读书笔记之:C++程序设计语言——题解
练习5.9 自引用



 、
、



程序代码如下:
 View Code
View Code
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
enum Context{
c_comment,cpp_comment,string_literal,char_literal,file_end
};
void handle_c_comment(){
char ch;
while(cin.get(ch)){
if(ch=='*'){
while(cin.get(ch)&&ch=='*')
;
if(ch=='/')
break;
}
}
}
void handle_cpp_comment(){
char ch;
while(cin.get(ch)&&ch!='\n')
;
}
void handle_literal(char delimiter){
cout<<delimiter;
char ch;
while(cin.get(ch)){
cout<<ch;
if(ch==delimiter)
break;
else if (ch=='\\')
cin.get(ch)&&cout<<ch;
}
}
Context handle_code(){
char ch;
while(cin.get(ch)){
switch(ch){
case '/':
if(!cin.get(ch)){
cout<<'/';
return file_end;
}
else {
if(ch=='*')
return c_comment;
else if(ch=='/')
return cpp_comment;
else{
cout<<'/';
cin.putback(ch);
break;
}
}
case '\"':
return string_literal;
case '\'':
return char_literal;
default:
cout<<ch;
}
}
return file_end;
}
int main(int argc,char**argv){
if(argc!=1){
cerr<<"This program takes no arguments.\n";
return -1;
}
else{
Context contxt;
while((contxt=handle_code())!=file_end)
switch(contxt){
case c_comment:
handle_c_comment();
break;
case cpp_comment:
handle_cpp_comment();
break;
case string_literal:
handle_literal('\"');
break;
case char_literal:
handle_literal('\'');
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
using namespace std;
enum Context{
c_comment,cpp_comment,string_literal,char_literal,file_end
};
void handle_c_comment(){
char ch;
while(cin.get(ch)){
if(ch=='*'){
while(cin.get(ch)&&ch=='*')
;
if(ch=='/')
break;
}
}
}
void handle_cpp_comment(){
char ch;
while(cin.get(ch)&&ch!='\n')
;
}
void handle_literal(char delimiter){
cout<<delimiter;
char ch;
while(cin.get(ch)){
cout<<ch;
if(ch==delimiter)
break;
else if (ch=='\\')
cin.get(ch)&&cout<<ch;
}
}
Context handle_code(){
char ch;
while(cin.get(ch)){
switch(ch){
case '/':
if(!cin.get(ch)){
cout<<'/';
return file_end;
}
else {
if(ch=='*')
return c_comment;
else if(ch=='/')
return cpp_comment;
else{
cout<<'/';
cin.putback(ch);
break;
}
}
case '\"':
return string_literal;
case '\'':
return char_literal;
default:
cout<<ch;
}
}
return file_end;
}
int main(int argc,char**argv){
if(argc!=1){
cerr<<"This program takes no arguments.\n";
return -1;
}
else{
Context contxt;
while((contxt=handle_code())!=file_end)
switch(contxt){
case c_comment:
handle_c_comment();
break;
case cpp_comment:
handle_cpp_comment();
break;
case string_literal:
handle_literal('\"');
break;
case char_literal:
handle_literal('\'');
break;
}
}
return 0;
}



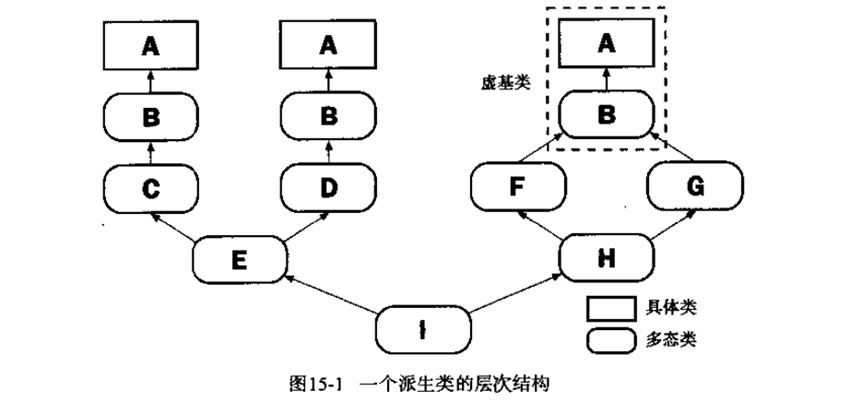







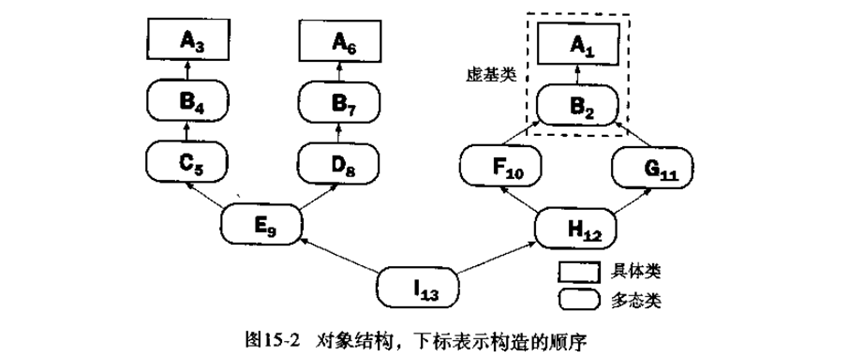

代码如下:
 View Code
View Code
#include <iostream>
#include <typeinfo>
using namespace std;
#define CTOR(CC){ \
cout<<#CC" Constructor:" \
<<typeid(*this).name()<<'\n';\
from_outside(this);\
cout<<'\n';\
}
#define DTOR(CC){ \
cout<<#CC " destructor: "\
<<typeid(*this).name()<<'\n';\
from_outside(this);\
cout<<'\n';\
}
struct A;
void from_outside(A *object);
struct A{
A() CTOR(A)
~A() DTOR(A)
};
void from_outside(A *object){
cout<<" Located at address: "<<(void*)object
<<"\nFrom outside: "<<typeid(*object).name()
<<endl;
}
struct B;
void from_outside(B *object);
struct B: A{
B() CTOR(B)
virtual ~B() DTOR(B)
};
void from_outside(B *object){
cout<<" Located at address: "<<(void*)object
<<"\nFrom outside: "<<typeid(*object).name()
<<endl;
}
struct C: B{
C() CTOR(C)
virtual ~C() DTOR(C)
};
struct D: B{
D() CTOR(D)
virtual ~D() DTOR(D)
};
struct E;
void from_outside(E* object);
struct E: C,D{
E() CTOR(E)
virtual ~E() DTOR(E)
};
void from_outside(E* object){
from_outside((C*)object);
from_outside((D*)object);
}
struct F: virtual B{
F() CTOR(F)
virtual ~F() DTOR(F)
};
struct G:virtual B{
G() CTOR(G)
virtual ~G() DTOR(G)
};
struct H:F,G{
H() CTOR(H)
virtual ~H() DTOR(H)
};
struct I;
void from_outside(I* object);
struct I:E,H{
I() CTOR(I)
virtual ~I() DTOR(I)
};
void from_outside(I* object){
from_outside((C*)object);
from_outside((D*)object);
from_outside((H*)object);
}
int main(){
I complex_obect;
cout <<"Total size of I-object :"<<sizeof (I)<<endl;
}
#include <typeinfo>
using namespace std;
#define CTOR(CC){ \
cout<<#CC" Constructor:" \
<<typeid(*this).name()<<'\n';\
from_outside(this);\
cout<<'\n';\
}
#define DTOR(CC){ \
cout<<#CC " destructor: "\
<<typeid(*this).name()<<'\n';\
from_outside(this);\
cout<<'\n';\
}
struct A;
void from_outside(A *object);
struct A{
A() CTOR(A)
~A() DTOR(A)
};
void from_outside(A *object){
cout<<" Located at address: "<<(void*)object
<<"\nFrom outside: "<<typeid(*object).name()
<<endl;
}
struct B;
void from_outside(B *object);
struct B: A{
B() CTOR(B)
virtual ~B() DTOR(B)
};
void from_outside(B *object){
cout<<" Located at address: "<<(void*)object
<<"\nFrom outside: "<<typeid(*object).name()
<<endl;
}
struct C: B{
C() CTOR(C)
virtual ~C() DTOR(C)
};
struct D: B{
D() CTOR(D)
virtual ~D() DTOR(D)
};
struct E;
void from_outside(E* object);
struct E: C,D{
E() CTOR(E)
virtual ~E() DTOR(E)
};
void from_outside(E* object){
from_outside((C*)object);
from_outside((D*)object);
}
struct F: virtual B{
F() CTOR(F)
virtual ~F() DTOR(F)
};
struct G:virtual B{
G() CTOR(G)
virtual ~G() DTOR(G)
};
struct H:F,G{
H() CTOR(H)
virtual ~H() DTOR(H)
};
struct I;
void from_outside(I* object);
struct I:E,H{
I() CTOR(I)
virtual ~I() DTOR(I)
};
void from_outside(I* object){
from_outside((C*)object);
from_outside((D*)object);
from_outside((H*)object);
}
int main(){
I complex_obect;
cout <<"Total size of I-object :"<<sizeof (I)<<endl;
}
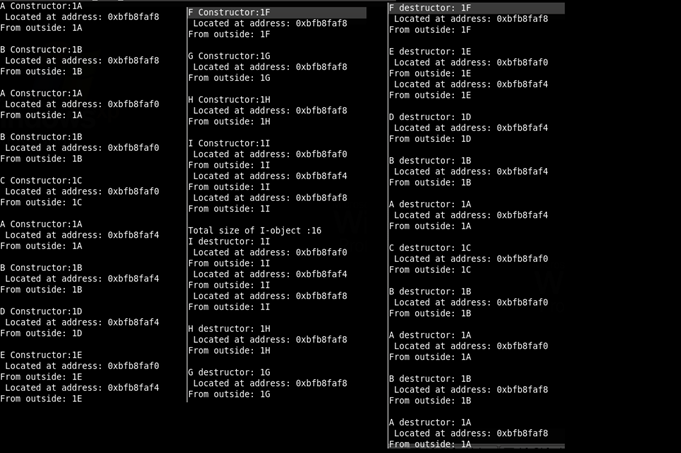
程序输出如下:
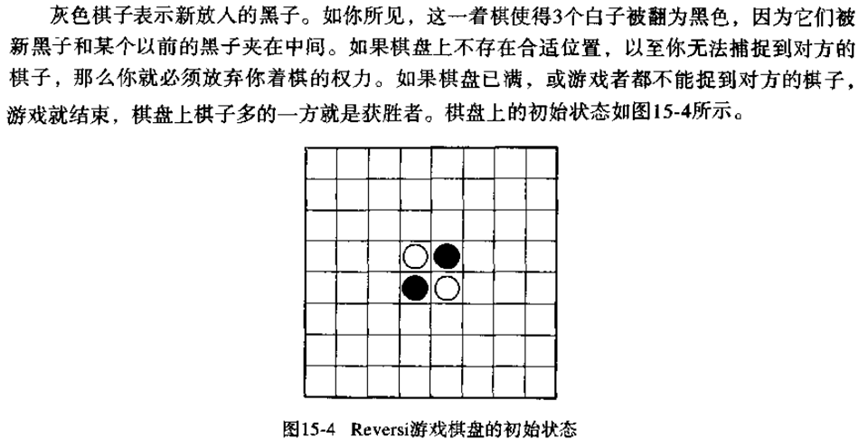






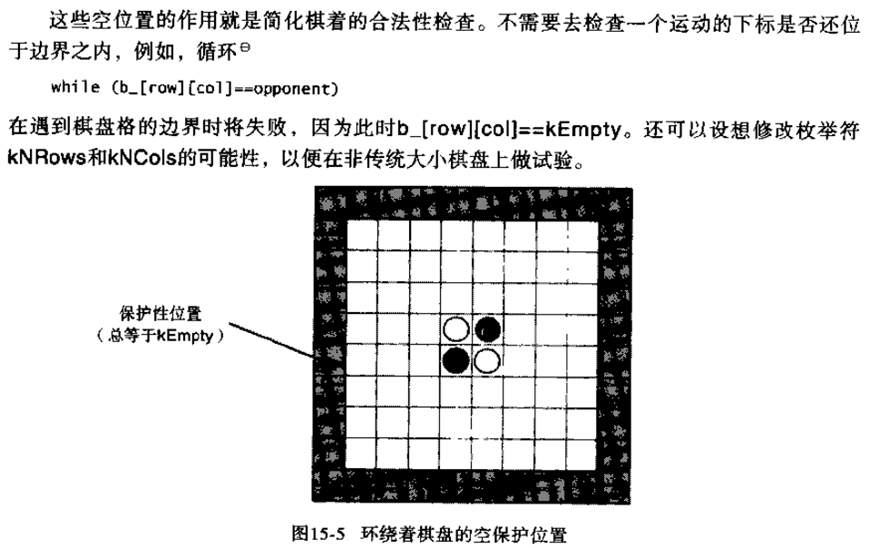






代码如下:
 View Code
View Code
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cctype>
#include <ctime>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
bool read_string(string &s){
int const buffer_size=100;
char buffer[buffer_size+1];
int i=0,c;
while((c=cin.get())&&cin&&isspace(c))
;
while((c=cin.get())&&cin&&!isspace(c)
&&i!=buffer_size){
buffer[i++]=char(c);
}
buffer[i]='\0';
s.assign(buffer,i);
if(cin){
cin.putback(c);
if(!isspace(c)){
string remainder;
read_string(remainder);
s.append(remainder);
}
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
bool read_string2(string& s){
int const buffer_size=100;
char buffer[buffer_size+1];
int i=0,c;
while((c=getc(stdin))!=EOF&&isspace(c))
;
while((c=getc(stdin))!=EOF&&!isspace(c)
&&i!=buffer_size){
buffer[i++]=char(c);
}
buffer[i]='\0';
s.assign(buffer,i);
if(c!=EOF){
ungetc(c,stdin);
if(!isspace(c)){
string remainder;
read_string(remainder);
s.append(remainder);
}
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
int main(){
string word;
int n=0;
bool not_eof;
clock_t start=clock();
#if defined(SIMPLE)
while(cin)
{
cin>>word;
n++;
}
#elif defined(SIMPLE2)
do{
not_eof=read_string(word);
++n;
}while(not_eof);
#else
do{
not_eof=read_string2(word);
++n;
}while(not_eof);
#endif
printf("Read %d words in %f seconds.\n",n,(clock()-start)*1.0/CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
return 0;
}
#include <string>
#include <cctype>
#include <ctime>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
bool read_string(string &s){
int const buffer_size=100;
char buffer[buffer_size+1];
int i=0,c;
while((c=cin.get())&&cin&&isspace(c))
;
while((c=cin.get())&&cin&&!isspace(c)
&&i!=buffer_size){
buffer[i++]=char(c);
}
buffer[i]='\0';
s.assign(buffer,i);
if(cin){
cin.putback(c);
if(!isspace(c)){
string remainder;
read_string(remainder);
s.append(remainder);
}
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
bool read_string2(string& s){
int const buffer_size=100;
char buffer[buffer_size+1];
int i=0,c;
while((c=getc(stdin))!=EOF&&isspace(c))
;
while((c=getc(stdin))!=EOF&&!isspace(c)
&&i!=buffer_size){
buffer[i++]=char(c);
}
buffer[i]='\0';
s.assign(buffer,i);
if(c!=EOF){
ungetc(c,stdin);
if(!isspace(c)){
string remainder;
read_string(remainder);
s.append(remainder);
}
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
int main(){
string word;
int n=0;
bool not_eof;
clock_t start=clock();
#if defined(SIMPLE)
while(cin)
{
cin>>word;
n++;
}
#elif defined(SIMPLE2)
do{
not_eof=read_string(word);
++n;
}while(not_eof);
#else
do{
not_eof=read_string2(word);
++n;
}while(not_eof);
#endif
printf("Read %d words in %f seconds.\n",n,(clock()-start)*1.0/CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
return 0;
}




