简明Python教程学习笔记10
14、Python标准库
(1)sys模块

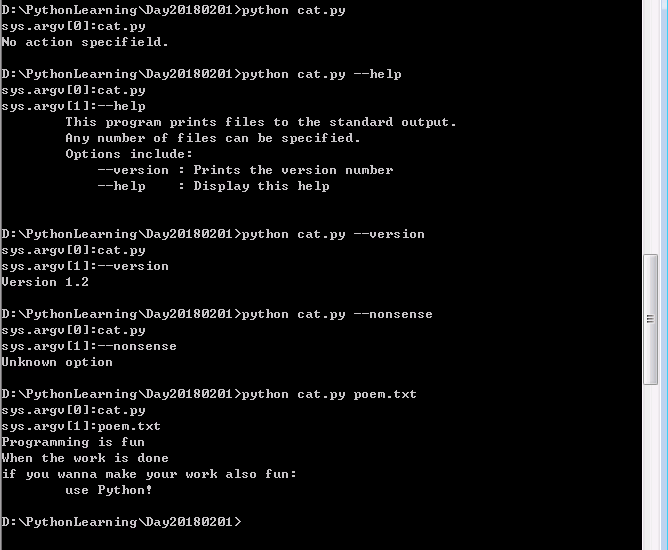
1 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 2 import sys 3 4 5 def readfile(filename): 6 """Print a file to the standard output.""" 7 f = file(filename) 8 while True: 9 line = f.readline() 10 if len(line) == 0: 11 break 12 print line, # notice comma 13 f.close() 14 15 16 # Script starts from here 17 if len(sys.argv) < 2: 18 for i in range(len(sys.argv)): 19 print "sys.argv[%d]:%s" % (i, sys.argv[i]) 20 print "No action specifield." 21 sys.exit() 22 23 if sys.argv[1].startswith("--"): 24 for i in range(len(sys.argv)): 25 print "sys.argv[%d]:%s" % (i, sys.argv[i]) 26 option = sys.argv[1][2:] 27 # fetch sys.argv[1] but without the first two characters 28 if option == "version": 29 print "Version 1.2" 30 elif option == "help": 31 print """\ 32 This program prints files to the standard output. 33 Any number of files can be specified. 34 Options include: 35 --version : Prints the version number 36 --help : Display this help 37 """ 38 else: 39 print "Unknown option" 40 sys.exit() 41 else: 42 for i in range(len(sys.argv)): 43 print "sys.argv[%d]:%s" % (i, sys.argv[i]) 44 for filename in sys.argv[1:]: 45 readfile(filename)
输出:
(2)os模块
这个模块包含普遍的操作系统功能。如果你希望你的程序能够与平台无关的话,这个模块是尤为重要的。
即它允许一个程序在编写后不需要任何改动,也不会发生任何问题,就可以在Linux和Windows下运行。
一个例子就是使用os.sep可以取代操作系统特定的路径分割符。
下面列出了一些在os模块中比较有用的部分。它们中的大多数都简单明了。
-
os.name字符串指示你正在使用的平台。比如对于Windows,它是'nt',而对于Linux/Unix用户,它是'posix'。 -
os.getcwd()函数得到当前工作目录,即当前Python脚本工作的目录路径。 -
os.getenv()和os.putenv()函数分别用来读取和设置环境变量。 -
os.listdir()返回指定目录下的所有文件和目录名。 -
os.remove()函数用来删除一个文件。 -
os.system()函数用来运行shell命令。 -
os.linesep字符串给出当前平台使用的行终止符。例如,Windows使用'\r\n',Linux使用'\n'而Mac使用'\r'。 -
os.path.split()函数返回一个路径的目录名和文件名。>>> os.path.split('/home/swaroop/byte/code/poem.txt')
('/home/swaroop/byte/code', 'poem.txt') -
os.path.isfile()和os.path.isdir()函数分别检验给出的路径是一个文件还是目录。 -
os.path.existe()函数用来检验给出的路径是否真地存在。
你可以利用Python标准文档去探索更多有关这些函数和变量的详细知识。你也可以使用help(sys)等等。




