stark——快速过滤list_filter
一、获取过滤字段
1、给自定义配置类配置list_filter
app01/stark.py:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | class BookConfig(ModelStark): list_display = ["title", "price", "publishDate"] modelform_class = BookModelForm search_fields = ['title', "price"] def patch_init(self, request, queryset): print(queryset) queryset.update(price=123) patch_init.short_description = "批量初始化" actions = [patch_init] list_filter = ["publish", "authors", ] # 一对多、多对多site.register(Book, BookConfig) |
2、构建实例方法获取过滤字段
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 | class ShowList(object): """展示页面类""" def __init__(self, config, data_list, request):... def get_filter_linktags(self): """获取过滤字段""" link_list = {} print("list_filter", self.config.list_filter) # list_filter ['publish', 'authors'] for filter_field in self.config.list_filter: print(filter_field) # 'publish' 'authors' # 获取字段对象 filter_field_obj = self.config.model._meta.get_field(filter_field) print(filter_field_obj) # app01.Book.publish app01.Book.authors print(type(filter_field_obj)) """ <class 'django.db.models.fields.related.ForeignKey'> <class 'django.db.models.fields.related.ManyToManyField'> from django.db.models.fields.related import ForeignKey from django.db.models.fields.related import ManyToManyField """ # 拿到关联表下的所有数据 # print("rel...", filter_field_obj.rel.to.objects.all()) # 版本问题失效 print("rel...", filter_field_obj.related_model.objects.all()) """ rel... <QuerySet [<Publish: 苹果出版社>, <Publish: 香蕉出版社>]> rel... <QuerySet [<Author: alex>, <Author: egon>]> """ return link_listclass ModelStark(object): """默认类,定制配置类""" list_display = ["__str__",] list_display_links = [] modelform_class = [] search_fields = [] actions = [] # 调用self.actions拿到的是函数 list_filter = [] |
注意:
(1)获取自定义配置类定义的list_filter列表
ShowList类对象,通过self.config.list_filter可以拿到当前访问页面对象自定义配置类配置的list_filter列表。
(2)根据字段字符串获取模型字段对象
1 2 3 | filter_field_obj = self.config.model._meta.get_field(filter_field)model_name = self.config.model._meta.model_name # 模型名 bookapp_label = self.config.model._meta.app_label # app名 app01 |
(3)根据一对多,多对多对象关联关系,得到关联模型表和数据
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | # 拿到关联表下的所有数据# print("rel...", filter_field_obj.rel.to.objects.all()) # 版本问题失效(filter_field_obj.rel.to是关联模型表)print("rel...", filter_field_obj.related_model.objects.all()) # 拿到对象下的关联数据"""rel... <QuerySet [<Publish: 苹果出版社>, <Publish: 香蕉出版社>]>rel... <QuerySet [<Author: alex>, <Author: egon>]>""" |
二、根据拿到的对象关联数据完成数据组织
1、get_filter_linktags方法组织返回链接字典
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | class ShowList(object): """展示页面类""" def get_filter_linktags(self): """获取过滤字段""" link_dic = {} print("list_filter", self.config.list_filter) # list_filter ['publish', 'authors'] for filter_field in self.config.list_filter: print(filter_field) # 'publish' 'authors' # 获取字段对象 filter_field_obj = self.config.model._meta.get_field(filter_field) print(filter_field_obj) # app01.Book.publish app01.Book.authors # 拿到关联表下的所有数据 # print("rel...", filter_field_obj.rel.to.objects.all()) # 版本问题失效 # print("rel...", filter_field_obj.related_model.objects.all()) # <QuerySet [<Publish: 苹果出版社>, <Publish: 香蕉出版社>]> data_list = filter_field_obj.related_model.objects.all() # <QuerySet [<Publish: 苹果出版社> temp = [] for obj in data_list: # obj是每一个对象 # print(obj) # 苹果出版社 香蕉出版社 alex egon # print(type(obj)) # <class 'app01.models.Publish'> <class 'app01.models.Author'> link_tag = "<a href=>%s</a>" % str(obj) # print(link_tag) # <a href=>苹果出版社</a> temp.append(link_tag) link_dic[filter_field] = temp # print(link_dic) # {'publish': ['<a href=>苹果出版社</a>', '<a href=>香蕉出版社</a>'], 'authors': ['<a href=>alex</a>', '<a href=>egon</a>']} return link_dic |
这里最重要就是理清楚每个变量的类型和含义:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | self.config.list_filter——['publish', 'authors']filter_field_obj—— app01.Book.publish、app01.Book.authorsfilter_field_obj.related_model.objects.all()——<QuerySet [<Publish: 苹果出版社>, <Publish: 香蕉出版社>]>、<QuerySet [<Author: alex>, <Author: egon>]>obj——苹果出版社 香蕉出版社 alex egon 数据类型:<class 'app01.models.Publish'> <class 'app01.models.Author'>link_tag——<a href=>苹果出版社</a>link_dic——{'publish': ['<a href=>苹果出版社</a>', '<a href=>香蕉出版社</a>'], 'authors': ['<a href=>alex</a>', '<a href=>egon</a>']} |
2、list_view.html构建显示
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | <h4>数据列表</h4><div class="container"> <div class="row"> <div class="col-md-9".....> <div class="col-md-3"> <div class="filter"> <h4>Filter</h4> {% for filter_field, linktags in show_list.get_filter_linktags.items %} <div> <p>{{ filter_field }}</p> {% for link in linktags %} <p>{{ link|safe }}</p> {% endfor %} </div> {% endfor %} </div> </div> </div></div> |
注意这里使用{{link|safe}}来实现取消转义。显示效果如下:
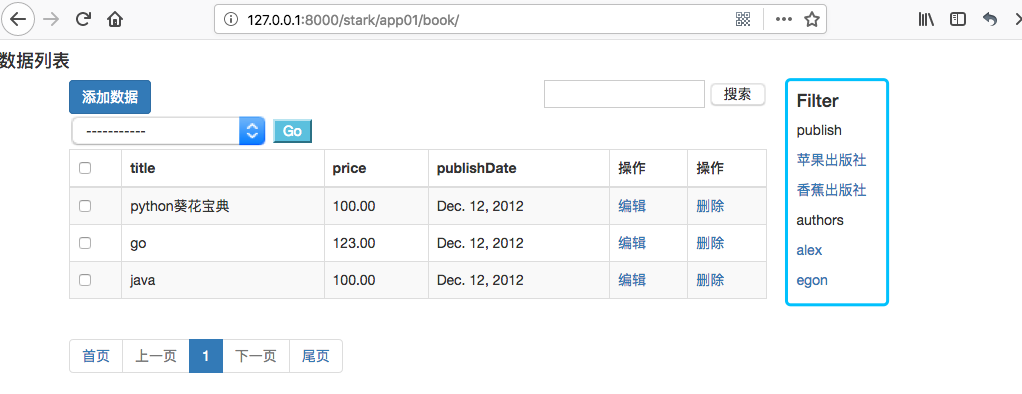
三、标签href处理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 | class ShowList(object): """展示页面类""" def get_filter_linktags(self): """获取过滤字段""" link_dic = {} print("list_filter", self.config.list_filter) # list_filter ['publish', 'authors'] for filter_field in self.config.list_filter: """循环每一个过滤字段""" import copy # self.request.GET # GET请求的所有数据 params = copy.deepcopy(self.request.GET) print(filter_field) # 'publish' 'authors' # 获取字段对象 filter_field_obj = self.config.model._meta.get_field(filter_field) print(filter_field_obj) # app01.Book.publish app01.Book.authors # 拿到关联表下的所有数据 # print("rel...", filter_field_obj.rel.to.objects.all()) # 版本问题失效 # print("rel...", filter_field_obj.related_model.objects.all()) # <QuerySet [<Publish: 苹果出版社>, <Publish: 香蕉出版社>]> data_list = filter_field_obj.related_model.objects.all() # <QuerySet [<Publish: 苹果出版社> temp = [] for obj in data_list: # obj是每一个对象 """循环每一个过滤字段关联的数据""" # 构成一个新字典 过滤字段:当前对象主键值 params[filter_field + "__id"] = obj.pk # 利用urlencode将键值对转化为a=1&b=2的格式 _url = params.urlencode() # print(obj) # 苹果出版社 香蕉出版社 alex egon # print(type(obj)) # <class 'app01.models.Publish'> <class 'app01.models.Author'> link_tag = "<a href='?%s'>%s</a>" % (_url, str(obj)) # print(link_tag) # <a href=>苹果出版社</a> temp.append(link_tag) link_dic[filter_field] = temp # print(link_dic) # {'publish': ['<a href=>苹果出版社</a>', '<a href=>香蕉出版社</a>'], 'authors': ['<a href=>alex</a>', '<a href=>egon</a>']} return link_dic |
注意:
1、copy.deepcopy()使用
-
直接赋值:其实就是对象的引用(别名)。
-
浅拷贝(copy):拷贝父对象,不会拷贝对象的内部的子对象。
-
深拷贝(deepcopy): copy 模块的 deepcopy 方法,完全拷贝了父对象及其子对象。
这里每循环一次过滤字段都会重新创建一个params。保证按钮对应路径的唯一性。
2、利用urlencode将键值对转化为a=1&b=2的格式
这里主要是应为发送的是get请求,请求数据必须是a=1&b=2的格式。
3、params = copy.deepcopy(self.request.GET)意义
self.request.GET获取的是GET请求的所有数据,多次点击可以实现get请求数据的拼接。打印params,在页面点击访问,控制台输出如下:
1 2 3 | params <QueryDict: {}> ——没有点击a标签params <QueryDict: {'authors__id': ['1']}> ——第一次点击params <QueryDict: {'authors__id': ['1'], 'publish__id': ['2']}> ——第二次点击 |
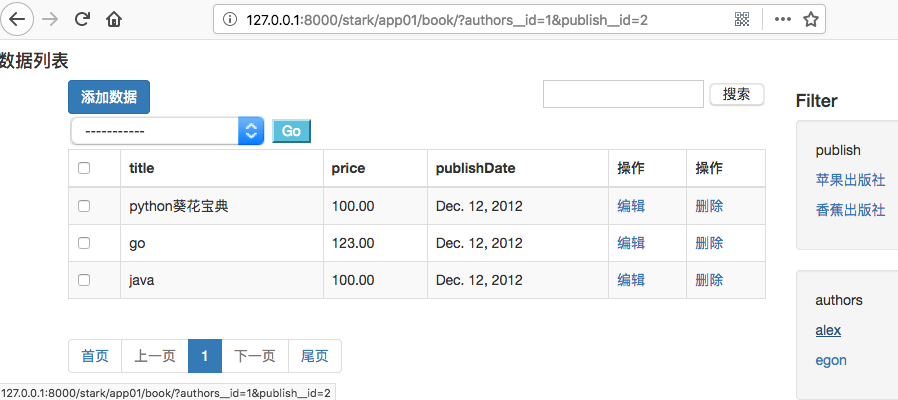
四、a标签点击后颜色变化
1、前置准备
(1)将过滤字段显示为大写
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | {% for filter_field, linktags in show_list.get_filter_linktags.items %} <div class="well"> {# upper方法改为大写 #} <p>{{ filter_field.upper }}</p> {% for link in linktags %} <p>{{ link|safe }}</p> {% endfor %} </div>{% endfor %} |
(2)取消a标签颜色
1 2 3 4 5 6 | <style> .filter a { text-decoration: none; /* 取消a标签颜色 */ color: grey; }</style> |
2、对当前get请求数据进行判断
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 | class ShowList(object): def get_filter_linktags(self): """获取过滤字段""" link_dic = {} print("list_filter", self.config.list_filter) # list_filter ['publish', 'authors'] for filter_field in self.config.list_filter: """循环每一个过滤字段""" import copy # self.request.GET # GET请求的所有数据 params = copy.deepcopy(self.request.GET) print("params", params) # cid是当前字段传过来的值 cid = self.request.GET.get(filter_field + "__id", 0) # 没有值的时候默认为None,None是不能进行int()转换的,因此在这里给它设置默认值为0 # print(filter_field) # 'publish' 'authors' # 获取字段对象 filter_field_obj = self.config.model._meta.get_field(filter_field) data_list = filter_field_obj.related_model.objects.all() # <QuerySet [<Publish: 苹果出版社> temp = [] for obj in data_list: # obj是每一个对象 """循环每一个过滤字段关联的数据""" # 构成一个新字典 过滤字段:当前对象主键值 params[filter_field + "__id"] = obj.pk # 利用urlencode将键值对转化为a=1&b=2的格式 _url = params.urlencode() if int(cid) == obj.pk: # get请求数据int转换后与对象主键值匹配,匹配成功添加active类 link_tag = "<a class='active' href='?%s'>%s</a>" % (_url, str(obj)) else: link_tag = "<a href='?%s'>%s</a>" % (_url, str(obj)) temp.append(link_tag) link_dic[filter_field] = temp return link_dic |
给模板添加样式:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | <style> .filter a { text-decoration: none; /* 取消a标签颜色 */ color: grey; } .active { color: red!important; /* 提升优先级 */ }</style> |
注意:
(1)cid是当前get请求传递的值
1 | cid = self.request.GET.get(filter_field + "__id", 0) |
需要注意的是在get请求没有值的时候,默认值是None,但是None是不能进行int()转换的,因此在这里给它设置默认值0.
(2)根据get请求的值和对象主键比对,给a标签添加avtice类
1 2 3 4 5 | if int(cid) == obj.pk: # get请求数据int转换后与对象主键值匹配,匹配成功添加active类 link_tag = "<a class='active' href='?%s'>%s</a>" % (_url, str(obj))else: link_tag = "<a href='?%s'>%s</a>" % (_url, str(obj)) |
(3)显示效果
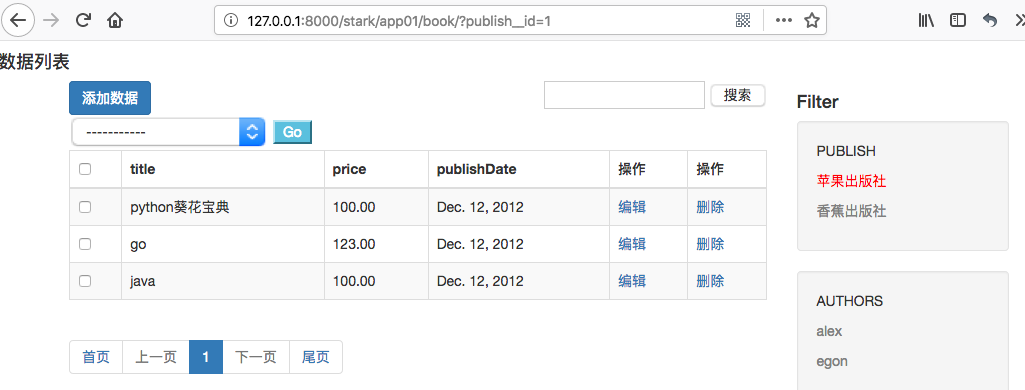
五、过滤器添加all按钮取消过滤
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 | class ShowList(object): def get_filter_linktags(self): """获取过滤字段""" link_dic = {} print("list_filter", self.config.list_filter) # list_filter ['publish', 'authors'] for filter_field in self.config.list_filter: """循环每一个过滤字段""" import copy # self.request.GET # GET请求的所有数据 params = copy.deepcopy(self.request.GET) print("params", params) # <QueryDict: {'publish__id': ['1']}> # cid是当前字段传过来的值 cid = self.request.GET.get(filter_field + "__id", 0) # 没有值的时候默认为None,None是不能进行int()转换的,因此在这里给它设置默认值为0 # 获取字段对象 filter_field_obj = self.config.model._meta.get_field(filter_field) data_list = filter_field_obj.related_model.objects.all() # <QuerySet [<Publish: 苹果出版社> temp = [] # 处理all标签 if params.get(filter_field + "__id"): del params[filter_field + "__id"] temp.append("<a href='?%s'>all</a>" % params.urlencode()) else: temp.append("<a class='active' href='#'>all</a>") # 默认是all的状态 # 处理数据标签 for obj in data_list: # obj是每一个对象 """循环每一个过滤字段关联的数据""" # 构成一个新字典 过滤字段:当前对象主键值 params[filter_field + "__id"] = obj.pk # 利用urlencode将键值对转化为a=1&b=2的格式 _url = params.urlencode() if int(cid) == obj.pk: # get请求数据int转换后与对象主键值匹配,匹配成功添加active类 link_tag = "<a class='active' href='?%s'>%s</a>" % (_url, str(obj)) else: link_tag = "<a href='?%s'>%s</a>" % (_url, str(obj)) temp.append(link_tag) link_dic[filter_field] = temp return link_dic |
注意:
1、在处理数据标签前,在temp临时数组中添加all的<a>标签
1 2 3 4 5 6 | # 处理all标签if params.get(filter_field + "__id"): del params[filter_field + "__id"] temp.append("<a href='?%s'>all</a>" % params.urlencode())else: temp.append("<a class='active' href='#'>all</a>") # 默认是all的状态 |
点击a标签由于href没有在?前填任何值,默认是将get请求发送给原函数处理。
params是深度复制了get请求的数据,因此每次点击a标签都在添加params的值:
1 2 3 | params <QueryDict: {}> ——没有点击a标签params <QueryDict: {'authors__id': ['1']}> ——第一次点击params <QueryDict: {'authors__id': ['1'], 'publish__id': ['2']}> ——第二次点击 |
params.get(filter_field + "__id") 就可以拿到对应的authors__id和publish__id.如果if判断拿不到值,说明还没有进行过滤,添加带有active类的a标签:<a class='active' href='#'>all</a>。all标签显示为激活状态。
如果if判断有值,通过del方法清除对应的params中的值,添加不带有active类的a标签:
1 | temp.append("<a href='?%s'>all</a>" % params.urlencode()) |
2、params.urlencode解析
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | # 访问http://127.0.0.1:8000/stark/app01/book/?authors__id=1&publish__id=1print("urlencode", params.urlencode)print("_url", params.urlencode())print("params", params)"""urlencode <bound method QueryDict.urlencode of <QueryDict: {'authors__id': ['1'], 'publish__id': ['1']}>>_url authors__id=1&publish__id=1params <QueryDict: {'authors__id': ['1'], 'publish__id': ['1']}>""" |
3、删改params不是修改get请求数据,而是修改a标签href值(本质)
通过点击按钮修改href值,修改每次发送的get请求数据。
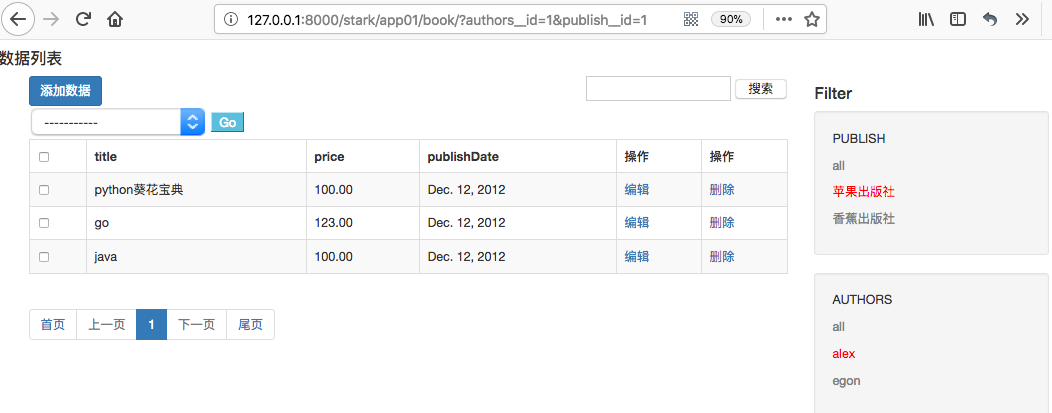
此时查看PUBLISH下的all按钮:
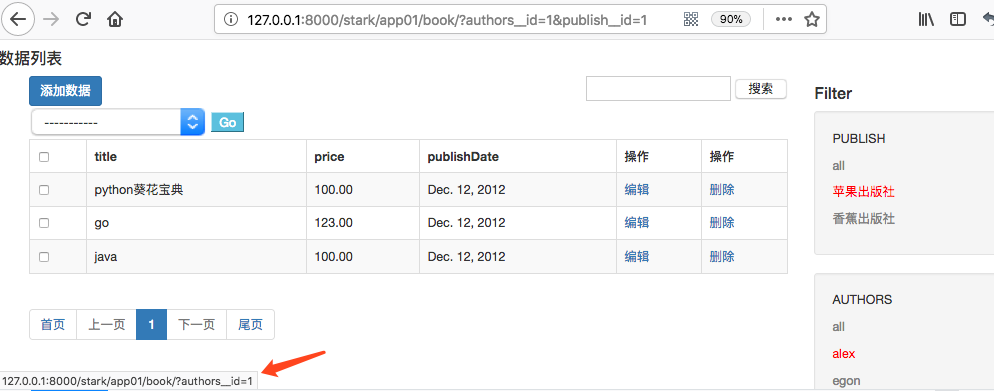
此时查看PUBLISH下的香蕉出版社:
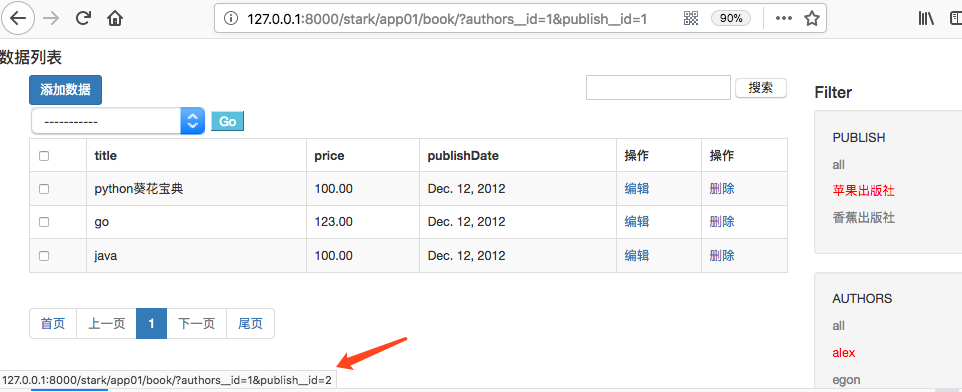
六、过滤实现
1、删除filter_field后面拼接的"__id"
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 | class ShowList(object): """展示页面类""" def __init__(self, config, data_list, request): self.config = config # 接收传递过来的配置类对象 ModelStark的实例对象 self.data_list = data_list # 接收传递过来的当前表的所有对象 self.request = request # <WSGIRequest: GET '/stark/app01/book/?page=2'> # 分页 data_count = self.data_list.count() current_page = int(self.request.GET.get("page", 1)) # 默认是第一页 base_path = self.request.path # /stark/app01/book/ self.pagination = Pagination(current_page, data_count, base_path, self.request.GET, per_page_num=3, pager_count=11,) # print("data_list", self.data_list) # data_list <QuerySet [<Book: python葵花宝典>, <Book: go>, <Book: java>]> self.page_data = self.data_list[self.pagination.start:self.pagination.end] # print("page_data", self.page_data) # page_data <QuerySet [<Book: python葵花宝典>]> # actions # self.actions = self.config.actions # 拿到配置好的函数对象列表 [patch_init,] self.actions = self.config.new_actions() # 拿到方法运行的返回结果 def get_filter_linktags(self): """获取过滤字段""" link_dic = {} print("list_filter", self.config.list_filter) # list_filter ['publish', 'authors'] for filter_field in self.config.list_filter: """循环每一个过滤字段""" import copy # self.request.GET # GET请求的所有数据 params = copy.deepcopy(self.request.GET) print("params", params) # <QueryDict: {'publish__id': ['1']}> # cid是当前字段传过来的值 cid = self.request.GET.get(filter_field, 0) # 没有值的时候默认为None,None是不能进行int()转换的,因此在这里给它设置默认值为0 # print(filter_field) # 'publish' 'authors' # 获取字段对象 filter_field_obj = self.config.model._meta.get_field(filter_field) # print(filter_field_obj) # app01.Book.publish app01.Book.authors # 拿到关联表下的所有数据 # print("rel...", filter_field_obj.rel.to.objects.all()) # 版本问题失效 # print("rel...", filter_field_obj.related_model.objects.all()) # <QuerySet [<Publish: 苹果出版社>, <Publish: 香蕉出版社>]> data_list = filter_field_obj.related_model.objects.all() # <QuerySet [<Publish: 苹果出版社> temp = [] # 处理all标签 if params.get(filter_field): print("_url", params.urlencode) del params[filter_field] temp.append("<a href='?%s'>all</a>" % params.urlencode()) else: temp.append("<a class='active' href='#'>all</a>") # 默认是all的状态 # 处理数据标签 for obj in data_list: # obj是每一个对象 """循环每一个过滤字段关联的数据""" # 构成一个新字典 过滤字段:当前对象主键值 params[filter_field] = obj.pk # 利用urlencode将键值对转化为a=1&b=2的格式 _url = params.urlencode() if int(cid) == obj.pk: # get请求数据int转换后与对象主键值匹配,匹配成功添加active类 link_tag = "<a class='active' href='?%s'>%s</a>" % (_url, str(obj)) else: # print(obj) # 苹果出版社 香蕉出版社 alex egon # print(type(obj)) # <class 'app01.models.Publish'> <class 'app01.models.Author'> link_tag = "<a href='?%s'>%s</a>" % (_url, str(obj)) # print(link_tag) # <a href=>苹果出版社</a> temp.append(link_tag) link_dic[filter_field] = temp # print(link_dic) # {'publish': ['<a href=>苹果出版社</a>', '<a href=>香蕉出版社</a>'], 'authors': ['<a href=>alex</a>', '<a href=>egon</a>']} return link_dic |
2、构建filter的Q对象(过滤条件)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | class ModelStark(object): def get_filter_condition(self, request): """拿到过滤条件""" filter_condition = Q() # 默认查询条件为且 and for filter_field, val in request.GET.items(): # 过滤字段、查询的值 去除fitler_field拼接的__id if filter_field in self.list_filter: # 只处理filter过滤列表的键值(分页等排除) filter_condition.children.append((filter_field, val)) return filter_condition |
注意get_filter_condition只处理filter过滤列表键值,需要将分页等请求数据排除。
3、在list_view方法中获取filter的Q对象完成过滤
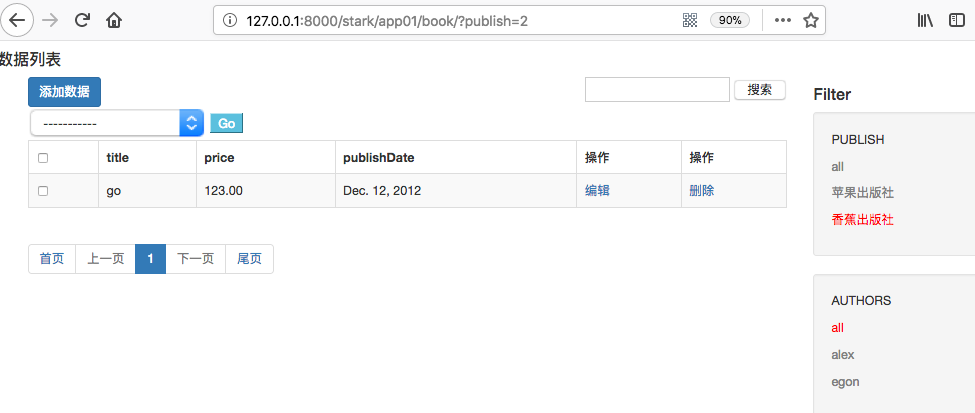
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 | class ModelStark(object): def list_view(self, request): if request.method == "POST": # action print("POST:", request.POST) action = request.POST.get("action") selected_pk = request.POST.getlist("selected_pk") # 拿到列表 # 反射 # self这里是配置类BookConfig,要在类中找到对应的函数 action_func = getattr(self, action) # patch_init # 拿到选中状态的pk值对象 queryset = self.model.objects.filter(pk__in=selected_pk) # <QuerySet [<Book: go>]> action_func(request, queryset) # 获取search的Q对象 search_condition = self.get_search_condition(request) # 获取filter构建Q对象 filter_condition = self.get_filter_condition(request) # 筛选当前表获取的数据 data_list = self.model.objects.all().filter(search_condition).filter(filter_condition) # 链式操作,二次过滤 # 获取showlist展示页面 show_list = ShowList(self, data_list, request) header_list = show_list.get_header() new_data_list = show_list.get_body() # 构建一个查看url add_url = self.get_add_url() print("add_url", add_url) return render(request, "list_view.html", locals()) |
注意这里是运用了链式操作,二次过滤。过滤效果显示如下:
七、一对多、多对多字段渲染处理
1、添加一对多、多对多字段 到list_display
app01/stark.py:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | class BookConfig(ModelStark): list_display = ["title", "price", "publishDate", "publish", "authors"] list_display_links = ["title"] modelform_class = BookModelForm search_fields = ['title', "price"] def patch_init(self, request, queryset): print(queryset) queryset.update(price=123) patch_init.short_description = "批量初始化" actions = [patch_init] list_filter = ["publish", "authors", ] # 一对多、多对多site.register(Book, BookConfig) |
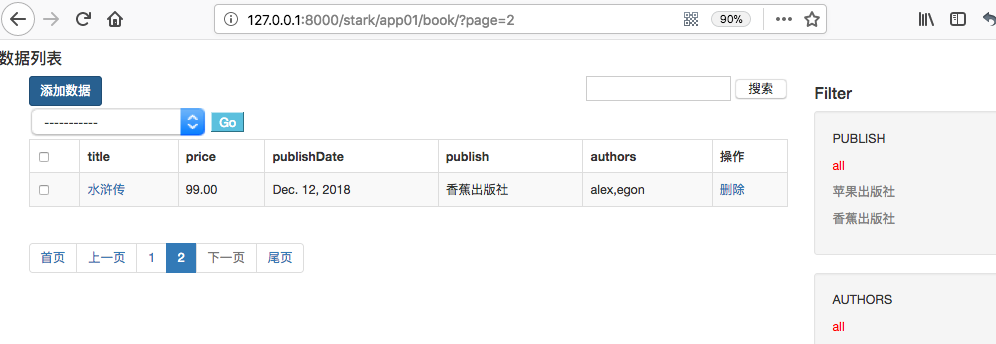
publish是一对多字段、authors是多对多字段。页面显示如下:
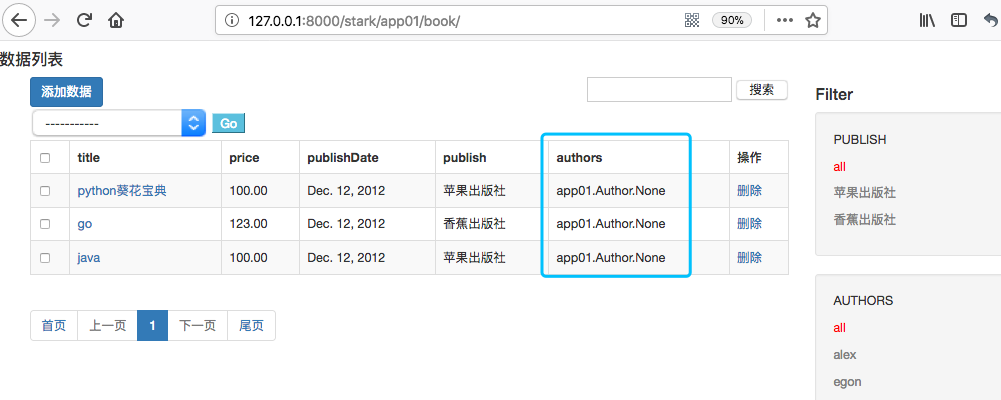
可以看到多对多字段无法正常显示,这个因为在service/stark.py中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 | class ShowList(object): """展示页面类""" def get_body(self): """构建表单数据""" new_data_list = [] # for obj in self.data_list: for obj in self.page_data: # 当前页面的数据 temp = [] for field in self.config.new_list_display(): # ["__str__", ] ["pk","name","age",edit] if callable(field): val = field(self.config, obj) else: val = getattr(obj, field) # 拿到的关联对象 处理不了多对多 if field in self.config.list_display_links: # _url = reverse("%s_%s_change" % (app_label, model_name), args=(obj.pk,)) _url = self.config.get_change_url(obj) val = mark_safe("<a href='%s'>%s</a>" % (_url, val)) temp.append(val) new_data_list.append(temp) return new_data_list |
get_body方法,val = getattr(obj, field)拿到的是关联对象,在一对一、一对多情况下,利用模型定了__str__可以正常显示名称,但是却无法处理多对多的情况。
2、多对多字段处理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 | class ShowList(object): """展示页面类""" def get_body(self): """构建表单数据""" new_data_list = [] # for obj in self.data_list: for obj in self.page_data: # 当前页面的数据 temp = [] for field in self.config.new_list_display(): # ["__str__", ] ["pk","name","age",edit] if callable(field): val = field(self.config, obj) else: from django.db.models.fields.related import ManyToManyField field_obj = self.config.model._meta.get_field(field) # 拿到字段对象 if isinstance(field_obj, ManyToManyField): # 判断是否是多对多 # 反射处理 增加.all # 多对多的情况 obj.field.all() ret = getattr(obj, field).all() # <QuerySet [<Author: alex>, <Author: egon>]> t = [] for obj in ret: t.append(str(obj)) val = ",".join(t) # 用join方法实现拼接 alex,egon else: # 非多对多的情况 val = getattr(obj, field) # 拿到的关联对象 处理不了多对多 if field in self.config.list_display_links: # _url = reverse("%s_%s_change" % (app_label, model_name), args=(obj.pk,)) _url = self.config.get_change_url(obj) val = mark_safe("<a href='%s'>%s</a>" % (_url, val)) temp.append(val) new_data_list.append(temp) return new_data_list |
显示效果:
注意:
(1)引入多对多类,利用isinstance判断对象是否是多对多对象
1 2 3 | from django.db.models.fields.related import ManyToManyFieldfield_obj = self.config.model._meta.get_field(field) # 拿到字段对象if isinstance(field_obj, ManyToManyField): # 判断是否是多对多 |
(2)利用反射处理多对多的情况
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | # 反射处理 增加.all# 多对多的情况 obj.field.all()ret = getattr(obj, field).all() # <QuerySet [<Author: alex>, <Author: egon>]>t = []for obj in ret: t.append(str(obj))val = ",".join(t) # 用join方法实现拼接 alex,egon |
(3)注意getattr(obj, field) 和getattr(obj, field).all()的区别
1 2 | print("ret",getattr(obj, field)) # ret app01.Author.Noneprint("ret", getattr(obj, field).all()) # ret <QuerySet [<Author: alex>, <Author: egon>]> |
(4)join()方法
用于将序列中的元素以指定的字符连接生成一个新的字符串。
1 2 3 | str = "-"seq = ("a", "b", "c") # 字符串序列print str.join( seq ) # a-b-c |
八、普通字段筛选
1、给list_filter添加普通字段"title"
app01/stark.py:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | class BookConfig(ModelStark): list_display = ["title", "price", "publishDate", "publish", "authors"] list_display_links = ["title"] modelform_class = BookModelForm search_fields = ['title', "price"] def patch_init(self, request, queryset): print(queryset) queryset.update(price=123) patch_init.short_description = "批量初始化" actions = [patch_init] list_filter = ["title", "publish", "authors", ] # 普通字段、一对多、多对多site.register(Book, BookConfig) |
添加后访问页面直接报错:
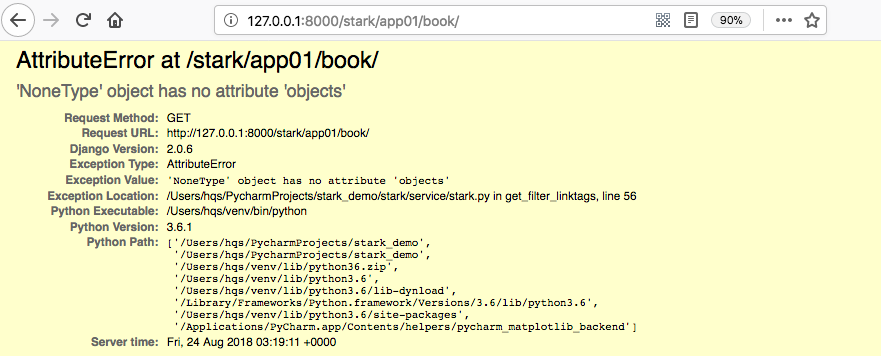
这是由于在ShowList类get_filter_linktags方法中:
1 2 3 4 | # 获取字段对象filter_field_obj = self.config.model._meta.get_field(filter_field)# 关联表下所有数据data_list = filter_field_obj.related_model.objects.all() # <QuerySet [<Publish: 苹果出版社> |
data_list这种取法只适用于一对一和一对多的情况。
2、处理过滤字段对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | from django.db.models.fields.related import ManyToManyField, ForeignKeyclass ShowList(object): """展示页面类""" def get_filter_linktags(self): """获取过滤字段""" link_dic = {} print("list_filter", self.config.list_filter) # list_filter ['publish', 'authors'] for filter_field in self.config.list_filter: """循环每一个过滤字段""" import copy params = copy.deepcopy(self.request.GET) cid = self.request.GET.get(filter_field, 0) # 获取字段对象 filter_field_obj = self.config.model._meta.get_field(filter_field) if isinstance(filter_field_obj, ForeignKey) or isinstance(filter_field_obj, ManyToManyField): data_list = filter_field_obj.related_model.objects.all() # <QuerySet [<Publish: 苹果出版社> else: # 普通字段直接查询 data_list = self.config.model.objects.all().values("pk", filter_field) # 主键值 字段对象值 |
引入ForeignKey和ManyToManyField类,利用isinstance判断是否是一对多、多对多对象。如果不是就是普通字段,直接查询处理。
3、处理数据标签对data_list做对应处理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | # 处理数据标签for obj in data_list: # obj是每一个对象 """循环每一个过滤字段关联的数据""" if isinstance(filter_field_obj, ForeignKey) or isinstance(filter_field_obj, ManyToManyField): # <QuerySet [<Publish: 苹果出版社>, <Publish: 香蕉出版社>]> pk = obj.pk text = str(obj) else: # 列表里面套着字典 data_list=[{"pk":1, "title":"go"},....] pk = obj.get("pk") text = obj.get(filter_field) # 构成一个新字典 过滤字段:当前对象主键值 params[filter_field] = pk # 利用urlencode将键值对转化为a=1&b=2的格式 _url = params.urlencode() if int(cid) == pk: # get请求数据int转换后与对象主键值匹配,匹配成功添加active类 link_tag = "<a class='active' href='?%s'>%s</a>" % (_url, text) else: # print(obj) # 苹果出版社 香蕉出版社 alex egon # print(type(obj)) # <class 'app01.models.Publish'> <class 'app01.models.Author'> link_tag = "<a href='?%s'>%s</a>" % (_url, text) |
两种data_list,一种是QuerySet,一种是数组套字典。两种数据类型的处理方式略有不同。
显示效果:
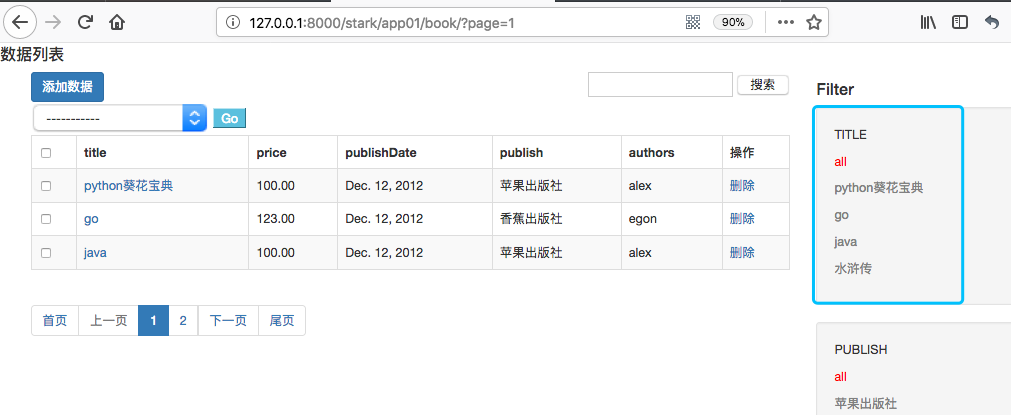
这样做完后点击TITLE下的过滤项是查不到任何对应数据的。这是因为默认传递的过滤字段都是PK值,但是针对普通字段过滤需要传递过滤字段值。
4、处理数据标签时过滤字段按情况拆分
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 | # 处理数据标签for obj in data_list: # obj是每一个对象(或者是数组) """循环每一个过滤字段关联的数据""" if isinstance(filter_field_obj, ForeignKey) or isinstance(filter_field_obj, ManyToManyField): # <QuerySet [<Publish: 苹果出版社>, <Publish: 香蕉出版社>]> pk = obj.pk text = str(obj) params[filter_field] = pk # 过滤字段:当前对象主键值 else: # 列表里面套着字典 data_list=[{"pk":1, "title":"go"},....] pk = obj.get("pk") text = obj.get(filter_field) params[filter_field] = text # 过滤字段:当前对象字段值 # 利用urlencode将键值对转化为a=1&b=2的格式 _url = params.urlencode() if cid == str(pk) or cid == text: # get请求数据int转换后与对象主键值匹配,匹配成功添加active类 link_tag = "<a class='active' href='?%s'>%s</a>" % (_url, text) else: # print(obj) # 苹果出版社 香蕉出版社 alex egon # print(type(obj)) # <class 'app01.models.Publish'> <class 'app01.models.Author'> link_tag = "<a href='?%s'>%s</a>" % (_url, text) # print(link_tag) # <a href=>苹果出版社</a> temp.append(link_tag) |
注意:
(1)params分拆为两种情况
一开始统一用params[filter_field] = pk 来设置过滤字段,但是设置普通过滤字段后,如果title=7这样是无法进行过滤的,必须让过滤字段等于"go"、"python"等字段值。因此将params也分拆为两种情况:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | if isinstance(filter_field_obj, ForeignKey) or isinstance(filter_field_obj, ManyToManyField): # <QuerySet [<Publish: 苹果出版社>, <Publish: 香蕉出版社>]> pk = obj.pk text = str(obj) params[filter_field] = pk # 过滤字段:当前对象主键值else: # 列表里面套着字典 data_list=[{"pk":1, "title":"go"},....] pk = obj.get("pk") text = obj.get(filter_field) params[filter_field] = text # 过滤字段:当前对象字段值 |
(2)cid(get请求数据)判断的调整
cid = self.request.GET.get(filter_field, 0) 由此可见cid是get请求传递的值,之前默认都是pk值,现在有可能是pk值也可能是"python"等普通字段。因此需要调整cid判断:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | if cid == str(pk) or cid == text: # get请求数据int转换后与对象主键值匹配,匹配成功添加active类 link_tag = "<a class='active' href='?%s'>%s</a>" % (_url, text)else: # print(obj) # 苹果出版社 香蕉出版社 alex egon # print(type(obj)) # <class 'app01.models.Publish'> <class 'app01.models.Author'> link_tag = "<a href='?%s'>%s</a>" % (_url, text) # print(link_tag) # <a href=>苹果出版社</a>temp.append(link_tag) |
(3)最终展示效果
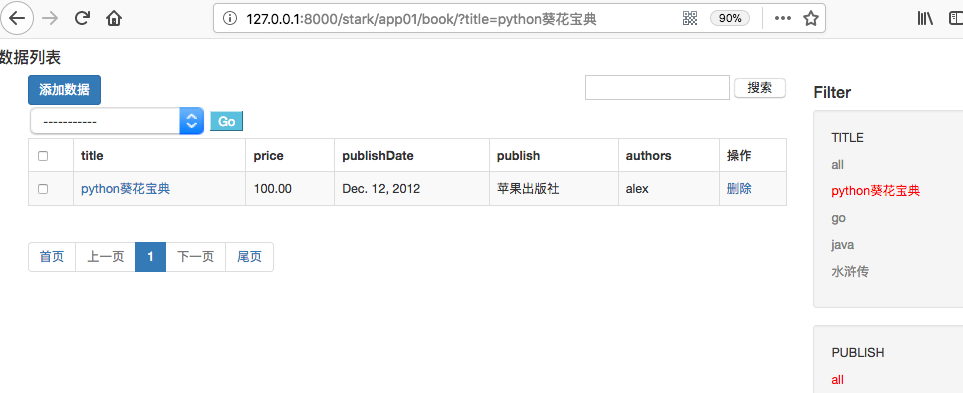
九、filter_list配置与否,决定是否显示FILTER
list_view.html:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | <div class="col-md-3"> {% if showlist.config.list_filter %} {# list_filter有值才显示FILTER #} <div class="filter"> <h4>Filter</h4> {% for filter_field, linktags in show_list.get_filter_linktags.items %} <div class="well"> {# upper方法改为大写 #} <p>{{ filter_field.upper }}</p> {% for link in linktags %} <p>{{ link|safe }}</p> {% endfor %} </div> {% endfor %} </div> {% endif %}</div> |




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术