Batch Normalization优化比较
一、Batch Normalization(批量标准化)的介绍以及理解
在神经网络中,在每一层上,通常是将该层的输入乘以权重矩阵加上偏移值,然后将计算结果使用激活函数进行非线性变换。但是随着网络深度的增加,其激活函数的输入值(W*X+B)的分布会发生变化。
可能会向激活函数取值的饱和区域延伸(比如:sigmoid函数,当激活函数输入值趋向于正比较大的正数或者比较小的负数时,因为其倒数很小,导致梯度消失。),使得收敛很慢,如图1所示。
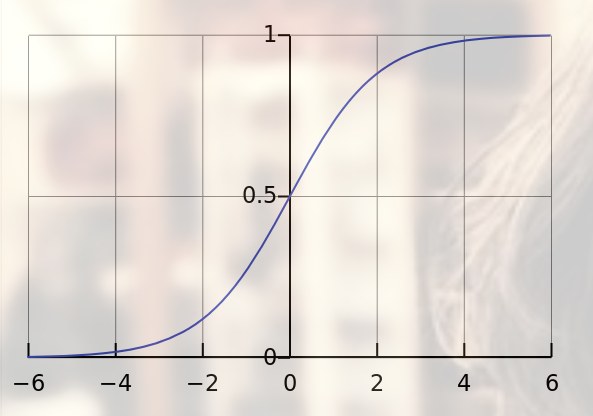
图1 sigmoid激活函数
而Batch Normalization是将数据进行处理,即将每一层激活函数的输入值转换成一个均值为0,方差为1的标准正态分布,这样就使得进入激活函数敏感的区域,加快训练的收敛速度。
BN的过程如图2所示。
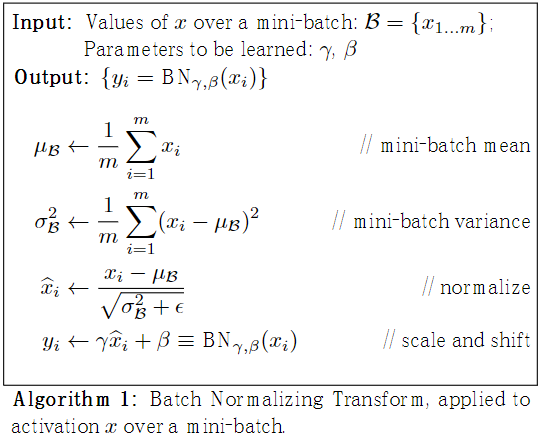
图2 BN算法流程
二、Batch Normalization训练优化比较
在MNIST数据集上进行验证:
如果is_bn设置成True,则使用BN进行训练,如果is_bn设置成False,则不使用BN进行训练,代码如下:

import tensorflow as tf import argparse old_v = tf.logging.get_verbosity() tf.logging.set_verbosity(tf.logging.ERROR) from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("/home/sxj/MNIST_data/", one_hot=True) tf.logging.set_verbosity(old_v) def arg_parse(): parser = argparse.ArgumentParser() parser.add_argument("--is_bn", default=True, type=str, help='whether using batch normalization or not') return parser.parse_args() def batch_norm_full(prev_layer, num_units): gamma = tf.Variable(tf.ones([num_units])) beta = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([num_units])) epsilon = 1e-3 batch_mean, batch_variance = tf.nn.moments(prev_layer, [0]) ema = tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage(decay=0.99)# 滑动平均的衰减系数 def mean_var_with_update(): ema_apply_op = ema.apply([batch_mean, batch_variance]) with tf.control_dependencies([ema_apply_op]): return tf.identity(batch_mean), tf.identity(batch_variance) mean, var = mean_var_with_update() with tf.control_dependencies([mean, var]): batch_normalized_output = tf.nn.batch_normalization(prev_layer, mean, var, beta, gamma, epsilon) return batch_normalized_output def batch_norm_conv(prev_layer, out_channels, is_training): gamma = tf.Variable(tf.ones([out_channels])) beta = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([out_channels])) pop_mean = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([out_channels]), trainable=False) pop_variance = tf.Variable(tf.ones([out_channels]), trainable=False) epsilon = 1e-3 axis = list(range(len(prev_layer.get_shape())-1)) def batch_norm_training(): batch_mean, batch_variance = tf.nn.moments(prev_layer, axis, keep_dims=False) ema = tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage(decay=0.99) # 滑动平均的衰减系数 def mean_var_with_update(): ema_apply_op = ema.apply([batch_mean, batch_variance]) with tf.control_dependencies([ema_apply_op]): return tf.identity(batch_mean), tf.identity(batch_variance) mean, var = mean_var_with_update() with tf.control_dependencies([mean, var]): return tf.nn.batch_normalization(prev_layer, mean, var, beta, gamma, epsilon) def batch_norm_inference(): return tf.nn.batch_normalization(prev_layer, pop_mean, pop_variance, beta, gamma, epsilon) batch_normalized_output = tf.cond(is_training, batch_norm_training, batch_norm_inference) return batch_normalized_output def train_inference(num_batches, batch_size, learning_rate, is_bn=True): inputs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784]) labels = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10]) is_training = tf.placeholder(tf.bool) # define weight def weight_variable(shape): initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.1) return tf.Variable(initial) # define bias def bias_variable(shape): initial = tf.constant(0.1, shape=shape) return tf.Variable(initial) # define conv def conv2d(x, w): return tf.nn.conv2d(x, w, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding="SAME") # define pooling def max_pool_2x2(x): return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding="SAME") x_image = tf.reshape(inputs, [-1, 28, 28, 1]) # level 1 w_conv1 = weight_variable([5, 5, 1, 32]) b_conv1 = bias_variable([32]) h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.add(conv2d(x_image, w_conv1), b_conv1)) h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1) # level 2 w_conv2 = weight_variable([5, 5, 32, 64]) b_conv2 = bias_variable([64]) if is_bn: # using Batch Normalization h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(batch_norm_conv(tf.add(conv2d(h_pool1, w_conv2), b_conv2), 64, is_training)) h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2) else: # not using Batch Normalization h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.add(conv2d(h_pool1, w_conv2), b_conv2)) h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2) w_fc1 = weight_variable([7 * 7 * 64, 1024]) b_fc1 = bias_variable([1024]) if is_bn: # using Batch Normalization h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1, 7 * 7 * 64]) h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(batch_norm_full(tf.add(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, w_fc1), b_fc1), 1024)) else: # not using Batch Normalization h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1, 7 * 7 * 64]) h_fc1 = tf.layers.dense(h_pool2_flat, 1024, activation=tf.nn.relu) # dropout keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32) h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1, keep_prob) if is_bn: layer2 = tf.layers.dense(h_fc1_drop, 10, activation=None) logits = batch_norm_full(layer2, 10) else: logits = tf.layers.dense(h_fc1_drop, 10, activation=None) model_loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits, labels=labels)) train_opt = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(model_loss) correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(logits, 1), tf.argmax(labels, 1)) accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32)) with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) if is_bn: file = open('with_bn.txt', 'w') else: file = open('without_bn.txt', 'w') for batch_i in range(num_batches): batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size) sess.run(train_opt, {inputs: batch_xs, labels: batch_ys, is_training: True, keep_prob: 0.5}) if batch_i % 100 == 0: loss, acc = sess.run([model_loss, accuracy], {inputs: mnist.validation.images, labels: mnist.validation.labels, is_training: False, keep_prob: 0.5}) print( 'Batch: {:>2}: Validation loss: {:>3.5f}, Validation accuracy: {:>3.5f}'.format(batch_i, loss, acc)) elif batch_i % 10 == 0: loss, acc = sess.run([model_loss, accuracy], {inputs: batch_xs, labels: batch_ys, is_training: False, keep_prob: 0.5}) print('Batch: {:>2}: Training loss: {:>3.5f}, Training accuracy: {:>3.5f}'.format(batch_i, loss, acc)) file.write(str(loss) + ' ' + str(acc)+'\r\n') acc = sess.run(accuracy, {inputs: mnist.validation.images, labels: mnist.validation.labels, is_training: False, keep_prob: 0.5}) print('Final validation accuracy: {:>3.5f}'.format(acc)) acc = sess.run(accuracy, {inputs: mnist.test.images, labels: mnist.test.labels, is_training: False, keep_prob: 0.5}) print('Final test accuracy: {:>3.5f}'.format(acc)) correct = 0 for i in range(100): correct += sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={inputs: [mnist.test.images[i]], labels: [mnist.test.labels[i]], is_training: False, keep_prob: 0.5}) print("Accuracy on 100 samples:", correct / 100) num_batches = 800 batch_size = 64 learning_rate = 0.002 tf.reset_default_graph() with tf.Graph().as_default(): args = arg_parse() if args.is_bn == 'True': is_bn = True elif args.is_bn == 'False': is_bn = False else: raise ValueError("Invalid is_bn, which should be 'True' or 'False") train_inference(num_batches, batch_size, learning_rate, is_bn)
到处数据,进行比较:
最终训练的精度比较如下(横坐标1个单位为10次迭代):
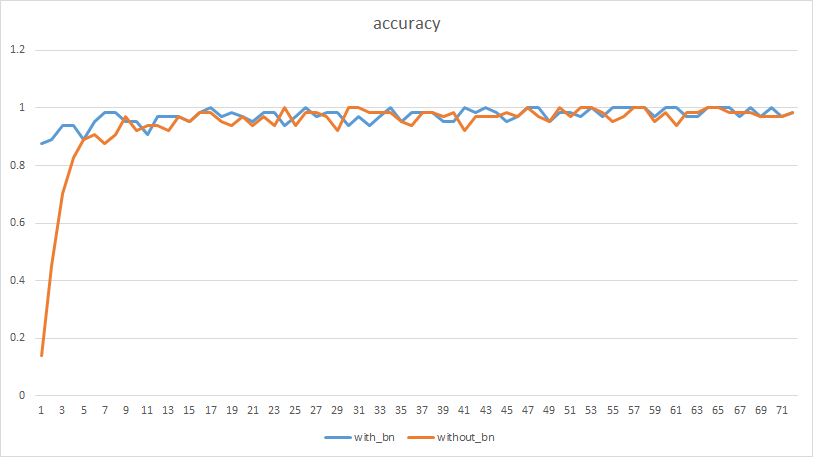
可见,经过BN之后,收敛快很多。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号