六、拓扑排序
1.实验目的
(1)掌握图的存储结构及其基本操作,学会定义图的邻接表存储结构,并能在实际中灵活应用;
(2)掌握拓扑排序算法;
(3)通过本实验的具体应用实例,灵活应用拓扑排序并进一步巩固队列/栈的运用。
2.实验内容
用邻接表形式存储以下有向无环图,进行拓扑排序,输出相应拓扑序列。若图中每个顶点都在拓扑序列中,说明图中无环。
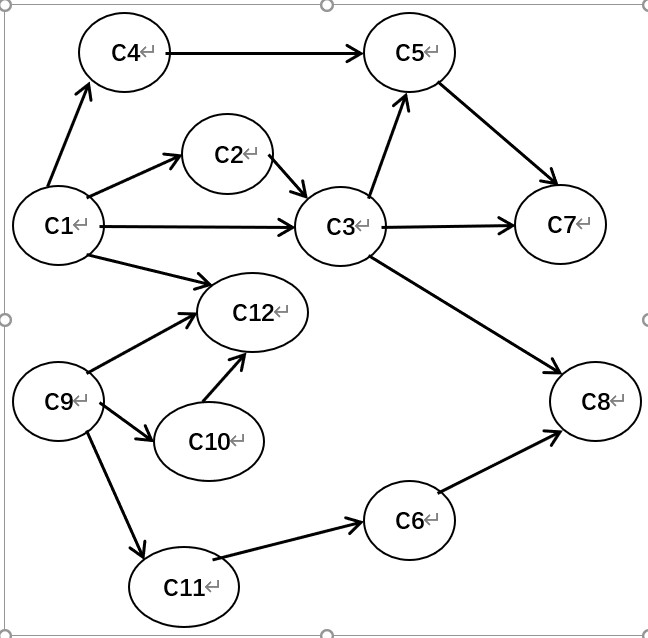
3.源程序和实验结果
#include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; const int STACK_INIT_SIZE = 20; //----------图的结构声明--------- typedef struct ArcNode { int adjvex; //该弧所指向的顶点的位置 struct ArcNode *nextarc; //指向下一条弧的指针 } ArcNode; //表结点 typedef struct VNode { string data; //顶点信息 ArcNode *firstarc; //指向第一条依附该顶点的弧的指针 } VNode; //头结点 typedef struct { VNode *AdjList; int vexnum, arcnum; } Graph; //有向图 //--------栈结构的声明-------- typedef struct { int *base; int *top; int stacksize; //当前已分配的存储空间,以元素为单位 } SqStack; //建造一个空栈 void InitStack(SqStack &S) { S.base = new int[STACK_INIT_SIZE]; if (!S.base) { cout << "存储分配失败" << endl; return; } S.top = S.base; S.stacksize = STACK_INIT_SIZE; } //InitStack // 插入元素e为新的栈顶元素 void Push(SqStack &S, int e) { *S.top = e; S.top++; } //Push // 若栈不空,删除S的栈顶元素,用e返回其值 void Pop(SqStack &S, int &e) { S.top--; e = *S.top; } //Pop //若栈为空,返回true,否则返回false bool StackEmpty(SqStack S) { if (S.top == S.base) return true; else return false; } // 有向图的初始化 void createGraph(Graph &g) { g.vexnum = 12; //顶点数目 g.arcnum = 16; //边的数目 g.AdjList = new VNode[g.vexnum]; //顶点的初始化 for (int i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++) { g.AdjList[i].data = "c" + std::to_string(i + 1); g.AdjList[i].firstarc = NULL; } //边的初始化 cout << "请输入边的起点和终点所对应的编号(0-11)" << endl; for (int i = 0; i < g.arcnum; i++) { int start, end; cin >> start >> end; ArcNode *a = new ArcNode; a->adjvex = end; a->nextarc = NULL; a->nextarc = g.AdjList[start].firstarc; g.AdjList[start].firstarc = a; /* 为什么我用 ArcNode a; a.adjvex=end; a.nextarc=NULL; a.nextarc=g.AdjList[start].firstarc; g.AdjList[start].first=a; 就是错的呢? */ } } // 输出图g的邻接表 void print(Graph g) { cout << endl << "有向图g的邻接表表示如下所示:" << endl; for (int i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++) { cout << "编号" << i << ": " << g.AdjList[i].data; ArcNode *p = g.AdjList[i].firstarc; while (p) { cout << "-->" << p->adjvex; p = p->nextarc; } cout << endl; } } //求各顶点的入度 void FindInDegree(Graph g, int *indegree) { for (int i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++) indegree[i] = 0; for (int i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++) { ArcNode *p = g.AdjList[i].firstarc; while (p) { indegree[p->adjvex]++; p = p->nextarc; } } } // 拓扑排序 void TopologicalSort(Graph g) { // 有向图g采用邻接表存储结构 //若g无回路,则输出g的顶点的一个拓扑序列 int *indegree = new int[g.vexnum]; FindInDegree(g, indegree); //测试 // for (int i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++) // cout << indegree[i] << endl; SqStack S; InitStack(S); // 建零入度顶点栈S for (int i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++) if (!indegree[i]) //入度为零这进栈 Push(S, i); int count = 0; //对输出顶点计数 while (!StackEmpty(S)) { int i; Pop(S, i); //输出i号顶点并计数 cout << i << " " << g.AdjList[i].data << endl; count++; for (ArcNode *p = g.AdjList[i].firstarc; p; p = p->nextarc) { int k = p->adjvex; //对i号顶点的每个邻接点的入度减1 if (!(--indegree[k])) //若入度为0,则入栈 Push(S, k); } //for } if (count < g.vexnum) { cout << "该有向图有回路" << endl; return; } } //TopologicalSort int main() { Graph g; createGraph(g); print(g); cout << endl << "有向图g的拓扑序列为:" << endl; TopologicalSort(g); return 0; }
测试数据:
0 1
0 2
0 3
0 11
1 2
2 4
2 6
2 7
3 4
4 6
5 7
8 9
8 10
8 11
9 11
10 5
输出结果截图:
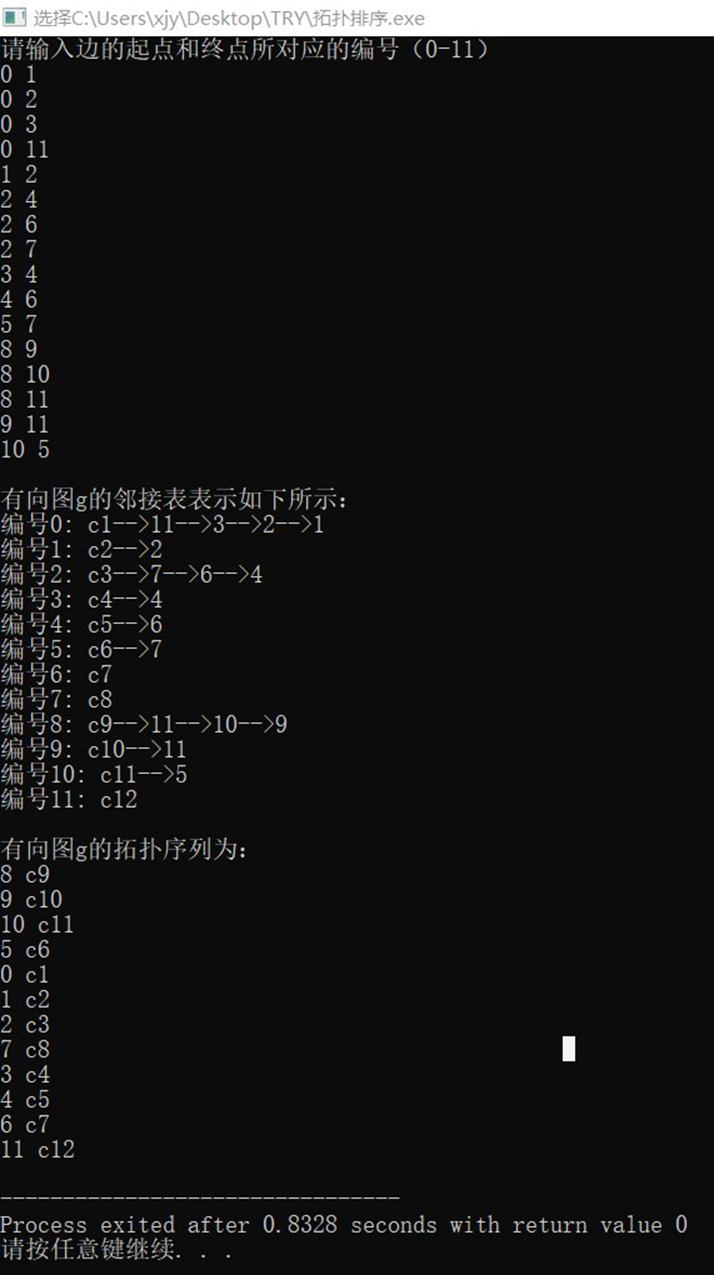
4.分析与讨论
本文作者:请去看诡秘之主
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/xjy881/p/15622058.html
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步