.java

package org.leno.export.util;
import java.util.Date;
public class Student {
private long id;
private String name;
private int age;
private boolean sex;
private Date birthday;
public Student() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Student(long id, String name, int age, boolean sex, Date birthday) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public boolean getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(boolean sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public Date getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
}
Book.java
 View Code
View Code
上面这两个类一目了然,就是两个简单的javabean风格的类。再看下面真正的重点类:
ExportExcel.java

package org.leno.export.util;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.*;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.util.HSSFColor;
/**
* 利用开源组件POI3.0.2动态导出EXCEL文档 转载时请保留以下信息,注明出处!
*
* @author leno
* @version v1.0
* @param <T>
* 应用泛型,代表任意一个符合javabean风格的类
* 注意这里为了简单起见,boolean型的属性xxx的get器方式为getXxx(),而不是isXxx()
* byte[]表jpg格式的图片数据
*/
public class ExportExcel<T> {
public void exportExcel(Collection<T> dataset, OutputStream out) {
exportExcel("测试POI导出EXCEL文档", null, dataset, out, "yyyy-MM-dd");
}
public void exportExcel(String[] headers, Collection<T> dataset,
OutputStream out) {
exportExcel("测试POI导出EXCEL文档", headers, dataset, out, "yyyy-MM-dd");
}
public void exportExcel(String[] headers, Collection<T> dataset,
OutputStream out, String pattern) {
exportExcel("测试POI导出EXCEL文档", headers, dataset, out, pattern);
}
/**
* 这是一个通用的方法,利用了JAVA的反射机制,可以将放置在JAVA集合中并且符号一定条件的数据以EXCEL 的形式输出到指定IO设备上
*
* @param title
* 表格标题名
* @param headers
* 表格属性列名数组
* @param dataset
* 需要显示的数据集合,集合中一定要放置符合javabean风格的类的对象。此方法支持的
* javabean属性的数据类型有基本数据类型及String,Date,byte[](图片数据)
* @param out
* 与输出设备关联的流对象,可以将EXCEL文档导出到本地文件或者网络中
* @param pattern
* 如果有时间数据,设定输出格式。默认为"yyy-MM-dd"
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void exportExcel(String title, String[] headers,
Collection<T> dataset, OutputStream out, String pattern) {
// 声明一个工作薄
HSSFWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook();
// 生成一个表格
HSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet(title);
// 设置表格默认列宽度为15个字节
sheet.setDefaultColumnWidth((short) 15);
// 生成一个样式
HSSFCellStyle style = workbook.createCellStyle();
// 设置这些样式
style.setFillForegroundColor(HSSFColor.SKY_BLUE.index);
style.setFillPattern(HSSFCellStyle.SOLID_FOREGROUND);
style.setBorderBottom(HSSFCellStyle.BORDER_THIN);
style.setBorderLeft(HSSFCellStyle.BORDER_THIN);
style.setBorderRight(HSSFCellStyle.BORDER_THIN);
style.setBorderTop(HSSFCellStyle.BORDER_THIN);
style.setAlignment(HSSFCellStyle.ALIGN_CENTER);
// 生成一个字体
HSSFFont font = workbook.createFont();
font.setColor(HSSFColor.VIOLET.index);
font.setFontHeightInPoints((short) 12);
font.setBoldweight(HSSFFont.BOLDWEIGHT_BOLD);
// 把字体应用到当前的样式
style.setFont(font);
// 生成并设置另一个样式
HSSFCellStyle style2 = workbook.createCellStyle();
style2.setFillForegroundColor(HSSFColor.LIGHT_YELLOW.index);
style2.setFillPattern(HSSFCellStyle.SOLID_FOREGROUND);
style2.setBorderBottom(HSSFCellStyle.BORDER_THIN);
style2.setBorderLeft(HSSFCellStyle.BORDER_THIN);
style2.setBorderRight(HSSFCellStyle.BORDER_THIN);
style2.setBorderTop(HSSFCellStyle.BORDER_THIN);
style2.setAlignment(HSSFCellStyle.ALIGN_CENTER);
style2.setVerticalAlignment(HSSFCellStyle.VERTICAL_CENTER);
// 生成另一个字体
HSSFFont font2 = workbook.createFont();
font2.setBoldweight(HSSFFont.BOLDWEIGHT_NORMAL);
// 把字体应用到当前的样式
style2.setFont(font2);
// 声明一个画图的顶级管理器
HSSFPatriarch patriarch = sheet.createDrawingPatriarch();
// 定义注释的大小和位置,详见文档
HSSFComment comment = patriarch.createComment(new HSSFClientAnchor(0,
0, 0, 0, (short) 4, 2, (short) 6, 5));
// 设置注释内容
comment.setString(new HSSFRichTextString("可以在POI中添加注释!"));
// 设置注释作者,当鼠标移动到单元格上是可以在状态栏中看到该内容.
comment.setAuthor("leno");
// 产生表格标题行
HSSFRow row = sheet.createRow(0);
for (short i = 0; i < headers.length; i++) {
HSSFCell cell = row.createCell(i);
cell.setCellStyle(style);
HSSFRichTextString text = new HSSFRichTextString(headers[i]);
cell.setCellValue(text);
}
// 遍历集合数据,产生数据行
Iterator<T> it = dataset.iterator();
int index = 0;
while (it.hasNext()) {
index++;
row = sheet.createRow(index);
T t = (T) it.next();
// 利用反射,根据javabean属性的先后顺序,动态调用getXxx()方法得到属性值
Field[] fields = t.getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (short i = 0; i < fields.length; i++) {
HSSFCell cell = row.createCell(i);
cell.setCellStyle(style2);
Field field = fields[i];
String fieldName = field.getName();
String getMethodName = "get"
+ fieldName.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase()
+ fieldName.substring(1);
try {
Class tCls = t.getClass();
Method getMethod = tCls.getMethod(getMethodName,
new Class[] {});
Object value = getMethod.invoke(t, new Object[] {});
// 判断值的类型后进行强制类型转换
String textValue = null;
// if (value instanceof Integer) {
// int intValue = (Integer) value;
// cell.setCellValue(intValue);
// } else if (value instanceof Float) {
// float fValue = (Float) value;
// textValue = new HSSFRichTextString(
// String.valueOf(fValue));
// cell.setCellValue(textValue);
// } else if (value instanceof Double) {
// double dValue = (Double) value;
// textValue = new HSSFRichTextString(
// String.valueOf(dValue));
// cell.setCellValue(textValue);
// } else if (value instanceof Long) {
// long longValue = (Long) value;
// cell.setCellValue(longValue);
// }
if (value instanceof Boolean) {
boolean bValue = (Boolean) value;
textValue = "男";
if (!bValue) {
textValue = "女";
}
} else if (value instanceof Date) {
Date date = (Date) value;
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat(pattern);
textValue = sdf.format(date);
} else if (value instanceof byte[]) {
// 有图片时,设置行高为60px;
row.setHeightInPoints(60);
// 设置图片所在列宽度为80px,注意这里单位的一个换算
sheet.setColumnWidth(i, (short) (35.7 * 80));
// sheet.autoSizeColumn(i);
byte[] bsValue = (byte[]) value;
HSSFClientAnchor anchor = new HSSFClientAnchor(0, 0,
1023, 255, (short) 6, index, (short) 6, index);
anchor.setAnchorType(2);
patriarch.createPicture(anchor, workbook.addPicture(
bsValue, HSSFWorkbook.PICTURE_TYPE_JPEG));
} else {
// 其它数据类型都当作字符串简单处理
textValue = value.toString();
}
// 如果不是图片数据,就利用正则表达式判断textValue是否全部由数字组成
if (textValue != null) {
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("^//d+(//.//d+)?$");
Matcher matcher = p.matcher(textValue);
if (matcher.matches()) {
// 是数字当作double处理
cell.setCellValue(Double.parseDouble(textValue));
} else {
HSSFRichTextString richString = new HSSFRichTextString(
textValue);
HSSFFont font3 = workbook.createFont();
font3.setColor(HSSFColor.BLUE.index);
richString.applyFont(font3);
cell.setCellValue(richString);
}
}
} catch (SecurityException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 清理资源
}
}
}
try {
workbook.write(out);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 测试学生
ExportExcel<Student> ex = new ExportExcel<Student>();
String[] headers = { "学号", "姓名", "年龄", "性别", "出生日期" };
List<Student> dataset = new ArrayList<Student>();
dataset.add(new Student(10000001, "张三", 20, true, new Date()));
dataset.add(new Student(20000002, "李四", 24, false, new Date()));
dataset.add(new Student(30000003, "王五", 22, true, new Date()));
// 测试图书
ExportExcel<Book> ex2 = new ExportExcel<Book>();
String[] headers2 = { "图书编号", "图书名称", "图书作者", "图书价格", "图书ISBN",
"图书出版社", "封面图片" };
List<Book> dataset2 = new ArrayList<Book>();
try {
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(
new FileInputStream("book.jpg"));
byte[] buf = new byte[bis.available()];
while ((bis.read(buf)) != -1) {
//
}
dataset2.add(new Book(1, "jsp", "leno", 300.33f, "1234567",
"清华出版社", buf));
dataset2.add(new Book(2, "java编程思想", "brucl", 300.33f, "1234567",
"阳光出版社", buf));
dataset2.add(new Book(3, "DOM艺术", "lenotang", 300.33f, "1234567",
"清华出版社", buf));
dataset2.add(new Book(4, "c++经典", "leno", 400.33f, "1234567",
"清华出版社", buf));
dataset2.add(new Book(5, "c#入门", "leno", 300.33f, "1234567",
"汤春秀出版社", buf));
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("E://a.xls");
OutputStream out2 = new FileOutputStream("E://b.xls");
ex.exportExcel(headers, dataset, out);
ex2.exportExcel(headers2, dataset2, out2);
out.close();
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "导出成功!");
System.out.println("excel导出成功!");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
不行,头有点晕^_^。呵呵,又是泛型,又是反射,又是正则表达式,又是重载,还有多参数列表和POI API。一下子蹦出来,实在让人吃不消。不管了,顶住看效果先。在本地运行后,我们发现在E://下生成了两份excel文件:学生记录和图书记录,并且 中文,数字,颜色,日期,图片等等一且正常。恩,太棒了。有人看到这里开始苦脸了:喂,我怎么一运行就报错啊!呵呵,看看什么错吧!哦,找不到文件,也就 是说你没有book.jpg嘛。好,拷贝一张小巧的图书图片命名为book.jpg放置到当前工程下吧。 注意,您千万别把张桌面大小的图片丢进去了^_^!看到效果了吧。现在我们再来简单梳理一下代码,实际上上面就做了一个导出excel的方法和一个本地测 试main()方法。并且代码的结构也很清晰,只是涉及的知识点稍微多一点。大家细心看看注释,结合要完成的功能,应该没有太大问题的。好啦,吃杯茶,擦 把汗,总算把这个类消化掉,你又进步了。咦,你不是说是在WEB环境下导出的吗?别急,因为导出就是一个下载的过程。我们只需要在服务器端写一个Jsp或 者Servlet组件完成输出excel到浏览器客户端的工作就好了。我们以Servlet为例,还是看代码吧:
Export.java
 View Code
View Code
写完之后,如果您不是用eclipse工具生成的Servlet,千万别忘了在web.xml上注册这个Servelt。我用的是Eclipse工具生成的servlet,自动注册了servlet,注册内容如下:

<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>Export</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/servlet/Export</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
而且同样的,拷贝一张小巧的图书图片命名为book.jpg放置到当前WEB根目录的/WEB-INF/下。部署好web工程,用浏览器访问Servlet看下效果吧!
我的访问地址是:http://localhost:8080/TestExportExcel/servlet/Export。 看看是不是下载成功了。呵呵,您可以将下载到本地的excel报表用打印机打印出来,这样您就大功告成了。完事了我们就思考:我们发现,我们做的方法,不 管是本地调用,还是在WEB服务器端用Servlet调用;不管是输出学生列表,还是图书列表信息,代码都几乎一样,而且这些数据我们很容器结合后台的 DAO操作数据库动态获取。恩,类和方法的通用性和灵活性开始有点感觉了。好啦,祝您学习愉快!
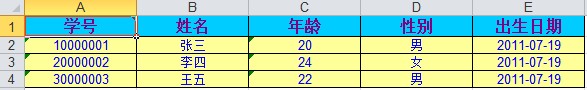
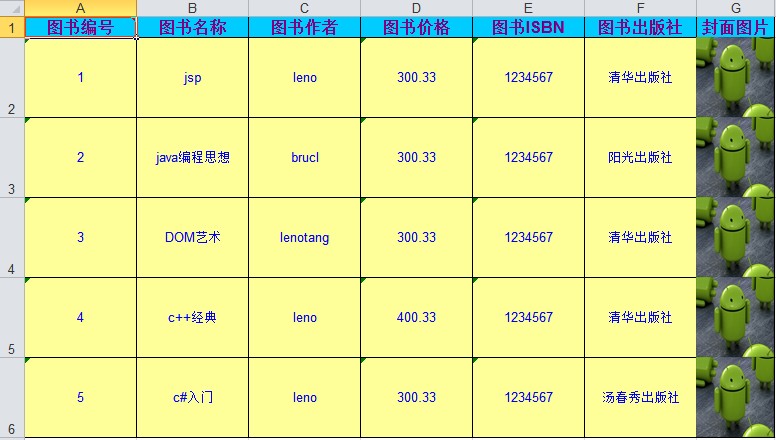
生成的两个excel文档内容分别如下,第一个是测试学生,第二个是测试图书。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号