迷宫问题
7-9 求解迷宫从入口到出口的路径 (15分)
求解迷宫从入口到出口的路径。输入一个迷宫,求从入口通向出口的可行路径。为简化问题,迷宫用二维数组 int maze[10][10]来存储障碍物的分布,假设迷宫的横向和纵向尺寸的大小是一样的,并由程序运行读入, 若读入迷宫大小的值是n(3<n<=10),则该迷宫横向或纵向尺寸都是n,规定迷宫最外面的一圈是障碍物,迷宫的入口是maze[1][1],出口是maze[n-2][n-2], 若maze[i][j] = 1代表该位置是障碍物,若maze[i][j] = 0代表该位置是可以行走的空位(0<=i<=n-1, 0<=j<=n-1)。求从入口maze[1][1]到出口maze[n-2][n-2]可以走通的路径。要求迷宫中只允许在水平或上下四个方向的空位上行走,走过的位置不能重复走,规定必须按向右、向下、向左、向上的顺序向前搜索试探。 如下这样一个迷宫:
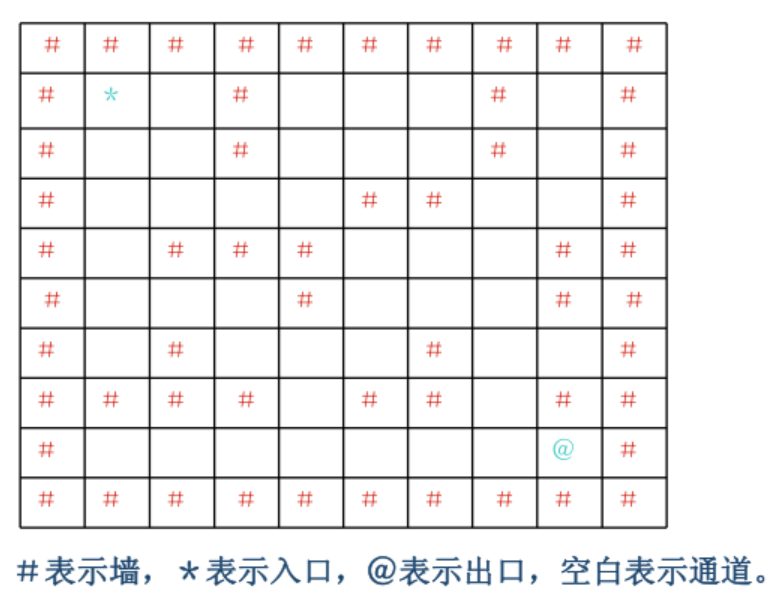
对应的二维数组表示:
int maze[10][10]={ {1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1}, {1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1}, {1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1}, {1,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,1}, {1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,1,1}, {1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,1}, {1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,1}, {1,1,1,1,0,1,1,0,1,1}, {1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1}, {1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1}};
输入格式:
输入迷宫大小的整数n, 以及n行和n列的二维数组(数组元素1代表障碍物,0代表空位)。
输出格式:
依次输出从入口到出口可行路径每个位置的行列下标(i,j),每个位置间用“,”分隔。若没有通路,输出:NO。
输入样例1:
4
1 1 1 1
1 0 1 1
1 0 0 1
1 1 1 1
输出样例1:
(1,1)(2,1)(2,2)
输入样例2:
10
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1
1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1
1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1
1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 1
1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
输出样例2:
(1,1)(1,2)(2,2)(3,2)(3,1)(4,1)(5,1)(5,2)(5,3)(6,3)(6,4)(6,5)(7,5)(8,5)(8,6)(8,7)(8,8)
实验代码(栈)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#define MaxSize 100
typedef struct
{
int i, j;
int di;
}Box;
typedef struct
{
Box data[MaxSize];
int top;
}StType;
int maze[MaxSize][MaxSize]; //迷宫数组
void InitStack(StType*& s) //初始化栈
{
s = (StType*)malloc(sizeof(StType));
s->top = -1;
}
void DestroyStack(StType*& s) //销毁栈
{
free(s);
}
bool StackEmpty(StType* s) //判断栈是否为空
{
return (s->top == -1);
}
bool Push(StType*& s, Box e) //进栈
{
if (s->top == MaxSize - 1)
return false;
s->top++;
s->data[s->top] = e;
return true;
}
bool Pop(StType*& s, Box& e) //出栈
{
if (s->top == -1)
return false;
e = s->data[s->top];
s->top--;
return true;
}
bool GetTop(StType*& s, Box& e) //取栈顶元素
{
if (s->top == -1)
return false;
e = s->data[s->top];
return true;
}
bool mgpath(int xi, int yi, int xe, int ye) //迷宫算法
{
Box path[MaxSize], e;
int i, j, di, i1, j1, k;
bool find;
StType* st;
InitStack(st);
e.i = xi;
e.j = yi;
e.di = -1;
Push(st, e);
maze[xi][yi] = -1;
while (!StackEmpty(st))
{
GetTop(st, e);
i = e.i;
j = e.j;
di = e.di;
if (i == xe && j == ye) //找到出口
{
k = 0;
while (!StackEmpty(st))
{
Pop(st, e);
path[k++] = e;
}
while (k >= 1)
{
k--;
printf("(%d,%d)", path[k].i, path[k].j);
}
DestroyStack(st);
return true;
}
find = false;
while (di < 4 && !find)
{
di++;
switch (di)
{
case 0:i1 = i; j1 = j + 1; break; //向右
case 1:i1 = i + 1; j1 = j; break; //向下
case 2:i1 = i; j1 = j - 1; break; //向左
case 3:i1 = i - 1; j1 = j; break; //向上
}
if (maze[i1][j1] == 0)
{
find = true;
}
}
if (find)
{
st->data[st->top].di = di;
e.i = i1;
e.j = j1;
e.di = -1;
Push(st, e);
maze[i1][j1] = -1;
}
else
{
Pop(st, e);
maze[e.i][e, j] = 0;
}
}
DestroyStack(st);
return false;
}
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
scanf("%d", &maze[i][j]);
}
}
if (!mgpath(1, 1, n-2, n-2))
printf("NO\n");
return 0;
}
实验代码(队列)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#define MaxSize 100
typedef struct
{
int i, j;
int pre;
}Box;
typedef struct
{
Box data[MaxSize];
int front, rear;
}QuType;
int maze[MaxSize][MaxSize];
void InitQueue(QuType*& q) //初始化队列
{
q = (QuType*)malloc(sizeof(QuType));
q->front = q->rear = -1;
}
void DestroyQueue(QuType*& q) //销毁队列
{
free(q);
}
bool QueueEmpty(QuType* q) //判断队列是否为空
{
return (q->front == q->rear);
}
bool enQueue(QuType*& q, Box e) //进队列
{
if (q->rear == MaxSize - 1)
return false;
q->rear++;
q->data[q->rear] = e;
return true;
}
bool deQueue(QuType*& q, Box& e) //出队列
{
if (q->front == q->rear)
return false;
q->front++;
e = q->data[q->front];
return true;
}
void print(QuType* qu, int front) //从队列qu中输出迷宫路径
{
int k = front, j;
do
{
j = k;
k = qu->data[k].pre;
qu->data[j].pre = -1;
} while (k != 0);
k = 0;
while (k < MaxSize)
{
if (qu->data[k].pre == -1)
{
printf("(%d,%d)", qu->data[k].i, qu->data[k].j);
}
k++;
}
}
bool mgpath(int xi, int yi, int xe, int ye) //迷宫算法
{
Box e;
int i, j, di, i1, j1;
QuType* qu;
InitQueue(qu);
e.i = xi;
e.j = yi;
e.pre = -1;
enQueue(qu, e);
maze[xi][yi] = -1;
while (!QueueEmpty(qu))
{
deQueue(qu, e);
i = e.i;
j = e.j;
if (i == xe && j == ye)
{
print(qu, qu->front);
DestroyQueue(qu);
return true;
}
for (di = 0; di < 4; di++)
{
switch (di)
{
case 0:i1 = i - 1; j1 = j; break;
case 1:i1 = i; j1 = j + 1; break;
case 2:i1 = i + 1; j1 = j; break;
case 3:i1 = i; j1 = j - 1; break;
}
if (maze[i1][j1] == 0)
{
e.i = i1;
e.j = j1;
e.pre = qu->front;
enQueue(qu, e);
maze[i1][j1] = -1;
}
}
}
DestroyQueue(qu);
return false;
}
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
scanf("%d", &maze[i][j]);
}
}
if (!mgpath(1, 1, n - 2, n - 2))
printf("NO\n");
return 0;
}


