shell脚本中的变量
在shell脚本中使用变量显得我们的脚本更加专业更像是一门语言,开个玩笑,变量的作用当然不是为了专业。如果你写了一个长达1000行的shell脚本,并且脚本中出现了某一个命令或者路径几百次。突然你觉得路径不对想换一下,那岂不是要更改几百次?你固然可以使用批量替换的命令,但是也是很麻烦,并且脚本显得臃肿了很多。变量的作用就是用来解决这个问题的。
来看一个示例:
#! /bin/bash ## author:Xiong Xuehao ## This is my first shell script. Using variables in scripts. d1=`date +%H:%M:%S` echo "The script begin at $d1" echo "now we will sleep 2 seconds" sleep 2 d2=`date +%H:%M:%S` echo "The script end at $d2"
在myfirstbash_002.sh中使用到了反引号(TAB键上方,1/!键左边的那个键),你是否还记得它的作用?’d1’和’d2’在脚本中作为变量出现,定义变量的格式为“变量名=变量的值”。当在脚本中引用变量时需要加上’$’符号。下面看看脚本执行结果吧:
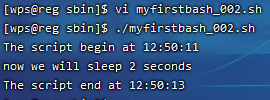
案例1:在shell脚本中使用数学计算
下面我们用shell计算两个数的和。
#! /bin/bash ## author:Xiong Xuehao ## This is my first shell script. Calculate the sum of two numbers. x=1 y=2 sum=$[$x+$y] echo "$x + $y sum is $sum"
数学计算要用’[ ]’括起来并且外头要带一个’$’。脚本结果为:
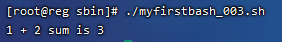
案例2:Shell脚本还可以和用户交互
Shell脚本和用户交互:
#! /bin/bash ## author:Xiong Xuehao ## This is my first shell script. Use read in the script. echo "Please input a number:" read x echo "Please input another number:" read y sum=$[$x+$y] echo "$x + $y sum is $sum"
这就用到了read命令了,它可以从标准输入获得变量的值,后跟变量名。”read x”表示x变量的值需要用户通过键盘输入得到。脚本执行过程如下:

我们不妨加上-x选项再来看看这个执行过程:
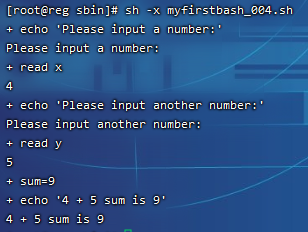
在myfirstbash_004.sh中还有更加简洁的方式:
#! /bin/bash ## author:Xiong Xuehao ## This is my first shell script. Use read in the script. read -p "Please input a number:" x read -p "Please input another number:" y sum=$[$x+$y] echo "$x + $y sum is $sum"
read -p 选项类似echo的作用。执行如下:
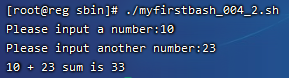
案例3:Shell脚本预设变量
你有没有用过这样的命令”/etc/init.d/iptables restart “ 前面的/etc/init.d/iptables 文件其实就是一个shell脚本,为什么后面可以跟一个”restart”? 这里就涉及到了shell脚本的预设变量。实际上,shell脚本在执行的时候后边是可以跟变量的,而且还可以跟多个。示例:
#! /bin/bash ## author:Xiong Xuehao ## This is my first shell script. Use preset variables. sum=$[$1+$2] echo "$1 + $2 sum is $sum"
执行过程如下:
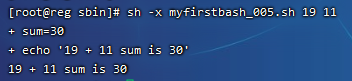
在脚本中,你会不会奇怪,哪里来的$1和$2,这其实就是shell脚本的预设变量,其中$1的值就是在执行的时候输入的1,而$2的值就是执行的时候输入的$2,当然一个shell脚本的预设变量是没有限制的,这回你明白了吧。另外还有一个$0,不过它代表的是脚本本身的名字。



