aws - Default VPC and default subnets
Default VPC components
When we create a default VPC, we do the following to set it up for you:
-
Create a VPC with a size
/16IPv4 CIDR block (172.31.0.0/16). This provides up to 65,536 private IPv4 addresses. -
Create a size
/20default subnet in each Availability Zone. This provides up to 4,096 addresses per subnet, a few of which are reserved for our use. -
Create an internet gateway and connect it to your default VPC.
-
Add a route to the main route table that points all traffic (
0.0.0.0/0) to the internet gateway. -
Create a default security group and associate it with your default VPC.
-
Create a default network access control list (ACL) and associate it with your default VPC.
-
Associate the default DHCP options set for your AWS account with your default VPC.
The following figure illustrates the key components that we set up for a default VPC.
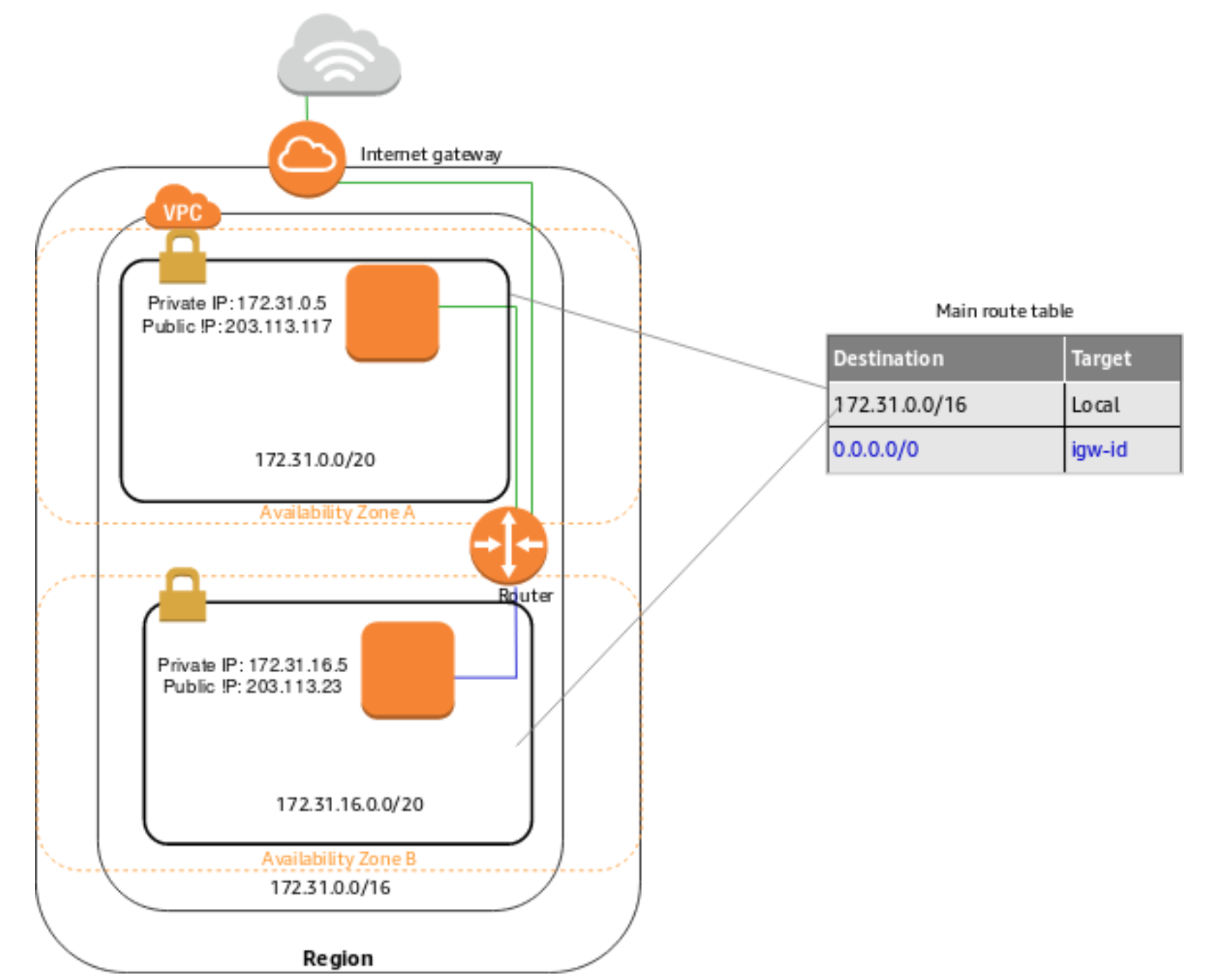
Default subnets
By default, a default subnet is a public subnet, because the main route table sends the subnet's traffic that is destined for the internet to the internet gateway. You can make a default subnet into a private subnet by removing the route from the destination 0.0.0.0/0 to the internet gateway. However, if you do this, no EC2 instance running in that subnet can access the internet.


