Azure-RBAC
role-based access control
How Azure RBAC works
The way you control access to resources using Azure RBAC is to assign Azure roles. This is a key concept to understand – it's how permissions are enforced.
A role assignment consists of three elements: security principal, role definition, and scope.
1. Security principal
A security principal is an object that represents a user, group, service principal, or managed identity that is requesting access to Azure resources. You can assign a role to any of these security principals.

2. Role definition
A role definition is a collection of permissions. It's typically just called a role. A role definition lists the operations that can be performed, such as read, write, and delete. Roles can be high-level, like owner, or specific, like virtual machine reader.
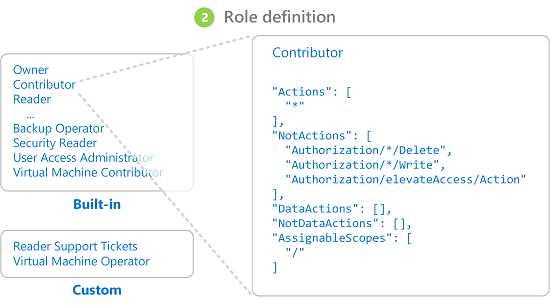
Azure includes several built-in roles that you can use.
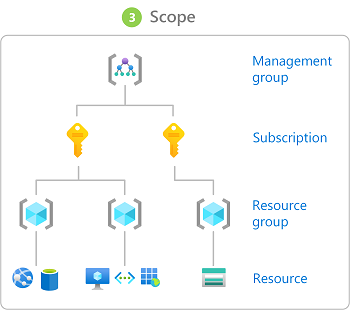
3. Scope
Scope is the set of resources that the access applies to. When you assign a role, you can further limit the actions allowed by defining a scope. This is helpful if you want to make someone a Website Contributor, but only for one resource group.
In Azure, you can specify a scope at four levels: management group, subscription, resource group, or resource. Scopes are structured in a parent-child relationship. You can assign roles at any of these levels of scope.