Scrapy框架之基于RedisSpider实现的分布式爬虫
需求:爬取的是基于文字的网易新闻数据(国内、国际、军事、航空)。
基于Scrapy框架代码实现数据爬取后,再将当前项目修改为基于RedisSpider的分布式爬虫形式。
一、基于Scrapy框架数据爬取实现
1、项目和爬虫文件创建
$ scrapy startproject wangyiPro
$ cd wangyiPro/
$ scrapy genspider wangyi news.163.com # 基于scrapy.Spider创建爬虫文件
2、爬虫文件编写——解析新闻首页获取四个板块的url
import scrapy
class WangyiSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = 'wangyi'
# allowed_domains = ['news.163.com']
start_urls = ['https://news.163.com/']
def parse(self, response):
lis = response.xpath('//div[@class="ns_area list"]/ul/li')
# 获取指定的四个列表元素(国内3、国际5、军事6、航空7)
indexes = [3, 4, 6, 7]
li_list = [] # 四个板块对应的li标签对象
for index in indexes:
li_list.append(lis[index])
# 获取四个板块中的超链和文字标题
for li in li_list:
url = li.xpath('./a/@href').extract_first()
title = li.xpath('./a/text()').extract_first() # 板块名称
print(url + ":" + title) # 测试
执行爬虫文件,控制台打印输出四个url,说明解析成功:
$ scrapy crawl wangyi --nolog
http://news.163.com/domestic/:国内
http://news.163.com/world/:国际
http://war.163.com/:军事
http://news.163.com/air/:航空
3、爬虫文件编写——对每个板块url发请求,进一步解析
import scrapy
class WangyiSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = 'wangyi'
# allowed_domains = ['news.163.com']
start_urls = ['https://news.163.com/']
def parse(self, response):
lis = response.xpath('//div[@class="ns_area list"]/ul/li')
# 获取指定的四个列表元素(国内3、国际5、军事6、航空7)
indexes = [3, 4, 6, 7]
li_list = [] # 四个板块对应的li标签对象
for index in indexes:
li_list.append(lis[index])
# 获取四个板块中的超链和文字标题
for li in li_list:
url = li.xpath('./a/@href').extract_first()
title = li.xpath('./a/text()').extract_first() # 板块名称
"""对每一个板块对应url发起请求,获取页面数据"""
# 调用scrapy.Request()方法发起get请求
yield scrapy.Request(url=url, callback=self.parseSecond)
def parseSecond(self, response):
"""声明回调函数"""
# 找到页面中新闻的共有标签类型,排除广告标签
div_list = response.xpath('//div[@class="data_row news_article clearfix"]')
print(len(div_list)) # 非空则验证xpath是正确的
for div in div_list:
# 文章标题
head = div.xpath('.//div[@class="news_title"]/h3/a/text()').extract_first()
# 文章url
url = div.xpath('.//div[@class="news_title"]/h3/a/@href').extract_first()
# 缩略图
imgUrl = div.xpath('./a/img/@src').extract_first()
# 发布时间和标签:提取列表中所有的元素
tag = div.xpath('.//div[@class="news_tag"]//text()').extract()
# 列表装化为字符串
tag = "".join(tag)
编写到这里时,再次执行爬虫脚本,会发现print(len(div_list))输出的是4个0,但是xpath表达式却是正确的。
这是由于新浪网的新闻列表信息是动态加载的,而爬虫程序向url发请求无法获取动态加载的页面信息。
因此需要selenium帮忙在程序中实例化一个浏览器对象,由浏览器对象向url发请求,再通过调用page_source属性拿到selenium实例化对象中获取的页面数据,这个数据中包含动态加载的数据内容。
二、将selenium应用到Scrapy项目中
需求分析:当点击国内超链进入国内对应的页面时,会发现当前页面展示的新闻数据是被动态加载出来的,如果直接通过程序对url进行请求,是获取不到动态加载出的新闻数据的。则就需要我们使用selenium实例化一个浏览器对象,在该对象中进行url的请求,获取动态加载的新闻数据。
响应对象response从下载器传给Spiders爬虫文件时,一定会穿过下载中间件。
可以在下载中间件对响应对象进行拦截,对响应对象中存储的页面数据进行篡改,将动态加载的页面数据加入到响应对象中。
通过selenium可以篡改响应数据,并将页面数据篡改成携带了新闻数据的数据。
1、selenium在scrapy中使用原理
当引擎将国内板块url对应的请求提交给下载器后,下载器进行网页数据的下载,然后将下载到的页面数据,封装到response中,提交给引擎,引擎将response在转交给Spiders。
Spiders接受到的response对象中存储的页面数据里是没有动态加载的新闻数据的。要想获取动态加载的新闻数据,则需要在下载中间件中对下载器提交给引擎的response响应对象进行拦截,切对其内部存储的页面数据进行篡改,修改成携带了动态加载出的新闻数据,然后将被篡改的response对象最终交给Spiders进行解析操作。
2、selenium在scrapy中使用流程总结
(1)在爬虫文件中导入webdriver类
from selenium import webdriver
(2)重写爬虫文件的构造方法
在构造方法中使用selenium实例化一个浏览器对象(因为浏览器对象只需要被实例化一次)
class WangyiSpider(scrapy.Spider):
def __init__(self):
# 实例化浏览器对象(保证只会被实例化一次)
self.bro = webdriver.Chrome(executable_path='/Users/hqs/ScrapyProjects/wangyiPro/wangyiPro/chromedriver')
(3)重写爬虫文件的closed(self,spider)方法
在其内部关闭浏览器对象。该方法是在爬虫结束时被调用。
class WangyiSpider(scrapy.Spider):
def closed(self, spider):
# 必须在整个爬虫结束后关闭浏览器
print('爬虫结束')
self.bro.quit() # 浏览器关闭
(4)重写下载中间件的process_response方法
让process_response方法对响应对象进行拦截,并篡改response中存储的页面数据。
(5)在配置文件中开启下载中间件
3、项目代码示例
(1)引入selenium定义浏览器开启和关闭
import scrapy
from selenium import webdriver
from wangyiPro.items import WangyiproItem
class WangyiSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = 'wangyi'
# allowed_domains = ['news.163.com']
start_urls = ['https://news.163.com/']
def __init__(self):
# 实例化浏览器对象(保证只会被实例化一次)
self.bro = webdriver.Chrome(executable_path='./wangyiPro/chromedrive')
def closed(self, spider):
# 必须在整个爬虫结束后关闭浏览器
print('爬虫结束')
self.bro.quit() # 浏览器关闭
(2)使用下载中间件拦截settings.py修改
# Enable or disable downloader middlewares
# See https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/downloader-middleware.html
DOWNLOADER_MIDDLEWARES = {
'wangyiPro.middlewares.WangyiproDownloaderMiddleware': 543,
}
(3)在下载中间件中进行拦截
让浏览器对象去发起get请求,获取四大版块对应的页面数据,浏览器对url发送请求,浏览器是可以获取到动态加载的页面数据的。
获取到这部分动态数据后,可以将这部分数据装回到拦截的response对象中去。然后将篡改好的response对象发给Spiders。
Spiders接收到response对象后,将response赋值给回调函数parseSecond的response参数中。
middlewares.py内容如下所示:
# 下载中间件
from scrapy.http import HtmlResponse # 通过这个类实例化的对象就是响应对象
import time
class WangyiproDownloaderMiddleware(object):
def process_request(self, request, spider):
"""
可以拦截请求
:param request:
:param spider:
:return:
"""
return None
def process_response(self, request, response, spider):
"""
可以拦截响应对象(下载器传递给Spider的响应对象)
:param request: 响应对象对应的请求对象
:param response: 拦截到的响应对象
:param spider: 爬虫文件中对应的爬虫类的实例
:return:
"""
print(request.url + "这是下载中间件")
# 响应对象中存储页面数据的篡改
if request.url in ['http://news.163.com/domestic/', 'http://news.163.com/world/', 'http://war.163.com/', 'http://news.163.com/air/']:
# 浏览器请求发送(排除起始url)
spider.bro.get(url=request.url)
# 滚轮拖动到底部会动态加载新闻数据,js操作滚轮拖动
js = 'window.scrollTo(0, document.body.scrollHeight)' # 水平方向不移动:0;竖直方向移动:窗口高度
spider.bro.execute_script(js) # 拖动到底部,获取更多页面数据
time.sleep(2) # js执行给页面2秒时间缓冲,让所有数据得以加载
# 页面数据page_text包含了动态加载出来的新闻数据对应的页面数据
page_text = spider.bro.page_source
# current_url就是通过浏览器发起请求所对应的url
# body是当前响应对象携带的数据值
return HtmlResponse(url=spider.bro.current_url, body=page_text, encoding="utf-8", request=request)
else:
# 四个板块之外的响应对象不做修改
return response # 这是原来的响应对象
三、爬虫代码完善及item处理
1、爬虫文件
import scrapy
from selenium import webdriver
from wangyiPro.items import WangyiproItem
class WangyiSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = 'wangyi'
# allowed_domains = ['news.163.com']
start_urls = ['https://news.163.com/']
def __init__(self):
# 实例化浏览器对象(保证只会被实例化一次)
self.bro = webdriver.Chrome(executable_path='/Users/hqs/ScrapyProjects/wangyiPro/wangyiPro/chromedriver')
def closed(self, spider):
# 必须在整个爬虫结束后关闭浏览器
print('爬虫结束')
self.bro.quit() # 浏览器关闭
def parse(self, response):
lis = response.xpath('//div[@class="ns_area list"]/ul/li')
# 获取指定的四个列表元素(国内3、国际5、军事6、航空7)
indexes = [3, 4, 6, 7]
li_list = [] # 四个板块对应的li标签对象
for index in indexes:
li_list.append(lis[index])
# 获取四个板块中的超链和文字标题
for li in li_list:
url = li.xpath('./a/@href').extract_first()
title = li.xpath('./a/text()').extract_first() # 板块名称
"""对每一个板块对应url发起请求,获取页面数据"""
# 调用scrapy.Request()方法发起get请求
yield scrapy.Request(url=url, callback=self.parseSecond, meta={'title': title})
def parseSecond(self, response):
"""声明回调函数"""
# 找到页面中新闻的共有标签类型,排除广告标签
div_list = response.xpath('//div[@class="data_row news_article clearfix"]')
# print(len(div_list)) # 非空则验证xpath是正确的
for div in div_list:
# 文章标题
head = div.xpath('.//div[@class="news_title"]/h3/a/text()').extract_first()
# 文章url
url = div.xpath('.//div[@class="news_title"]/h3/a/@href').extract_first()
# 缩略图
imgUrl = div.xpath('./a/img/@src').extract_first()
# 发布时间和标签:提取列表中所有的元素
tag = div.xpath('.//div[@class="news_tag"]//text()').extract()
# 列表装化为字符串
tags = []
for t in tag:
t = t.strip(' \n \t') # 去除空格 \n换行 \t相当于tab
tags.append(t) # 重新装载到列表中
tag = "".join(tags)
# 获取meta传递的数据值
title = response.meta['title']
# 实例化item对象,将解析到的数据值存储到item对象中
item = WangyiproItem()
item['head'] = head
item['url'] = url
item['imgUrl'] = imgUrl
item['tag'] = tag
item['title'] = title
# 对url发起请求,获取对应页面中存储的新闻内容数据
yield scrapy.Request(url=url, callback=self.getContent, meta={"item":item})
def getContent(self, response):
"""新闻内容解析的回调函数"""
# 获取传递过来的item对象
item = response.meta['item']
# 解析当前页码中存储的页面数据
# 由于新闻的段落可能有多个,每个段落在一个p标签中。因此使用extract()方法
content_list = response.xpath('//div[@class="post_text"]/p/text()').extract()
# 列表转字符串(字符串才能保持在item对象中)
content = "".join(content_list)
item["content"] = content
# item对象提交给管道
yield item
注意:
(1)将解析到的数据值存储到item对象
由于爬虫做了两次解析,因此如何将第一次解析的数据加入item对象是最大的难点。
解决方法:meta属性请求传参。
# 对url发起请求,获取对应页面中存储的新闻内容数据
yield scrapy.Request(url=url, callback=self.getContent, meta={"item":item})
对文章url发起请求,欲获取对应页面中存储的新闻内容数据,调用新的回调函数getContent。
(2)新闻内容解析后将item对象提交给管道
class WangyiSpider(scrapy.Spider):
"""同上省略"""
def getContent(self, response):
"""新闻内容解析的回调函数"""
# 获取传递过来的item对象
item = response.meta['item']
# 解析当前页码中存储的页面数据
# 由于新闻的段落可能有多个,每个段落在一个p标签中。因此使用extract()方法
content_list = response.xpath('//div[@class="post_text"]/p/text()').extract()
# 列表转字符串(字符串才能保持在item对象中)
content = "".join(content_list)
item["content"] = content
# item对象提交给管道
yield item
2、items.py文件
import scrapy
class WangyiproItem(scrapy.Item):
# define the fields for your item here like:
# name = scrapy.Field()
head = scrapy.Field()
url = scrapy.Field()
imgUrl = scrapy.Field()
tag = scrapy.Field()
title = scrapy.Field()
content = scrapy.Field()
3、管道文件pipeline.py处理
(1)pipelines.py
class WangyiproPipeline(object):
def process_item(self, item, spider):
print(item['title']+ ':'+ item['content'])
return item
(2)settings.py中放开管道
# Configure item pipelines
# See https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html
ITEM_PIPELINES = {
'wangyiPro.pipelines.WangyiproPipeline': 300,
}
(3)执行爬虫输出爬取的新闻信息

四、UA池和代理池在Scrapy中应用
1、下载中间件介绍
下载中间件(Downloader Middlewares) 位于scrapy引擎和下载器之间的一层组件。
- 作用:
(1)引擎将请求传递给下载器过程中, 下载中间件可以对请求进行一系列处理。比如设置请求的 User-Agent,设置代理等
(2)在下载器完成将Response传递给引擎中,下载中间件可以对响应进行一系列处理。比如进行gzip解压等。
我们主要使用下载中间件处理请求,一般会对请求设置随机的User-Agent ,设置随机的代理。目的在于防止爬取网站的反爬虫策略。
2、UA池:User-Agent池
-
作用:尽可能多的将scrapy工程中的请求伪装成不同类型的浏览器身份。
-
操作流程:
1.在下载中间件中拦截请求
2.将拦截到的请求的请求头信息中的UA进行篡改伪装
3.在配置文件中开启下载中间件
-
代码实现:
# 在middlewares.py中单独给UA池封装一个下载中间件的类
from scrapy.contrib.downloadermiddleware.useragent import UserAgentMiddleware
import random
class RandomUserAgent(UserAgentMiddleware): # 继承UserAgentMiddleware
def process_request(self, request, spider):
"""每次拦截请求,都会从列表中随机抽选一个ua赋值给当前拦截的请求"""
# 从列表中随机抽选出一个ua值
ua = random.choice(user_agent_list)
# 请求头信息设置,赋值随机抽取的ua(当前拦截请求ua写入操作)
request.headers.setdefault('User-Agent', ua)
user_agent_list = [
"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.1 "
"(KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/22.0.1207.1 Safari/537.1",
"Mozilla/5.0 (X11; CrOS i686 2268.111.0) AppleWebKit/536.11 "
"(KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/20.0.1132.57 Safari/536.11",
"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/536.6 "
"(KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/20.0.1092.0 Safari/536.6",
"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.2) AppleWebKit/536.6 "
"(KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/20.0.1090.0 Safari/536.6",
"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.2; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.1 "
"(KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/19.77.34.5 Safari/537.1",
"Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/536.5 "
"(KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/19.0.1084.9 Safari/536.5",
"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.0) AppleWebKit/536.5 "
"(KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/19.0.1084.36 Safari/536.5",
"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/536.3 "
"(KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/19.0.1063.0 Safari/536.3",
"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 5.1) AppleWebKit/536.3 "
"(KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/19.0.1063.0 Safari/536.3",
"Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_8_0) AppleWebKit/536.3 "
"(KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/19.0.1063.0 Safari/536.3",
"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.2) AppleWebKit/536.3 "
"(KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/19.0.1062.0 Safari/536.3",
"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/536.3 "
"(KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/19.0.1062.0 Safari/536.3",
"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.2) AppleWebKit/536.3 "
"(KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/19.0.1061.1 Safari/536.3",
"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/536.3 "
"(KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/19.0.1061.1 Safari/536.3",
"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1) AppleWebKit/536.3 "
"(KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/19.0.1061.1 Safari/536.3",
"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.2) AppleWebKit/536.3 "
"(KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/19.0.1061.0 Safari/536.3",
"Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/535.24 "
"(KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/19.0.1055.1 Safari/535.24",
"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.2; WOW64) AppleWebKit/535.24 "
"(KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/19.0.1055.1 Safari/535.24"
]
3、代理池
-
作用:尽可能多的将scrapy工程中的请求的IP设置成不同的。
-
操作流程:
1.在下载中间件中拦截请求
2.将拦截到的请求的IP修改成某一代理IP
3.在配置文件中开启下载中间件
-
代码实现:
# 在middlewares.py中单独给代理池封装一个下载中间件的类
# 批量对拦截的请求进行Ip更换
class Proxy(object):
def process_request(self, request, spider):
# 对拦截到的请求url进行判断(协议头到底是http还是https)
# 代理IP对协议头有严格区分
# request.url返回值形式:http://www.xxx.com/
h = request.url.split(":")[0] # 切割获取协议头
if h == "https":
ip = random.choice(PROXY_https)
# 利用meta修改代理ip
request.meta['proxy'] = 'https://' + ip
else:
ip = random.choice(PROXY_http)
request.meta['proxy'] = 'http://' + ip
# 可被选用的代理IP——去www.goubanjia.com获取免费代理IP
PROXY_http = [
'153.180.102.104:80',
'195.208.131.189:56055',
]
PROXY_https = [
'120.83.49.90:9000',
'95.189.112.214:35508',
]
注意:请求url的协议头到底是http还是https。
4、settings.py中开启ua池、代理池
# Enable or disable downloader middlewares
# See https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/downloader-middleware.html
DOWNLOADER_MIDDLEWARES = {
'wangyiPro.middlewares.WangyiproDownloaderMiddleware': 543,
'wangyiPro.middlewares.RandomUserAgent': 542,
'wangyiPro.middlewares.Proxy': 541,
}
5、总结
每发一个请求,这个请求都会被中间件拦截,对当前请求的ip和user-agent进行更换。
目的是攻克网站的反爬机制,因为每发一个请求,它的代理ip和ua都是不一样的,门户网站就很难发现当前爬取的载体是一个爬虫。
五、基于RedisSpider分布式爬虫实现
1、爬虫类代码修改
(1)导包并修改爬虫类父类
from scrapy_redis.spiders import RedisSpider
# class WangyiSpider(scrapy.Spider):
class WangyiSpider(RedisSpider):
注意:这里将爬虫类的父类,修改成RedisSpider。
(2)注释start_urls,以redis_key代替
# start_urls = ['https://news.163.com/']
redis_key = 'wangyi'
redis_key属性:表示调度器队列的名称。
2、redis数据库配置文件redis.conf配置
# 不注释时,只允许本机的客户端连接
# bind 127.0.0.1
# yes改为no,关闭redis的保护模式,客户端可以对服务器进行读写操作
protected-mode no
3、项目settings.py配置
(1)爬虫程序不在redis本机时,指定redis地址
管道默认会连接且将数据存储到本机的redis服务中,如果想要连接存储到其他redis服务中需要在settings.py中进行如下配置
# 如果redis服务器不在自己本机,则需要做如下配置
REDIS_HOST = '192.168.31.31' # redis数据库所在机器的Ip地址
REDIS_PORT = 6379
# 可选配置
# REDIS_ENCODING = 'utf-8'
# REDIS_PARAMS = {'password':'123456'} # 如果redis数据库有密码时配置
(2)使用scrapy-redis组件中封装好的管道
使用scrapy-redis组件中封装好的可以被共享的管道。
可以将每台机器爬取到的数据存储通过该管道存储到redis数据库中,从而实现了多台机器的管道共享。
# Configure item pipelines
# See https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html
ITEM_PIPELINES = {
# 'wangyiPro.pipelines.WangyiproPipeline': 300,
'scrapy_redis.pipelines.RedisPipeline': 400,
}
(3)使用scrapy-redis组件中封装好的调度器
使用scrapy-redis组件中封装好的调度器,将所有的url存储到该指定的调度器中,从而实现了多台机器的调度器共享。
以下代码可在settings.py中任意位置粘贴:
# 使用scrapy-redis组件的去重队列
DUPEFILTER_CLASS = "scrapy_redis.dupefilter.RFPDupeFilter"
# 使用scrapy-redis组件自己的调度器
SCHEDULER = "scrapy_redis.scheduler.Scheduler" # 核心配置
# 是否允许暂停
SCHEDULER_PERSIST = True # 值为True表示:宕机恢复服务时,从宕机的那个地方开始爬取,不用从头开始
4、项目运行
(1)基于配置文件开启redis服务器
# MAC/Linux
$ pwd
/Users/hqs/redis-5.0.2
$ src/redis-server redis.conf
# windows
$ redis-server.exe redis-windows.conf
(2)执行爬虫文件
$ pwd
/Users/hqs/ScrapyProjects/wangyiPro/wangyiPro/spiders
$ scrapy runspider wangyi.py
(3)在redis客户端中,将起始url扔到调度器队列
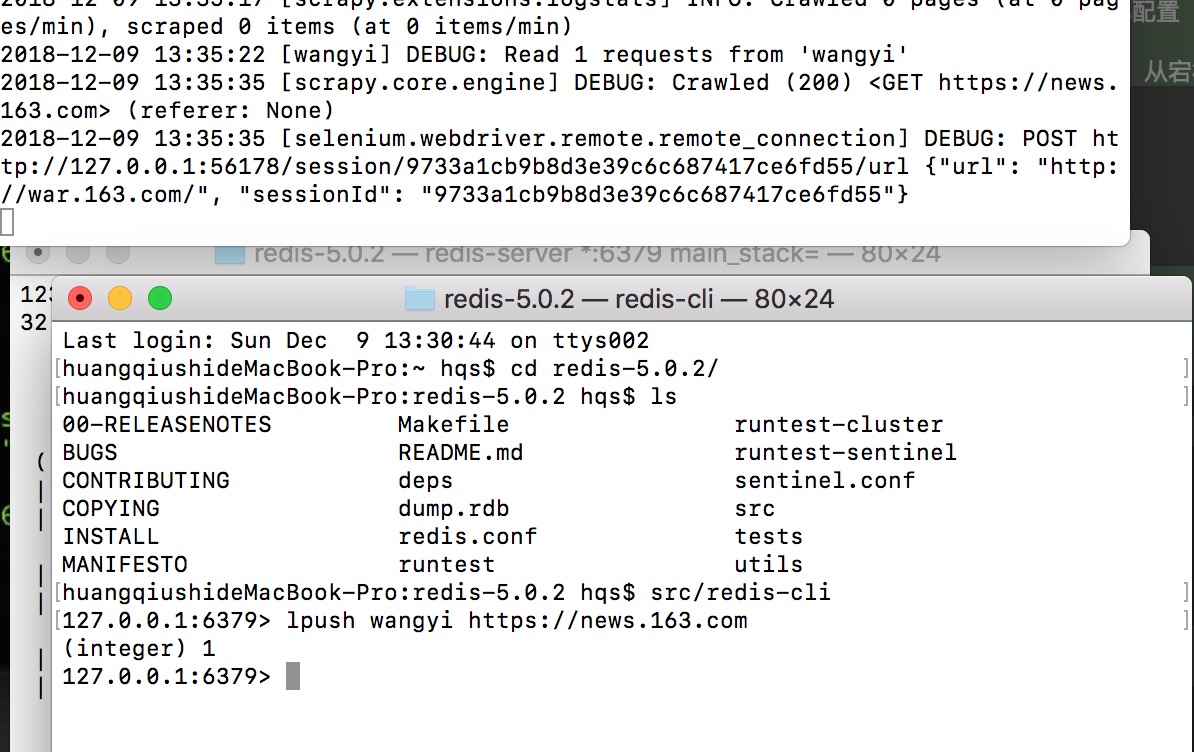
$ src/redis-cli
127.0.0.1:6379> lpush wangyi https://news.163.com
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> keys *
1) "data"
2) "qiubai:items"
3) "name"
4) "qiubai:dupefilter"
5) "wangyi:items"
127.0.0.1:6379> lrange wangyi:items 0 -1 # 从头到尾查看数据值
提交起始url后,爬虫开始干活:




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术