让我们制作一个Toast吧
Toast是一种转瞬即逝的对话框,它在淡出之前会显示几秒钟。Toast不需要焦点,而且是非模态的,因此,它们不会中断当前活跃的应用程序。
Toast最好的地方是它可以告知用户事件,而不需要强迫用户打开一个Activity或阅读一个Notification。它为运行在后台的Service,在不中断前台应用程序的前提下,告知用户事件提供了理想的机制。
Toast类包含一个静态的makeText方法,用来创建一个标准的Toast显示窗口。传入应用程序上下文、显示的文本和要显示的时间(LENGTH_SHORT或者LENGTH_LONG)来构建一个新的Toast。一旦Toast已经创建完成,调用show方法来显示它,如下面的代码片段所示:
Context context = getApplicationContext();
String msg = “To health and happiness!”;
int duration = Toast.LENGTH_SHORT;
Toast toast = Toast.makeText(context, msg, duration);
toast.show();
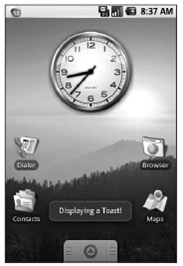
图8-1 显示了一个Toast。在它淡出前,它将在屏幕上保持2秒左右的时间。在它可见的时候,其后的应用程序还能保持完全的响应和交互。
图 8-1
定制Toast
标准的Toast文本消息窗口一般来说应该是足用了,但在一些情形中,你可能想要定制它的外观和屏幕位置。你可以通过设定它的显示位置和指定可选的View或Layout来修改一个Toast。
下面的代码片段显示了如何用setGravity方法来将一个Toast布局在屏幕的底部:
Context context = getApplicationContext();
String msg = “To the bride an groom!”;
int duration = Toast.LENGTH_SHORT;
Toast toast = Toast.makeText(context, msg, duration);
int offsetX = 0;
int offsetY = 0;
toast.setGravity(Gravity.BOTTOM, offsetX, offsetY);
toast.show();
当仅靠一个文本消息不能完成任务时,你可以指定一个自定义的View或Layout来显示一个更加复杂更加美观的外观。使用setView方法,你可以指定任何View(包括Layout),在转瞬即逝的文本窗口中显示。
例如,下面的片段指定了一个Layout,它包含第4章中创建的指南针构件和一个TextView,来作为一个Toast显示。
Context context = getApplicationContext();
String msg = “Cheers!”;
int duration = Toast.LENGTH_LONG;
Toast toast = Toast.makeText(context, msg, duration);
toast.setGravity(Gravity.TOP, 0, 0);
LinearLayout ll = new LinearLayout(context);
ll.setOrientation(LinearLayout.VERTICAL);
TextView myTextView = new TextView(context);
CompassView cv = new CompassView(context);
myTextView.setText(msg);
int lHeight = LinearLayout.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT;
int lWidth = LinearLayout.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT;
ll.addView(cv, new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(lHeight, lWidth));
ll.addView(myTextView, new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(lHeight, lWidth));
ll.setPadding(40, 50, 0, 50);
toast.setView(ll);
toast.show();
上面的Toast显示如图8-2所示。
图 8-2
在工作者线程中使用Toast
作为GUI组件,Toast必须在GUI线程中打开,否则会抛出一个线程异常。在下面的例子中,Handler用来保证Toast在GUI线程中打开:
private void mainProcessing() {
Thread thread = new Thread(null, doBackgroundThreadProcessing, “Background”);
thread.start();
}
private Runnable doBackgroundThreadProcessing = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
backgroundThreadProcessing();
}
};
private void backgroundThreadProcessing() {
handler.post(doUpdateGUI);
}
// Runnable that executes the update GUI method.
private Runnable doUpdateGUI = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
Context context = getApplicationContext();
String msg = “To open mobile development!”;
int duration = Toast.LENGTH_SHORT;
Toast.makeText(context, msg, duration).show();
}
};