Matplotlib绘图设置--- 图例设置
plt.legend()和ax.legend()参数设置
自动会将每条线的标签与其风格、颜色进行匹配。
plt.legend(*args, **kwargs)
Place a legend on the axes.
Call signatures::
legend()
legend(labels)
legend(handles, labels)
The call signatures correspond to three different ways how to use
this method.
**1. Automatic detection of elements to be shown in the legend**
The elements to be added to the legend are automatically determined,
when you do not pass in any extra arguments.
In this case, the labels are taken from the artist. You can specify
them either at artist creation or by calling the
:meth:`~.Artist.set_label` method on the artist::
line, = ax.plot([1, 2, 3], label='Inline label')
ax.legend()
or::
line, = ax.plot([1, 2, 3])
line.set_label('Label via method')
ax.legend()
Specific lines can be excluded from the automatic legend element
selection by defining a label starting with an underscore.
This is default for all artists, so calling `Axes.legend` without
any arguments and without setting the labels manually will result in
no legend being drawn.
**2. Labeling existing plot elements**
To make a legend for lines which already exist on the axes
(via plot for instance), simply call this function with an iterable
of strings, one for each legend item. For example::
ax.plot([1, 2, 3])
ax.legend(['A simple line'])
Note: This way of using is discouraged, because the relation between
plot elements and labels is only implicit by their order and can
easily be mixed up.
**3. Explicitly defining the elements in the legend**
For full control of which artists have a legend entry, it is possible
to pass an iterable of legend artists followed by an iterable of
legend labels respectively::
legend((line1, line2, line3), ('label1', 'label2', 'label3'))
Parameters
----------
handles : sequence of `.Artist`, optional
A list of Artists (lines, patches) to be added to the legend.
Use this together with *labels*, if you need full control on what
is shown in the legend and the automatic mechanism described above
is not sufficient.
The length of handles and labels should be the same in this
case. If they are not, they are truncated to the smaller length.
labels : sequence of strings, optional
A list of labels to show next to the artists.
Use this together with *handles*, if you need full control on what
is shown in the legend and the automatic mechanism described above
is not sufficient.
Other Parameters
----------------
loc : str or pair of floats, default: :rc:`legend.loc` ('best' for axes, 'upper right' for figures)
The location of the legend.
The strings
``'upper left', 'upper right', 'lower left', 'lower right'``
place the legend at the corresponding corner of the axes/figure.
The strings
``'upper center', 'lower center', 'center left', 'center right'``
place the legend at the center of the corresponding edge of the
axes/figure.
The string ``'center'`` places the legend at the center of the axes/figure.
The string ``'best'`` places the legend at the location, among the nine
locations defined so far, with the minimum overlap with other drawn
artists. This option can be quite slow for plots with large amounts of
data; your plotting speed may benefit from providing a specific location.
The location can also be a 2-tuple giving the coordinates of the lower-left
corner of the legend in axes coordinates (in which case *bbox_to_anchor*
will be ignored).
For back-compatibility, ``'center right'`` (but no other location) can also
be spelled ``'right'``, and each "string" locations can also be given as a
numeric value:
=============== =============
Location String Location Code
=============== =============
'best' 0
'upper right' 1
'upper left' 2
'lower left' 3
'lower right' 4
'right' 5
'center left' 6
'center right' 7
'lower center' 8
'upper center' 9
'center' 10
=============== =============
bbox_to_anchor : `.BboxBase`, 2-tuple, or 4-tuple of floats
Box that is used to position the legend in conjunction with *loc*.
Defaults to `axes.bbox` (if called as a method to `.Axes.legend`) or
`figure.bbox` (if `.Figure.legend`). This argument allows arbitrary
placement of the legend.
Bbox coordinates are interpreted in the coordinate system given by
`bbox_transform`, with the default transform
Axes or Figure coordinates, depending on which ``legend`` is called.
If a 4-tuple or `.BboxBase` is given, then it specifies the bbox
``(x, y, width, height)`` that the legend is placed in.
To put the legend in the best location in the bottom right
quadrant of the axes (or figure)::
loc='best', bbox_to_anchor=(0.5, 0., 0.5, 0.5)
A 2-tuple ``(x, y)`` places the corner of the legend specified by *loc* at
x, y. For example, to put the legend's upper right-hand corner in the
center of the axes (or figure) the following keywords can be used::
loc='upper right', bbox_to_anchor=(0.5, 0.5)
ncol : integer
The number of columns that the legend has. Default is 1.
prop : None or :class:`matplotlib.font_manager.FontProperties` or dict
The font properties of the legend. If None (default), the current
:data:`matplotlib.rcParams` will be used.
fontsize : int or float or {'xx-small', 'x-small', 'small', 'medium', 'large', 'x-large', 'xx-large'}
Controls the font size of the legend. If the value is numeric the
size will be the absolute font size in points. String values are
relative to the current default font size. This argument is only
used if `prop` is not specified.
numpoints : None or int
The number of marker points in the legend when creating a legend
entry for a `.Line2D` (line).
Default is ``None``, which will take the value from
:rc:`legend.numpoints`.
scatterpoints : None or int
The number of marker points in the legend when creating
a legend entry for a `.PathCollection` (scatter plot).
Default is ``None``, which will take the value from
:rc:`legend.scatterpoints`.
scatteryoffsets : iterable of floats
The vertical offset (relative to the font size) for the markers
created for a scatter plot legend entry. 0.0 is at the base the
legend text, and 1.0 is at the top. To draw all markers at the
same height, set to ``[0.5]``. Default is ``[0.375, 0.5, 0.3125]``.
markerscale : None or int or float
The relative size of legend markers compared with the originally
drawn ones.
Default is ``None``, which will take the value from
:rc:`legend.markerscale`.
markerfirst : bool
If *True*, legend marker is placed to the left of the legend label.
If *False*, legend marker is placed to the right of the legend
label.
Default is *True*.
frameon : None or bool
Control whether the legend should be drawn on a patch
(frame).
Default is ``None``, which will take the value from
:rc:`legend.frameon`.
fancybox : None or bool
Control whether round edges should be enabled around the
:class:`~matplotlib.patches.FancyBboxPatch` which makes up the
legend's background.
Default is ``None``, which will take the value from
:rc:`legend.fancybox`.
shadow : None or bool
Control whether to draw a shadow behind the legend.
Default is ``None``, which will take the value from
:rc:`legend.shadow`.
framealpha : None or float
Control the alpha transparency of the legend's background.
Default is ``None``, which will take the value from
:rc:`legend.framealpha`. If shadow is activated and
*framealpha* is ``None``, the default value is ignored.
facecolor : None or "inherit" or a color spec
Control the legend's background color.
Default is ``None``, which will take the value from
:rc:`legend.facecolor`. If ``"inherit"``, it will take
:rc:`axes.facecolor`.
edgecolor : None or "inherit" or a color spec
Control the legend's background patch edge color.
Default is ``None``, which will take the value from
:rc:`legend.edgecolor` If ``"inherit"``, it will take
:rc:`axes.edgecolor`.
mode : {"expand", None}
If `mode` is set to ``"expand"`` the legend will be horizontally
expanded to fill the axes area (or `bbox_to_anchor` if defines
the legend's size).
bbox_transform : None or :class:`matplotlib.transforms.Transform`
The transform for the bounding box (`bbox_to_anchor`). For a value
of ``None`` (default) the Axes'
:data:`~matplotlib.axes.Axes.transAxes` transform will be used.
title : str or None
The legend's title. Default is no title (``None``).
title_fontsize: str or None
The fontsize of the legend's title. Default is the default fontsize.
borderpad : float or None
The fractional whitespace inside the legend border.
Measured in font-size units.
Default is ``None``, which will take the value from
:rc:`legend.borderpad`.
labelspacing : float or None
The vertical space between the legend entries.
Measured in font-size units.
Default is ``None``, which will take the value from
:rc:`legend.labelspacing`.
handlelength : float or None
The length of the legend handles.
Measured in font-size units.
Default is ``None``, which will take the value from
:rc:`legend.handlelength`.
handletextpad : float or None
The pad between the legend handle and text.
Measured in font-size units.
Default is ``None``, which will take the value from
:rc:`legend.handletextpad`.
borderaxespad : float or None
The pad between the axes and legend border.
Measured in font-size units.
Default is ``None``, which will take the value from
:rc:`legend.borderaxespad`.
columnspacing : float or None
The spacing between columns.
Measured in font-size units.
Default is ``None``, which will take the value from
:rc:`legend.columnspacing`.
handler_map : dict or None
The custom dictionary mapping instances or types to a legend
handler. This `handler_map` updates the default handler map
found at :func:`matplotlib.legend.Legend.get_legend_handler_map`.
Returns
-------
:class:`matplotlib.legend.Legend` instance
#label参数设置简易图例
plt.plot(x, np.sin(x), '-g', label='sin(x)')
plt.plot(x, np.cos(x), ':b', label='cos(x)')
plt.axis('equal')
#显示和设置图例
plt.legend()
#设置绘图风格
plt.style.use('classic')
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(x, np.sin(x), '-b', label='Sine')
ax.plot(x, np.cos(x), '--r', label='Cosine')
ax.axis('equal')
leg = ax.legend()
#loc设置图例位置,frameon设置边框
ax.legend(loc='upper left', frameon=False)
fig
#ncol设置图例标签列数
ax.legend(frameon=False, loc='lower center', ncol=2)
fig

#fancybox设置圆角边框,shadow增加阴影,framealpha改变外框透明度,borderpad设置文字间距
ax.legend(fancybox=True, framealpha=1, shadow=True, borderpad=1)
fig
选择图例显示元素
#np.newaxis设置排序的方向
#y是通过广播功能得到一个4 * len(x)维数的数组
y = x[:, np.newaxis] + np.pi * np.arange(0, 2, 0.5)
#方法一:统一绘制
#lines变量时一组plt.Line2D实例
lines = plt.plot(x, y)
#选取其中的图形进行设置标签
plt.legend(lines[:2], ['first','second'], loc='best')
#方法二:分别绘制
plt.plot(x, y[:,0], label='first')
plt.plot(x, y[:,1], label='second')
plt.plot(x, y[:,2:])
plt.legend(framealpha=1, frameon=True, loc='best')
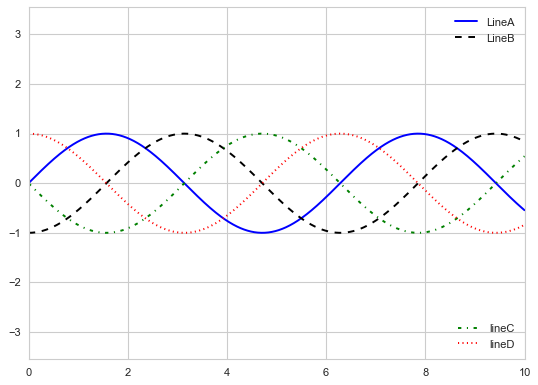
同时显示多图例
在Matplotlib中一般标准legend接口只能为一张图创建一个图例,如果用plt.legend()或ax.legend()创建第二图例时,第一图例会被覆盖。但是,可通过从头开始创建一个新的图例艺术家对象(legend artist),然后用底层的(lower-level)ax.add_artist()方法在图上添加第二个图例。
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
lines = []
styles = ['-','--','-.',':']
colors = ['b','k','g','r']
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 1000)
for i in range(len(styles)):
lines += ax.plot(x, np.sin(x-i * np.pi/2),
styles[i], color=colors[i])
ax.axis('equal')
#设置第一个图例要显示的元素和标签
ax.legend(lines[:2], ['LineA','LineB'],
loc='upper right', frameon=False)
#根据一个Legend对象用add_artist方法添加第二个图例要显示的元素和标签
from matplotlib.legend import Legend
leg = Legend(ax, lines[2:], ['lineC','lineD'],
loc='lower right', frameon=False)
ax.add_artist(leg);
分类:
Matplotlib







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 一起来玩mcp_server_sqlite,让AI帮你做增删改查!!