简单回测框架开发
一、上下文数据存储
tushare发生了重大改版,不再直接提供免费服务。需要用户注册获取token,并获取足够积分才能使用sdk调用接口。
1、获取股票交易日信息保存到csv文件
没有找到csv文件时:获取股票交易日信息并导出到csv文件。
如果有找到csv文件,则直接读取数据。
注意:新版tushare需要先设置token和初始化pro接口。
import numpy as np import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import tushare as ts # 财经数据包 """ 获取所有股票交易日信息,保存在csv文件中 """ # 设置token ts.set_token('2cfd07xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx9077e1') # 初始化pro接口 pro = ts.pro_api() try: trade_cal = pd.read_csv("trade_cal.csv") """ print(trade_cal) Unnamed: 0 exchange cal_date is_open 0 0 SSE 19901219 1 1 1 SSE 19901220 1 2 2 SSE 19901221 1 """ except: # 获取交易日历数据 trade_cal = pro.trade_cal() # 输出到csv文件中 trade_cal.to_csv("trade_cal.csv")
2、定制股票信息类
注意:日期格式变为了纯数字,cal_date是日期信息,is_open列是判断是否开市的信息。
class Context: def __init__(self, cash, start_date, end_date): """ 股票信息 :param cash: 现金 :param start_date: 量化策略开始时间 :param end_date: 量化策略结束时间 :param positions: 持仓股票和对应的数量 :param benchmark: 参考股票 :param date_range: 开始-结束之间的所有交易日 :param dt: 当前日期 (循环时当前日期会发生变化) """ self.cash = cash self.start_date = start_date self.end_date = end_date self.positions = {} # 持仓信息 self.benchmark = None self.date_range = trade_cal[ (trade_cal["is_open"] == 1) & \ (trade_cal["cal_date"] >= start_date) & \ (trade_cal["cal_date"] <= end_date) ]
3、使用context查看交易日历信息
context = Context(10000, 20160101, 20170101) print(context.date_range) """ Unnamed: 0 exchange cal_date is_open 9147 9147 SSE 20160104 1 9148 9148 SSE 20160105 1 9149 9149 SSE 20160106 1 9150 9150 SSE 20160107 1 9151 9151 SSE 20160108 1 ... ... ... ... ... 9504 9504 SSE 20161226 1 9505 9505 SSE 20161227 1 9506 9506 SSE 20161228 1 9507 9507 SSE 20161229 1 9508 9508 SSE 20161230 1 """
二、获取历史数据
前面可以看到trade_cal获取的的日期数据都默认解析为了数字,并不方便使用,将content类修改如下:
CASH = 100000 START_DATE = '20160101' END_DATE = '20170101' class Context: def __init__(self, cash, start_date, end_date): """ 股票信息 :param cash: 现金 :param start_date: 量化策略开始时间 :param end_date: 量化策略结束时间 :param positions: 持仓股票和对应的数量 :param benchmark: 参考股票 :param date_range: 开始-结束之间的所有交易日 :param dt: 当前日期 (循环时当前日期会发生变化) """ self.cash = cash self.start_date = start_date self.end_date = end_date self.positions = {} # 持仓信息 self.benchmark = None self.date_range = trade_cal[ (trade_cal["is_open"] == 1) & \ (str(trade_cal["cal_date"]) >= start_date) & \ (str(trade_cal["cal_date"]) <= end_date) ] # 时间对象 # self.dt = datetime.datetime.strftime("", start_date) self.dt = dateutil.parser.parse((start_date)) context = Context(CASH, START_DATE, END_DATE)
设置Context对象默认参数:CASH、START_DATE、END_DATE。
1、自定义股票历史行情函数
获取某股票count天的历史行情,每运行一次该函数,日期范围后移。
def attribute_history(security, count, fields=('open','close','high','low','vol')): """ 获取某股票count天的历史行情,每运行一次该函数,日期范围后移 :param security: 股票代码 :param count: 天数 :param fields: 字段 :return: """ end_date = int((context.dt - datetime.timedelta(days=1)).strftime('%Y%m%d')) # print(end_date, type(end_date)) # 20161231 <class 'int'> start_date = trade_cal[(trade_cal['is_open'] == 1) & \ (trade_cal['cal_date']) <= end_date] \ [-count:].iloc[0,:]['cal_date'] # 剪切过滤到开始日期return attribute_daterange_history(security, start_date, end_date, fields)
2、tushare新接口daily获取行情
接口:daily,获取股票行情数据,或通过通用行情接口获取数据,包含了前后复权数据。
注意:日期都填YYYYMMDD格式,比如20181010。
df = pro.daily(ts_code='000001.SZ', start_date='20180701', end_date='20180718') """ ts_code trade_date open high ... change pct_chg vol amount 0 000001.SZ 20180718 8.75 8.85 ... -0.02 -0.23 525152.77 460697.377 1 000001.SZ 20180717 8.74 8.75 ... -0.01 -0.11 375356.33 326396.994 2 000001.SZ 20180716 8.85 8.90 ... -0.15 -1.69 689845.58 603427.713 3 000001.SZ 20180713 8.92 8.94 ... 0.00 0.00 603378.21 535401.175 4 000001.SZ 20180712 8.60 8.97 ... 0.24 2.78 1140492.31 1008658.828 5 000001.SZ 20180711 8.76 8.83 ... -0.20 -2.23 851296.70 744765.824 6 000001.SZ 20180710 9.02 9.02 ... -0.05 -0.55 896862.02 803038.965 7 000001.SZ 20180709 8.69 9.03 ... 0.37 4.27 1409954.60 1255007.609 8 000001.SZ 20180706 8.61 8.78 ... 0.06 0.70 988282.69 852071.526 9 000001.SZ 20180705 8.62 8.73 ... -0.01 -0.12 835768.77 722169.579 10 000001.SZ 20180704 8.63 8.75 ... -0.06 -0.69 711153.37 617278.559 11 000001.SZ 20180703 8.69 8.70 ... 0.06 0.70 1274838.57 1096657.033 12 000001.SZ 20180702 9.05 9.05 ... -0.48 -5.28 1315520.13 1158545.868 """
3、自定义获取某时段历史行情函数
获取某股票某时段的历史行情。
def attribute_daterange_history(security, start_date,end_date, fields=('open', 'close', 'high', 'low', 'vol')): """ 获取某股票某段时间的历史行情 :param security: 股票代码 :param start_date: 开始日期 :param end_date: 结束日期 :param field: 字段 :return: """ try: # 本地有读文件 f = open(security + '.csv', 'r') df = pd.read_csv(f, index_col ='date', parse_dates=['date']).loc[start_date:end_date, :] except: # 本地没有读取接口 df = pro.daily(ts_code=security, start_date=str(start_date), end_date=str(end_date)) print(df) """ ts_code trade_date open high ... change pct_chg vol amount 0 600998.SH 20160219 18.25 18.97 ... 0.10 0.55 110076.55 203849.292 1 600998.SH 20160218 18.80 19.29 ... -0.35 -1.88 137882.15 259670.566 2 600998.SH 20160217 19.25 19.25 ... -0.70 -3.62 120175.69 225287.565 3 600998.SH 20160216 18.99 19.49 ... 0.07 0.36 110166.63 211909.372 4 600998.SH 20160215 17.19 19.39 ... 1.50 8.43 134845.79 252147.191 .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 266 600998.SH 20150109 17.50 17.64 ... -0.52 -2.97 185493.27 318920.850 267 600998.SH 20150108 18.39 18.54 ... -0.69 -3.79 141380.21 254272.384 268 600998.SH 20150107 18.36 18.36 ... -0.19 -1.03 107884.49 195598.076 269 600998.SH 20150106 17.58 18.50 ... 0.71 4.02 208083.99 374072.880 270 600998.SH 20150105 17.78 17.97 ... -0.40 -2.21 184730.66 324766.514 """ return df[list(fields)] print(attribute_daterange_history('600998.SH', '20150104', '20160220'))
打印结果如下:
""" open close high low vol 0 18.25 18.41 18.97 18.19 110076.55 1 18.80 18.31 19.29 18.30 137882.15 2 19.25 18.66 19.25 18.42 120175.69 3 18.99 19.36 19.49 18.90 110166.63 4 17.19 19.29 19.39 17.15 134845.79 .. ... ... ... ... ... 266 17.50 16.98 17.64 16.93 185493.27 267 18.39 17.50 18.54 17.47 141380.21 268 18.36 18.19 18.36 17.95 107884.49 269 17.58 18.38 18.50 17.25 208083.99 270 17.78 17.67 17.97 17.05 184730.66 """
4、获取当天的行情数据
依然是使用daily函数获取当天行情数据。
START_DATE = '20160107' def get_today_data(security): """ 获取当天行情数据 :param security: 股票代码 :return: """ today = context.dt.strftime('%Y%m%d') print(today) # 20160107 try: f = open(security + '.csv', 'r') data = pd.read_csv(f, index_col='date', parse_date=['date']).loc[today,:] except FileNotFoundError: data = pro.daily(ts_code=security, trade_date=today).iloc[0, :] return data print(get_today_data('601318.SH'))
执行显示2016年1月7日的601318的行情数据:
ts_code 601318.SH trade_date 20160107 open 34 high 34.52 low 33 close 33.77 pre_close 34.53 change -0.76 pct_chg -2.2 vol 236476 amount 796251
三、基础下单函数
定义_order()函数模拟下单。
1、行情为空处理
修改get_today_data函数,为空时的异常处理:
def get_today_data(security): """ 获取当天行情数据 :param security: 股票代码 :return: """ today = context.dt.strftime('%Y%m%d') print(today) # 20160107 try: f = open(security + '.csv', 'r') data = pd.read_csv(f, index_col='date', parse_date=['date']).loc[today,:] except FileNotFoundError: data = pro.daily(ts_code=security, trade_date=today).iloc[0, :] except KeyError: data = pd.Series() # 为空,非交易日或停牌 return data
2、下单各种异常情况预处理
def _order(today_data, security, amount): """ 下单 :param today_data: get_today_data函数返回数据 :param security: 股票代码 :param amount: 股票数量 正:买入 负:卖出 :return: """ # 股票价格 p = today_data['close'] if len(today_data) == 0: print("今日停牌") return if int(context.cash) - int(amount * p) < 0: amount = int(context.cash / p) print("现金不足, 已调整为%d!" % amount) # 因为一手是100要调整为100的倍数 if amount % 100 != 0: if amount != -context.positions.get(security, 0): # 全部卖出不必是100的倍数 amount = int(amount / 100) * 100 print("不是100的倍数,已调整为%d" % amount) if context.positions.get(security, 0) < -amount: # 卖出大于持仓时成立 # 调整为全仓卖出 amount = -context.positions[security] print("卖出股票不能够持仓,已调整为%d" % amount)
3、更新持仓
def _order(today_data, security, amount): """ 下单 :param today_data: get_today_data函数返回数据 :param security: 股票代码 :param amount: 股票数量 正:买入 负:卖出 :return: """ # 股票价格 p = today_data['open'] """各种特殊情况""" # 新的持仓数量 context.positions[security] = context.positions.get(security, 0) + amount # 新的资金量 买:减少 卖:增加 context.cash -= amount * float(p) if context.positions[security] == 0: # 全卖完删除这条持仓信息 del context.positions[security] _order(get_today_data("600138.SH"), "600138.SH", 100) print(context.positions)
交易完成,显示持仓如下:
{'600138.SH': 100}
尝试购买125股:
_order(get_today_data("600138.SH"), "600138.SH", 125) print(context.positions) """ 不是100的倍数,已调整为100 {'600138.SH': 100} """
四、四种常用下单函数
def order(security, amount): """买/卖多少股""" today_data = get_today_data(security) _order(today_data, security, amount) def order_target(security, amount): """买/卖到多少股""" if amount < 0: print("数量不能为负数,已调整为0") amount = 0 today_data = get_today_data(security) hold_amount = context.positions.get(security, 0) # T+1限制没加入 # 差值 delta_amount = amount - hold_amount _order(today_data, security, delta_amount) def order_value(security, value): """买/卖多少钱的股票""" today_date = get_today_data(security) amount = int(value / today_date['open']) _order(today_date, security, amount) def order_target_value(security, value): """买/卖到多少钱的股""" today_data = get_today_data(security) if value < 0: print("价值不能为负,已调整为0") value = 0 # 已有该股价值多少钱 hold_value = context.positions.get(security, 0) * today_data['open'] # 还要买卖多少价值的股票 delta_value = value - hold_value order_value(security, delta_value)
测试买卖如下所示:
order('600318.SH', 100) order_value('600151.SH', 3000) order_target('600138.SH', 100) print(context.positions) """ 不是100的倍数,已调整为200 {'600318.SH': 100, '600151.SH': 200, '600138.SH': 100} """
五、回测框架
开发用户调用回测框架接口。
1、运行函数及收益率
前面context中的dt取的是start_date,但实际上这个值应该取start_date开始的第一个交易日。因此将Context对象做如下修改:
class Context: def __init__(self, cash, start_date, end_date): """ 股票信息 """ self.cash = cash self.start_date = start_date self.end_date = end_date self.positions = {} # 持仓信息 self.benchmark = None self.date_range = trade_cal[ (trade_cal["is_open"] == 1) & \ ((trade_cal["cal_date"]) >= int(start_date)) & \ ((trade_cal["cal_date"]) <= int(end_date)) ] # dt:start_date开始的第一个交易日 # self.dt = datetime.datetime.strftime("", start_date) # self.dt = dateutil.parser.parse((start_date)) self.dt = None
然后将dt的赋值放在run()函数中:
def run(): plt_df = pd.DataFrame(index=context.date_range['cal_date'], columns=['value']) # 初始的钱 init_value = context.cash # 用户初始化接口 initialize(context) # 保存前一交易日的价格 last_price = {} # 赋值dt为第一个交易日 for dt in context.date_range['cal_date']: context.dt = dateutil.parser.parse(str(dt)) # 调用用户编写的handle_data handle_data(context) value = context.cash for stock in context.positions: today_data = get_today_data(stock) # 考虑停牌的情况 if len(today_data) == 0: p = last_price[stock] else: p = today_data['open'] last_price[stock] = p value += p * context.positions[stock] plt_df.loc[dt, 'value'] = value # 收益率 plt_df['ratio'] = (plt_df['value'] - init_value) / init_value print(plt_df['ratio']) """ cal_date 20160107 0.00000 20160108 -0.00101 20160111 -0.00113 20160112 -0.00140 20160113 0.00296 20160114 -0.00219 20160115 0.00291 20160118 -0.00304 """ """ initialize和handle_data是用户操作 """ def initialize(context): pass def handle_data(context): order('600138.SH', 100) run()
由于之前设置的时间太长不方便测试,将交易结束时间设置为2016年2月7日。执行后打印每日收益率如上所示。
2、基准收益率
Context中benchmark参考股票的默认值是None。
class Context: def __init__(self, cash, start_date, end_date): """ 股票信息 :param cash: 现金 :param start_date: 量化策略开始时间 :param end_date: 量化策略结束时间 :param positions: 持仓股票和对应的数量 :param benchmark: 参考股票 :param date_range: 开始-结束之间的所有交易日 :param dt: 当前日期 (循环时当前日期会发生变化) """ self.cash = cash self.start_date = start_date self.end_date = end_date self.positions = {} # 持仓信息 self.benchmark = None
3、基准股设置
添加set_benchmark函数获取用户在initialize()函数中设置的基准股。
def set_benchmark(security): """只支持一只股票的基准""" context.benchmark = security def initialize(context): # 设置基准股 set_benchmark("600008.SH") def run(): plt_df = pd.DataFrame(index=context.date_range['cal_date'], columns=['value']) # 初始的钱 init_value = context.cash # 用户初始化接口 initialize(context) # 保存前一交易日的价格 last_price = {}
4、基准收益率计算
这里将计算的基准收益率赋值到plt_df时一直会出现问题,显示NaN。这是由于:Series的index和df的index是否一致,如果不一致,那么就会造成在不一致的索引上的值全部为NaN。
def run(): plt_df = pd.DataFrame(index=context.date_range['cal_date'], columns=['value']) # 初始的钱 init_value = context.cash # 用户初始化接口 initialize(context) """代码略""" # 收益率 plt_df['ratio'] = (plt_df['value'] - init_value) / init_value # 基准股 bm_df = attribute_daterange_history(context.benchmark, context.start_date, context.end_date) # 基准股初始价 bm_init = bm_df['open'][1] bm_series = (bm_df['open'] - bm_init).values # 去索引 # 基准收益率 # Series的index和df的index是否一致,如果不一致,那么就会造成在不一致的索引上的值全部为NaN plt_df['benchmark_ratio'] = bm_series / bm_init print(plt_df) """ value ratio benchmark_ratio cal_date 20160107 100000 0.00000 0.020115 20160108 99899 -0.00101 0.000000 20160111 99887 -0.00113 -0.010057 20160112 99860 -0.00140 -0.028736 20160113 100296 0.00296 -0.022989 20160114 99781 -0.00219 -0.043103 20160115 100291 0.00291 -0.011494 20160118 99696 -0.00304 0.020115 20160119 100128 0.00128 0.116379 """ """ initialize和handle_data是用户操作 """ def initialize(context): # 设置基准股 set_benchmark("600008.SH") def handle_data(context): order('600138.SH', 100) run()
如上可以看到收益率和基准收益率都已经添加到了plt_df对象中。
5、绘图
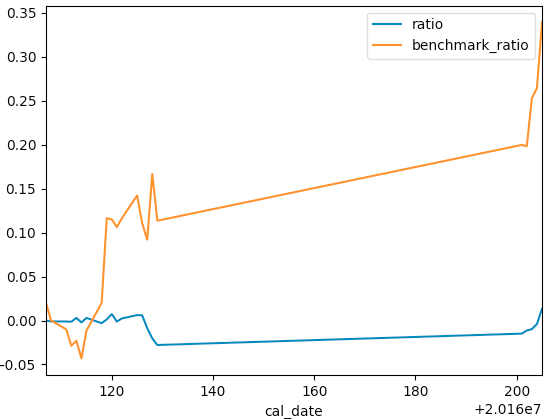
def run(): plt_df = pd.DataFrame(index=context.date_range['cal_date'], columns=['value']) # 初始的钱 init_value = context.cash """省略代码""" # 收益率 plt_df['ratio'] = (plt_df['value'] - init_value) / init_value # 基准股 bm_df = attribute_daterange_history(context.benchmark, context.start_date, context.end_date) # 基准股初始价 bm_init = bm_df['open'][1] bm_series = (bm_df['open'] - bm_init).values # 去索引 # 基准收益率 # Series的index和df的index是否一致,如果不一致,那么就会造成在不一致的索引上的值全部为NaN plt_df['benchmark_ratio'] = bm_series / bm_init # 绘图 plt_df[['ratio', 'benchmark_ratio']].plot() plt.show()
执行后绘图如下所示:
六、用户使用模拟
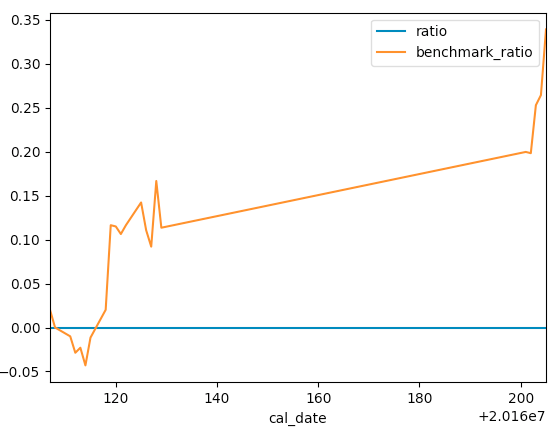
""" initialize和handle_data是用户操作 """ def initialize(context): # 设置基准股 set_benchmark("600008.SH") g.p1 = 5 g.p2 = 60 g.security = '600138.SH' def handle_data(context): print(context) print(g.security, g.p2) hist = attribute_history(g.security, g.p2) # 后五日均线值 ma5 = hist['close'][-g.p1:].mean() ma60 = hist['close'].mean() if ma5 > ma60 and g.security not in context.positions: # 金叉有多少买多少 order_value(g.security, context.cash) elif ma5 < ma60 and g.security in context.positions: order_target(g.security, 0) run()
执行策略绘图如下:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号