接口(Interface)是对某些属性和方法的一个抽象概括,方便让一个类(Class)对象进行调用,但这个类对象必须实现该接口的全部成员(方法和属性),即为这些接口成员添加执行代码,如果不愿意添加内容,则可以提供一个“空”的执行方式(没有函数代码)。例如:一个类继承了IList接口,则这个类在定义时,内部代码必须包括IList接口的全部成员(属性和方法)的实现,包括:方法和属性
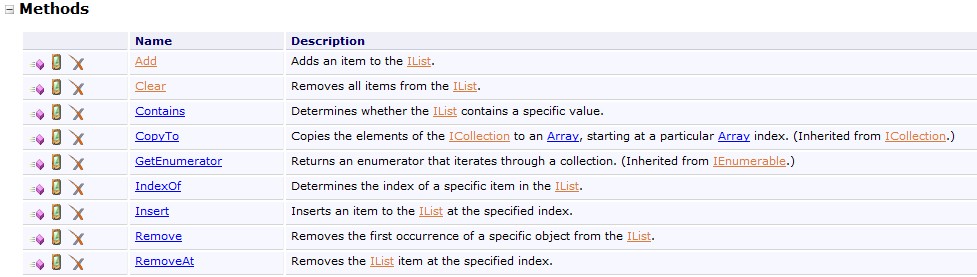
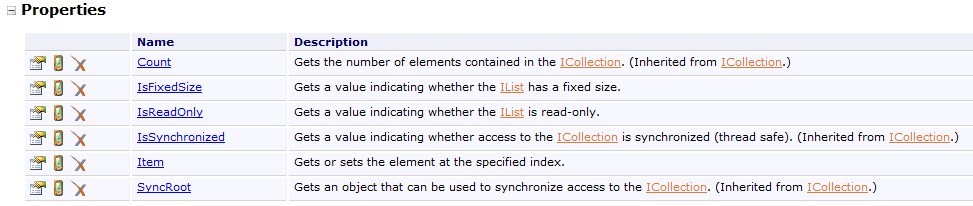
示例代码如下(参考自MSDN IList示例代码):
 View Code
View Code
1 using System;
2 using System.Collections;
3
4 class Program
5 {
6 static void Main()
7 {
8 SimpleList test = new SimpleList();
9
10 // Populate the List
11 Console.WriteLine("Populate the List");
12 test.Add("one");
13 test.Add("two");
14 test.Add("three");
15 test.Add("four");
16 test.Add("five");
17 test.Add("six");
18 test.Add("seven");
19 test.Add("eight");
20 test.PrintContents();
21 Console.WriteLine();
22
23 // Remove elements from the list
24 Console.WriteLine("Remove elements from the list");
25 test.Remove("six");
26 test.Remove("eight");
27 test.PrintContents();
28 Console.WriteLine();
29
30 // Add an element to the end of the list
31 Console.WriteLine("Add an element to the end of the list");
32 test.Add("nine");
33 test.PrintContents();
34 Console.WriteLine();
35
36 // Insert an element into the middle of the list
37 Console.WriteLine("Insert an element into the middle of the list");
38 test.Insert(4, "number");
39 test.PrintContents();
40 Console.WriteLine();
41
42 // Check for specific elements in the list
43 Console.WriteLine("Check for specific elements in the list");
44 Console.WriteLine("List contains \"three\": {0}", test.Contains("three"));
45 Console.WriteLine("List contains \"ten\": {0}", test.Contains("ten"));
46 }
47 } // class Program
48
49 class SimpleList : IList
50 {
51 private object[] _contents = new object[8];
52 private int _count;
53
54 public SimpleList()
55 {
56 _count = 0;
57 }
58
59 // IList Members
60 public int Add(object value)
61 {
62 if (_count < _contents.Length)
63 {
64 _contents[_count] = value;
65 _count++;
66
67 return (_count - 1);
68 }
69 else
70 {
71 return -1;
72 }
73 }
74
75 public void Clear()
76 {
77 _count = 0;
78 }
79
80 public bool Contains(object value)
81 {
82 bool inList = false;
83 for (int i = 0; i < Count; i++)
84 {
85 if (_contents[i] == value)
86 {
87 inList = true;
88 break;
89 }
90 }
91 return inList;
92 }
93
94 public int IndexOf(object value)
95 {
96 int itemIndex = -1;
97 for (int i = 0; i < Count; i++)
98 {
99 if (_contents[i] == value)
100 {
101 itemIndex = i;
102 break;
103 }
104 }
105 return itemIndex;
106 }
107
108 public void Insert(int index, object value)
109 {
110 if ((_count + 1 <= _contents.Length) && (index < Count) && (index >= 0))
111 {
112 _count++;
113
114 for (int i = Count - 1; i > index; i--)
115 {
116 _contents[i] = _contents[i - 1];
117 }
118 _contents[index] = value;
119 }
120 }
121
122 public bool IsFixedSize
123 {
124 get
125 {
126 return true;
127 }
128 }
129
130 public bool IsReadOnly
131 {
132 get
133 {
134 return false;
135 }
136 }
137
138 public void Remove(object value)
139 {
140 RemoveAt(IndexOf(value));
141 }
142
143 public void RemoveAt(int index)
144 {
145 if ((index >= 0) && (index < Count))
146 {
147 for (int i = index; i < Count - 1; i++)
148 {
149 _contents[i] = _contents[i + 1];
150 }
151 _count--;
152 }
153 }
154
155 public object this[int index]
156 {
157 get
158 {
159 return _contents[index];
160 }
161 set
162 {
163 _contents[index] = value;
164 }
165 }
166
167 // ICollection Members
168
169 public void CopyTo(Array array, int index)
170 {
171 int j = index;
172 for (int i = 0; i < Count; i++)
173 {
174 array.SetValue(_contents[i], j);
175 j++;
176 }
177 }
178
179 public int Count
180 {
181 get
182 {
183 return _count;
184 }
185 }
186
187 public bool IsSynchronized
188 {
189 get
190 {
191 return false;
192 }
193 }
194
195 // Return the current instance since the underlying store is not
196 // publicly available.
197 public object SyncRoot
198 {
199 get
200 {
201 return this;
202 }
203 }
204
205 // IEnumerable Members
206
207 public IEnumerator GetEnumerator()
208 {
209 // Refer to the IEnumerator documentation for an example of
210 // implementing an enumerator.
211 throw new Exception("The method or operation is not implemented.");
212 }
213
214 public void PrintContents()
215 {
216 Console.WriteLine("List has a capacity of {0} and currently has {1} elements.", _contents.Length, _count);
217 Console.Write("List contents:");
218 for (int i = 0; i < Count; i++)
219 {
220 Console.Write(" {0}", _contents[i]);
221 }
222 Console.WriteLine();
223 }
224 }
2 using System.Collections;
3
4 class Program
5 {
6 static void Main()
7 {
8 SimpleList test = new SimpleList();
9
10 // Populate the List
11 Console.WriteLine("Populate the List");
12 test.Add("one");
13 test.Add("two");
14 test.Add("three");
15 test.Add("four");
16 test.Add("five");
17 test.Add("six");
18 test.Add("seven");
19 test.Add("eight");
20 test.PrintContents();
21 Console.WriteLine();
22
23 // Remove elements from the list
24 Console.WriteLine("Remove elements from the list");
25 test.Remove("six");
26 test.Remove("eight");
27 test.PrintContents();
28 Console.WriteLine();
29
30 // Add an element to the end of the list
31 Console.WriteLine("Add an element to the end of the list");
32 test.Add("nine");
33 test.PrintContents();
34 Console.WriteLine();
35
36 // Insert an element into the middle of the list
37 Console.WriteLine("Insert an element into the middle of the list");
38 test.Insert(4, "number");
39 test.PrintContents();
40 Console.WriteLine();
41
42 // Check for specific elements in the list
43 Console.WriteLine("Check for specific elements in the list");
44 Console.WriteLine("List contains \"three\": {0}", test.Contains("three"));
45 Console.WriteLine("List contains \"ten\": {0}", test.Contains("ten"));
46 }
47 } // class Program
48
49 class SimpleList : IList
50 {
51 private object[] _contents = new object[8];
52 private int _count;
53
54 public SimpleList()
55 {
56 _count = 0;
57 }
58
59 // IList Members
60 public int Add(object value)
61 {
62 if (_count < _contents.Length)
63 {
64 _contents[_count] = value;
65 _count++;
66
67 return (_count - 1);
68 }
69 else
70 {
71 return -1;
72 }
73 }
74
75 public void Clear()
76 {
77 _count = 0;
78 }
79
80 public bool Contains(object value)
81 {
82 bool inList = false;
83 for (int i = 0; i < Count; i++)
84 {
85 if (_contents[i] == value)
86 {
87 inList = true;
88 break;
89 }
90 }
91 return inList;
92 }
93
94 public int IndexOf(object value)
95 {
96 int itemIndex = -1;
97 for (int i = 0; i < Count; i++)
98 {
99 if (_contents[i] == value)
100 {
101 itemIndex = i;
102 break;
103 }
104 }
105 return itemIndex;
106 }
107
108 public void Insert(int index, object value)
109 {
110 if ((_count + 1 <= _contents.Length) && (index < Count) && (index >= 0))
111 {
112 _count++;
113
114 for (int i = Count - 1; i > index; i--)
115 {
116 _contents[i] = _contents[i - 1];
117 }
118 _contents[index] = value;
119 }
120 }
121
122 public bool IsFixedSize
123 {
124 get
125 {
126 return true;
127 }
128 }
129
130 public bool IsReadOnly
131 {
132 get
133 {
134 return false;
135 }
136 }
137
138 public void Remove(object value)
139 {
140 RemoveAt(IndexOf(value));
141 }
142
143 public void RemoveAt(int index)
144 {
145 if ((index >= 0) && (index < Count))
146 {
147 for (int i = index; i < Count - 1; i++)
148 {
149 _contents[i] = _contents[i + 1];
150 }
151 _count--;
152 }
153 }
154
155 public object this[int index]
156 {
157 get
158 {
159 return _contents[index];
160 }
161 set
162 {
163 _contents[index] = value;
164 }
165 }
166
167 // ICollection Members
168
169 public void CopyTo(Array array, int index)
170 {
171 int j = index;
172 for (int i = 0; i < Count; i++)
173 {
174 array.SetValue(_contents[i], j);
175 j++;
176 }
177 }
178
179 public int Count
180 {
181 get
182 {
183 return _count;
184 }
185 }
186
187 public bool IsSynchronized
188 {
189 get
190 {
191 return false;
192 }
193 }
194
195 // Return the current instance since the underlying store is not
196 // publicly available.
197 public object SyncRoot
198 {
199 get
200 {
201 return this;
202 }
203 }
204
205 // IEnumerable Members
206
207 public IEnumerator GetEnumerator()
208 {
209 // Refer to the IEnumerator documentation for an example of
210 // implementing an enumerator.
211 throw new Exception("The method or operation is not implemented.");
212 }
213
214 public void PrintContents()
215 {
216 Console.WriteLine("List has a capacity of {0} and currently has {1} elements.", _contents.Length, _count);
217 Console.Write("List contents:");
218 for (int i = 0; i < Count; i++)
219 {
220 Console.Write(" {0}", _contents[i]);
221 }
222 Console.WriteLine();
223 }
224 }
看书过程中,我想过,既然接口的成员方法不定义内容,需要我们自己在继承接口的类中来编写实现代码,那为啥要接口定义这些方法呢?定义这些方法的目的,难道不是不是去做MSDN中所说的功能么?
为此,这个问题我想了很久。终于想明白了。大致思路为:一个接口定义了若干成员方法,并定义了这些方法的返回对象类型,如果一个类继承接口后,需要实现这些方法,设计执行代码,就是为了让我们自己来实现这个接口,以便于在自己或其他人调用这个方法。之所以继承接口来实现方法,就是利用接口的高度抽象概括的职能,更多的时候,我们都是自己写代码给别人调用,而这个时候,我们设计接口,定义成员方法,就是为了方便将这个代码集合分类整合,将一些实现特殊功能的属性和方法放在接口里,通过其它类来实现它们。这就是利用接口实现方法的意义所在。






