ultra fast lane detection读后感及使用情况(附训练好的模型及libtorch端代码)
ultra fast lane detection提供了很好的源码,根据演示视频来看,效果似乎不赖,很有必要试一试该算法。
一、基本情况
作者知乎:超快的车道线检测 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
简单来说,作者认为卷积层形式的输出,导致局部感受野小,很明显车道线识别需要结合全局特征来分析。而全连接层形式的输出,运用了全局特征,也就没有感受野的问题。
另外,作者把这个问题转化为了分类问题。也就是如下图所示。
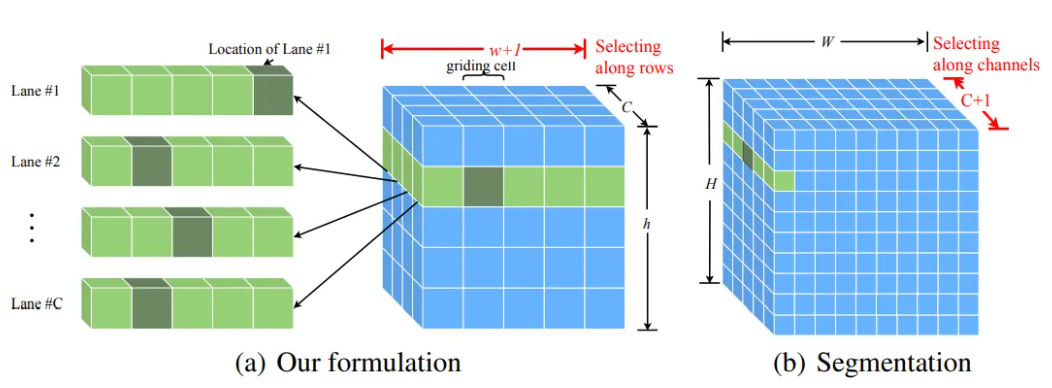
C是车道线数目,h和w则是图像长宽相关的cell,类似于锚点。w方向上的通道是w+1个,最后一位输出的是有无该通道。
大概意思,就是用h和w预测第c个车道的大概位置,然后按照下面的公式,算具体位置:
![]()
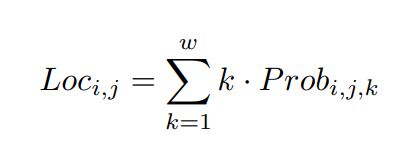
损失函数还考量到相邻的位置附近,因此有了,后两个损失函数就是邻近位置的二阶差分,邻近概率的差分。
二、使用情况
作者在github上已经给出了开源库。要求先设置configs下的py,我选了culane数据集(比较大,大概50多个G),因此修改了culane.py。
需要注意的是,culane数据集有黑夜的数据集,但貌似没有特殊天气的数据。
如果要使用tusimple数据集,要使用scripts下的convert_tusimple.py生成train_gt.txt。(运行时记得加 设置--root E:\tusimple数据集 )
之后就在pycharm进行了训练。
以下是笔者使用的libtorch C++端的代码,另外需要提醒一点(如果对数据的存储与运算不熟悉的话)
CPU类型下大多数函数都可以使用,但是推理速度比较慢。CUDA类型下并行速度快,但是有些函数不能用,遍历计算速度很慢,需要转为CPU类型。
#include <torch/script.h>
#include <torch/torch.h>
#include<ATen/ATen.h>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <windows.h>
using namespace torch::indexing;
using namespace std;
int tusimple_row_anchor[56] = {64, 68, 72, 76, 80, 84, 88, 92, 96, 100, 104, 108, 112,
116, 120, 124, 128, 132, 136, 140, 144, 148, 152, 156, 160, 164,
168, 172, 176, 180, 184, 188, 192, 196, 200, 204, 208, 212, 216,
220, 224, 228, 232, 236, 240, 244, 248, 252, 256, 260, 264, 268,
272, 276, 280, 284};
int culane_row_anchor[18] = {121, 131, 141, 150, 160, 170, 180, 189, 199, 209, 219, 228, 238, 248, 258, 267, 277, 287};
void tusimple_lane(at::Tensor& input, cv::Mat& img)
{
int lane_num = 4;
int length_cell = 56;
int width = 100;
int topk_n = 3;
double w_scale = img.cols / (double)width;
double h_scale = img.rows / (double)(length_cell*2);
input = input.to(torch::kCPU);//CPU for Ergodic computation,CUDA for Parallel computation
for (int i = 0; i < length_cell; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < lane_num; j++)
{
double lane_loc = 0;
double sum_w = 0;
double sum = 0;
auto cut = input.index({ Slice(torch::indexing::None),Slice(torch::indexing::None), Slice(i,i + 1), Slice(j,j + 1) });
cut = torch::softmax(cut, 1).view(-1);
if (cut[width].item<float>() > 0.5)
{
continue;
}
std::vector<float> tesnor2vec(cut.data_ptr<float>(), cut.data_ptr<float>() + cut.numel());
for (int s = 0; s < width; s++)
{
sum += tesnor2vec[s];
sum_w += tesnor2vec[s] * s;
}
lane_loc = (sum_w / sum) * w_scale;
//std::tuple<torch::Tensor, torch::Tensor> result = cut.topk(2, -1);
//auto top_scores = std::get<0>(result).view(-1);//{1,10} 变成 {10}
//auto top_idxs = std::get<1>(result).view(-1);
/*if (cut[width].item<float>() > 0.5)
{
continue;
}
if(top_idxs[0].item().toInt()!=width)
{
lane_loc = top_idxs[0].item().toInt() * w_scale;
}
else
{
lane_loc= top_idxs[1].item().toInt() * w_scale;
}*/
cv::Scalar temp;
switch (j)
{
case 0:
temp = cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0);
break;
case 1:
temp = cv::Scalar(255, 0, 0);
break;
case 2:
temp = cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0);
break;
case 3:
temp = cv::Scalar(0, 0, 255);
break;
}
cv::circle(img, cv::Point(lane_loc, tusimple_row_anchor[i]), 5, temp, -1);
}
}
//
void culane_lane(at::Tensor& input, cv::Mat& img)
{
int lane_num = 4;
int length_cell = 18;
int width = 200;
int topk_n =3;
double w_scale = img.cols/(double)width;
double h_scale = img.rows/(double)length_cell;
input = input.to(torch::kCPU);//CPU for Ergodic computation,CUDA for Parallel computation
for(int i=0;i<length_cell;i++)
for (int j = 0; j < lane_num; j++)
{
double lane_loc = 0;
double sum_w = 0;
double sum = 0;
auto cut = input.index({ Slice(torch::indexing::None),Slice(torch::indexing::None), Slice(i,i + 1), Slice(j,j + 1) });
cut = torch::softmax(cut, 1).view(-1);
if (cut[width].item<float>() > 0.5)
{
continue;
}
std::vector<float> tesnor2vec(cut.data_ptr<float>(), cut.data_ptr<float>() + cut.numel());
for (int s = 0; s < width; s++)
{
sum += tesnor2vec[s];
sum_w += tesnor2vec[s] * s;
}
lane_loc = (sum_w / sum )* w_scale;
cv::Scalar temp;
switch (j)
{
case 0:
temp = cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0);
break;
case 1:
temp = cv::Scalar(255, 0, 0);
break;
case 2:
temp = cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0);
break;
case 3:
temp = cv::Scalar(0, 0, 255);
break;
}
cv::circle(img, cv::Point(lane_loc, culane_row_anchor[i]), 5, temp, -1);
}
}
int main()
{
torch::jit::script::Module module = torch::jit::load("C:\\Users\\lvdon\\source\\repos\\C_test\\lane_det\\lane.torchscript_gpu.pt");
torch::DeviceType device_type = torch::kCUDA;
module.to(device_type);
module.eval();
cv::VideoCapture cap("G:\\视频\\弯道\\cv2_curve.mp4");
//cv::VideoWriter vw;
//vw.open("C:\\Users\\lvdon\\source\\repos\\C_test\\test.mp4", //路径
// CV_FOURCC('m', 'p', '4', 'v'), //编码格式
// 30, //帧率
// cv::Size(800,
// 288));//尺寸
cv::Mat img;
cv::Mat ori;
cap.read(img);
int width = img.size().width;
int height = img.size().height;
int count = 0;
while (true)
{
clock_t start = clock();
count++;
cap >> img;
if (img.empty())
{
cout << "play end" << endl;
break;
}
else if (count % 1 != 0)
{
continue;
}
//img = cv::imread("E:\\train_lane\\driver_182_30frame\\05312333_0003.MP4\\00000.jpg");
cv::resize(img, img, cv::Size(600, 288));
cv::copyMakeBorder(img, img,0, 0, 100, 100, cv::BORDER_CONSTANT, cv::Scalar(0, 0,0));
cv::cvtColor(img, img, cv::COLOR_BGR2RGB); // BGR -> RGB
img.convertTo(img, CV_32FC3, 1.0f / 255.0f); // normalization 1/255
auto tensor_img = torch::from_blob(img.data, { 1, img.rows, img.cols, img.channels() },torch::kFloat).to(device_type);
tensor_img = tensor_img.permute({ 0, 3, 1, 2 }).contiguous(); // BHWC -> BCHW (Batch, Channel, Height, Width)
std::vector<torch::jit::IValue> inputs;
inputs.emplace_back(tensor_img);
auto output = module.forward(inputs).toTensor();
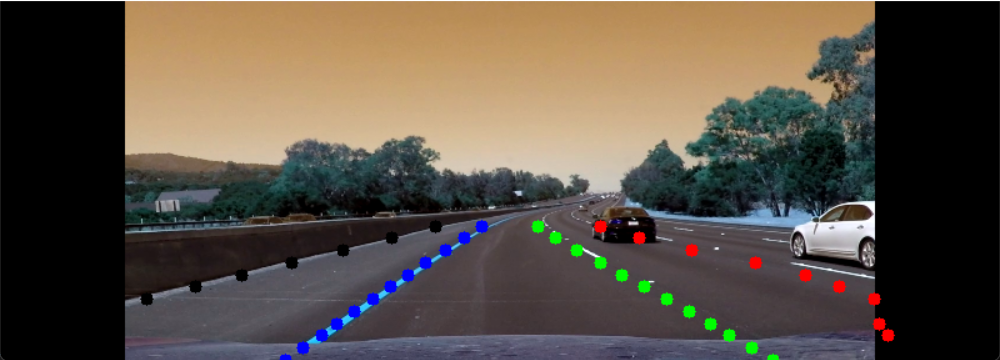
culane_lane(output,img);
cout << "cost time:" << clock() - start << endl;
//cv::imshow("result", img);
img.convertTo(img, CV_8UC3,255);//need to convert to CV_8UC3 for save the video
cv::imshow("result", img);
//vw << img;
//cv::imshow("result", img);
cv::waitKey(1);
}
return NULL;
}
模型链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1MZhkt87aWFb771gwUBxH6A?pwd=LDHL 提取码: LDHL
转载前,请注明来源。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号