使用Pytorch手动训练VGG11
在前面的博客中我们提到如何用pytorch搭建一个VGG11网络框架;
在本博客中,我们将使用之前搭建的VGG11网络,同时对其进行手动训练,使我们可以更好的理解模型建立和训练的过程;
主要内容:
- 数据集和目录结构——使用数字手写辨识来训练VGG11
- 编码部分:
1)数据集准备;
2)训练和验证模型;
3)优化器
4)验证每个epoch的精度;
- 分析训练的损失和精度;
- 在图像上训练和测试数据
一、数据集和目录结构
数据集:手写体 Digit MNIST
使用torchvision.dataset模块加载;
目录结构:
├── input │ └── test_data │ ├── eight.jpg │ ├── two.jpg │ └── zero.jpg ├── outputs │ ├── accuracy.jpg │ └── loss.jpg | ... ├── src │ ├── data │ │ └── MNIST │ ... │ ├── models.py │ ├── test.py │ └── train.py
二、 编码部分:
1) 网络模型脚本:VGG11模型的加载,见 使用Pytorch搭建VGG网络——以VGG11为例
2)训练脚本train.py的编写:
2.1)相关包的导入:
1 import torch 2 import torchvision 3 import torchvision.transforms as transforms 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 import matplotlib 6 import torch.nn as nn 7 import torch.optim as optim 8 from tqdm import tqdm 9 from models import VGG11 10 matplotlib.style.use('ggplot')
2.2)定义模型的参数及设备:
1 device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu') 2 print(f"[INFO]: Computation device: {device}") 3 epochs = 10 4 batch_size = 32
出现了OOM(out of memory)错误的话,可以减少batch到16、8或者4,来迎合你的GPU;
2.3) 图像变换
1 # our transforms will differ a bit from the VGG paper 2 # as we are using the MNIST dataset, so, we will directly resize... 3 # ... the images to 224x224 and not crop them and we will not use... 4 # ... any random flippings also 5 train_transform = transforms.Compose( 6 [transforms.Resize((224, 224)), 7 transforms.ToTensor(), 8 transforms.Normalize(mean=(0.5), std=(0.5))]) 9 valid_transform = transforms.Compose( 10 [transforms.Resize((224, 224)), 11 transforms.ToTensor(), 12 transforms.Normalize(mean=(0.5), std=(0.5))])
注:原始论文中有图像的翻转flipping,在我们的训练中是不需要的;
Line6把图像进行resize()
line7把图像变成tensor
line7标准化处理;
————————————————————————————————
2.4)数据的加载
接下来准备训练和验证数据集以及data loaders。
1 # training dataset and data loader 2 train_dataset = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root='./data', train=True, 3 download=True, 4 transform=train_transform) 5 train_dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset, 6 batch_size=batch_size, 7 shuffle=True) 8 # validation dataset and dataloader 9 valid_dataset = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root='./data', train=False, 10 download=True, 11 transform=valid_transform) 12 valid_dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(valid_dataset, 13 batch_size=batch_size, 14 shuffle=False)
2.5)模型的初始化、损失函数以及优化器
1 # instantiate the model 2 model = VGG11(in_channels=1, num_classes=10).to(device) 3 # total parameters and trainable parameters 4 total_params = sum(p.numel() for p in model.parameters()) 5 print(f"[INFO]: {total_params:,} total parameters.") 6 total_trainable_params = sum( 7 p.numel() for p in model.parameters() if p.requires_grad) 8 print(f"[INFO]: {total_trainable_params:,} trainable parameters.") 9 # the loss function 10 criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() 11 # the optimizer 12 optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01, momentum=0.9, 13 weight_decay=0.0005)
- 处理的MNIS是灰度图像,所以输入通道为1;输出的类别是10;
- 使用的是交叉熵损失函数;SGD用于进行参数更新;
2.6)训练函数
1 # training 2 def train(model, trainloader, optimizer, criterion): 3 model.train() 4 print('Training') 5 train_running_loss = 0.0 6 train_running_correct = 0 7 counter = 0 8 for i, data in tqdm(enumerate(trainloader), total=len(trainloader)): 9 counter += 1 10 11 image, labels = data 12 image = image.to(device) 13 labels = labels.to(device) 14 15 optimizer.zero_grad() 16 # forward pass 17 outputs = model(image) 18 # calculate the loss 19 loss = criterion(outputs, labels) 20 train_running_loss += loss.item() 21 # calculate the accuracy 22 _, preds = torch.max(outputs.data, 1) 23 train_running_correct += (preds == labels).sum().item() 24 loss.backward() 25 optimizer.step() 26 27 epoch_loss = train_running_loss / counter 28 epoch_acc = 100. * (train_running_correct / len(trainloader.dataset)) 29 return epoch_loss, epoch_acc
- 迭代训练数据加载器,提取标签和图像;
- 加载图像和标签到计算设备上;
- 前向传播,计算损失和精度;后向传播损失;
- 返回目前epoch的损失和精度;
2.8)验证函数:
验证函数有一些不同。对每个epoch中,我们将会计算损失和精度;
我们将对每个类别计算精度,评估在每个epoch中我们的模型表现力;
1 # validation 2 def validate(model, testloader, criterion): 3 model.eval() 4 5 # we need two lists to keep track of class-wise accuracy 6 class_correct = list(0. for i in range(10)) 7 class_total = list(0. for i in range(10)) 8 print('Validation') 9 valid_running_loss = 0.0 10 valid_running_correct = 0 11 counter = 0 12 with torch.no_grad(): 13 for i, data in tqdm(enumerate(testloader), total=len(testloader)): 14 counter += 1 15 16 image, labels = data 17 image = image.to(device) 18 labels = labels.to(device) 19 # forward pass 20 outputs = model(image) 21 # calculate the loss 22 loss = criterion(outputs, labels) 23 valid_running_loss += loss.item() 24 # calculate the accuracy 25 _, preds = torch.max(outputs.data, 1) 26 valid_running_correct += (preds == labels).sum().item() 27 # calculate the accuracy for each class 28 correct = (preds == labels).squeeze() 29 for i in range(len(preds)): 30 label = labels[i] 31 class_correct[label] += correct[i].item() 32 class_total[label] += 1 33 34 epoch_loss = valid_running_loss / counter 35 epoch_acc = 100. * (valid_running_correct / len(testloader.dataset)) 36 # print the accuracy for each class after evey epoch 37 # the values should increase as the training goes on 38 print('\n') 39 for i in range(10): 40 print(f"Accuracy of digit {i}: {100*class_correct[i]/class_total[i]}") 41 return epoch_loss, epoch_acc
2.9)训练过程:
1 # start the training 2 # lists to keep track of losses and accuracies 3 train_loss, valid_loss = [], [] 4 train_acc, valid_acc = [], [] 5 for epoch in range(epochs): 6 print(f"[INFO]: Epoch {epoch+1} of {epochs}") 7 8 train_epoch_loss, train_epoch_acc = train(model, train_dataloader, 9 optimizer, criterion) 10 valid_epoch_loss, valid_epoch_acc = validate(model, valid_dataloader, 11 criterion) 12 train_loss.append(train_epoch_loss) 13 valid_loss.append(valid_epoch_loss) 14 train_acc.append(train_epoch_acc) 15 valid_acc.append(valid_epoch_acc) 16 17 print('\n') 18 print(f"Training loss: {train_epoch_loss:.3f}, training acc: {train_epoch_acc:.3f}") 19 print(f"Validation loss: {valid_epoch_loss:.3f}, validation acc: {valid_epoch_acc:.3f}") 20 21 print('-'*50)
- 把训练和验证的损失和精度存储到train_loss、valid_loss以及train_acc和valid_acc中;
- 在每个epoch中,我们打印训练和损失的指标;
最后的步骤存储在训练的模型中,绘制出损失和精度图;
三、分析训练的损失和精度;
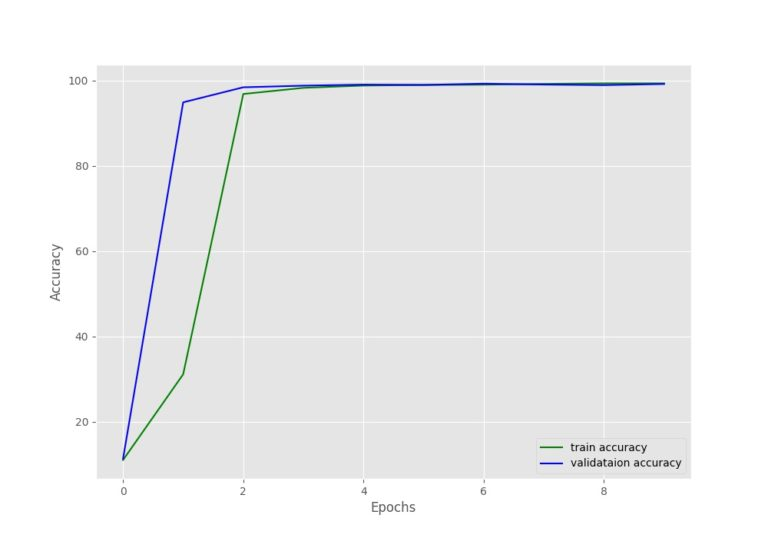
图1 精度图
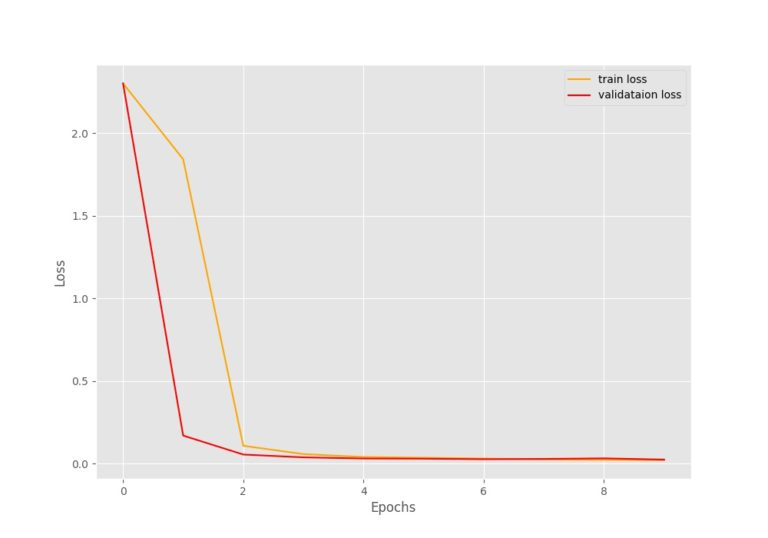
图2 损失图
四、对新的图像进行推断
1 import torch 2 import cv2 3 import glob as glob 4 import torchvision.transforms as transforms 5 import numpy as np 6 from models import VGG11
加载训练的权重,定义Transforms
1 # inferencing on CPU 2 device = 'cpu' 3 # initialize the VGG11 model 4 model = VGG11(in_channels=1, num_classes=10) 5 # load the model checkpoint 6 checkpoint = torch.load('../outputs/model.pth') 7 # load the trained weights 8 model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['model_state_dict']) 9 model.to(device) 10 model.eval() 11 # simple image transforms 12 transform = transforms.Compose([ 13 transforms.ToPILImage(), 14 transforms.Resize((224, 224)), 15 transforms.ToTensor(), 16 transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.5], 17 std=[0.5]) 18 ])
读图像并将其传入模型中
1 # get all the test images path 2 image_paths = glob.glob('../input/test_data/*.jpg') 3 for i, image_path in enumerate(image_paths): 4 orig_img = cv2.imread(image_path) 5 # convert to grayscale to make the image single channel 6 image = cv2.cvtColor(orig_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) 7 image = transform(image) 8 # add one extra batch dimension 9 image = image.unsqueeze(0).to(device) 10 # forward pass the image through the model 11 outputs = model(image) 12 # get the index of the highest score 13 # the highest scoring indicates the label for the Digit MNIST dataset 14 label = np.array(outputs.detach()).argmax() 15 print(f"{image_path.split('/')[-1].split('.')[0]}: {label}") 16 # put the predicted label on the original image 17 cv2.putText(orig_img, str(label), (15, 50), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 18 2, (0, 255, 0), 2) 19 # show and save the resutls 20 cv2.imshow('Result', orig_img) 21 cv2.waitKey(0) 22 cv2.imwrite(f"../outputs/result_{i}.jpg", orig_img)
总结:
本文我们主要训练了一个VGG11的神经网络从手写体MNIST数据集中;
我们以模型的初始化、训练模型和观察模型的精度即损失为主线进行了说明;
最后在新的数据集上对模型进行了验证。


